Pedigree Analysis Questions: Genetics Practice
advertisement

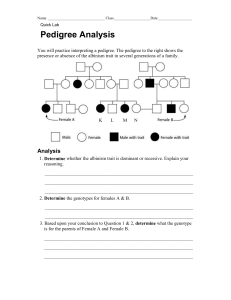
Pedigree Analysis Question Sheet Question A 1. 2. I 3. 4. II 5. 6. 7. 8. III 11. 9. IV 10. V In the above pedigree, the affected individuals are shown shaded. None of the marriage partners from outside these two families are heterozygous for the trait. 1. How is this particular trait inherited? 2. How many offspring are shown in the second generation? 3. If individual #10 mated with individual # 11, what are the chances of them producing an offspring who is affected? 4. Indicate the genotypes of individuals # 1 10. (Write clearly above the number.) (Allow the dominant trait to be “A” and the recessive trait to be “a” – NOTE: Some may have two possible genotypes) Pedigree Analysis Question Sheet Version B The following pedigree represents the inheritance pattern for the sex-linked, recessive trait colourblindness in humans. The person making this pedigree did NOT identify the carriers of the trait, just those with or without colour blindness. You have to identify the genotypes of all individuals, by writing the genotype clearly above the number. To do this you will use the allele symbols XB for normal colour vision and Xb for the colour-blindness. You must also use the appropriate symbols for the genders. Fill in the genotypes of each of the 23 individuals shown. If the complete genotype can not be determined from the data provided then the symbol X—MUST be used for the unknown allele. 1. 5. 2. 6. 7. 12. 18. 3. 13. 19. 8. 14. 20. 9. 4. 10. 15. 21. 16. 11. 17. 22. 23. Pedigree Analysis Question Sheet Version C Pedigree A Pedigree B Pedigree C Pedigree D Pedigree E Possible Inheritance patterns: Autosomal recessive Autosomal dominant X-linked recessive X-linked dominant Y-linked 1. For each of the pedigrees above, indicate which of the 5 inheritance patterns are possible (there may be more than one possible). Explain your reasoning in each case. 2. Give the genotype for each of the affected individuals in pedigree C. Longer Answer Questions Pedigree Analysis Answer Sheet Version A 1. The trait is autosomal recessive 2. Six offspring are shown in the second generation 3. There is a 25% chance 4. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. xi. Aa Aa AA aa Aa Aa Aa Aa Aa or AA aa AA or Aa Longer Answer Questions Pedigree Analysis Answer Sheet Version B One mark for each genotype, and one mark for each explanation. #1 XBY male and does not have trait #4 XBXb female and must be heterozygous as one of her sons has trait #7 XBX-- female and can not tell if she is homozygous or heterozygous must use X— #9 XbXb female and must be homozygous recessive as she has the trait #14. XBXb female and must be heterozygous as mother was XbXb and father was XBY #18. XBXb female and must be heterozygous as she gets Xb from father but does not have the trait #21 XbY is male and has the trait Longer Answer Questions Pedigree Analysis Answer Sheet Version C 1. Pedigree A Autosomal Recessive X-linked Recessive Neither parent has the trait but one offspring expressed it Neither parent has it but one SON expressed it Pedigree B X-linked Recessive Both of the daughters express the trait, neither SON does, both parents have it Pedigree C Autosomal Recessive Neither parent expresses the trait but one son and one daughter express the trait Pedigree D X-linked dominant Both daughters express the trait, inherited from the fathers affected X chromosome, neither son expresses the trait Only the daughters inherited the faulty chromosome from the father by chance Autosomal Dominant Pedigree E Y-linked Autosomal Dominant Only the males in the family are affected by the disorder. Only the sons inherited the faulty chromosome from the father by chance 2. Let ‘A’ stand for the dominant allele and ‘a’ stand for the recessive allele for this gene. The affected individuals will be homozygous recessive for the trait Genotype = aa