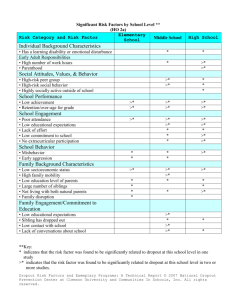
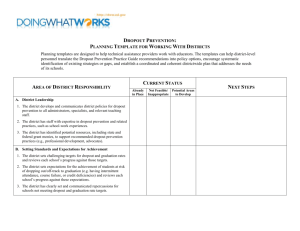
logic model school attendance initiative (sai) 2011-2012
advertisement
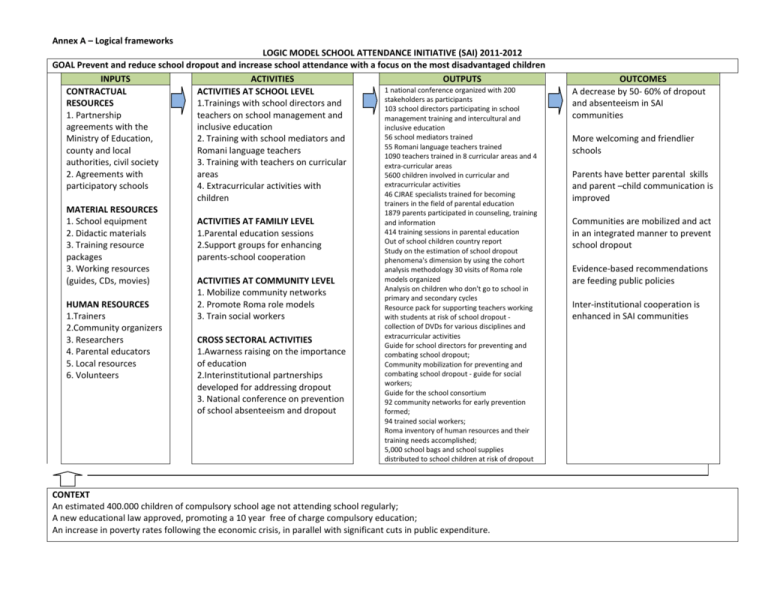
Annex A – Logical frameworks LOGIC MODEL SCHOOL ATTENDANCE INITIATIVE (SAI) 2011-2012 GOAL Prevent and reduce school dropout and increase school attendance with a focus on the most disadvantaged children INPUTS ACTIVITIES OUTPUTS 1 national conference organized with 200 CONTRACTUAL ACTIVITIES AT SCHOOL LEVEL stakeholders as participants RESOURCES 1.Trainings with school directors and 103 school directors participating in school 1. Partnership teachers on school management and management training and intercultural and agreements with the inclusive education inclusive education 56 school mediators trained Ministry of Education, 2. Training with school mediators and 55 Romani language teachers trained county and local Romani language teachers 1090 teachers trained in 8 curricular areas and 4 authorities, civil society 3. Training with teachers on curricular extra-curricular areas 2. Agreements with areas 5600 children involved in curricular and extracurricular activities participatory schools 4. Extracurricular activities with 46 CJRAE specialists trained for becoming children trainers in the field of parental education MATERIAL RESOURCES 1879 parents participated in counseling, training 1. School equipment ACTIVITIES AT FAMILIY LEVEL and information 414 training sessions in parental education 2. Didactic materials 1.Parental education sessions Out of school children country report 3. Training resource 2.Support groups for enhancing Study on the estimation of school dropout packages parents-school cooperation phenomena's dimension by using the cohort 3. Working resources analysis methodology 30 visits of Roma role models organized (guides, CDs, movies) ACTIVITIES AT COMMUNITY LEVEL Analysis on children who don't go to school in 1. Mobilize community networks primary and secondary cycles HUMAN RESOURCES 2. Promote Roma role models Resource pack for supporting teachers working 1.Trainers 3. Train social workers with students at risk of school dropout collection of DVDs for various disciplines and 2.Community organizers extracurricular activities 3. Researchers CROSS SECTORAL ACTIVITIES Guide for school directors for preventing and 4. Parental educators 1.Awarness raising on the importance combating school dropout; 5. Local resources of education Community mobilization for preventing and combating school dropout - guide for social 6. Volunteers 2.Interinstitutional partnerships workers; developed for addressing dropout Guide for the school consortium 3. National conference on prevention 92 community networks for early prevention of school absenteeism and dropout formed; 94 trained social workers; Roma inventory of human resources and their training needs accomplished; 5,000 school bags and school supplies distributed to school children at risk of dropout CONTEXT An estimated 400.000 children of compulsory school age not attending school regularly; A new educational law approved, promoting a 10 year free of charge compulsory education; An increase in poverty rates following the economic crisis, in parallel with significant cuts in public expenditure. OUTCOMES A decrease by 50- 60% of dropout and absenteeism in SAI communities More welcoming and friendlier schools Parents have better parental skills and parent –child communication is improved Communities are mobilized and act in an integrated manner to prevent school dropout Evidence-based recommendations are feeding public policies Inter-institutional cooperation is enhanced in SAI communities LOGIC MODEL SCHOOL ATTENDANCE INITIATIVE (SAI) 2012-2013 GOAL Prevent and reduce school dropout and increase school attendance with a focus on the most disadvantaged children INPUTS ACTIVITIES OUTPUTS CONTRACTUAL ACTIVITIES AT SCHOOL LEVEL 1 national conference organized with RESOURCES 1.Trainings with school directors and 300 stakeholders as participants 1. Partnership teachers on school management and 176 school directors participated in agreements with the inclusive education school management training Ministry of Education, 2. Training with school mediators and 93 school directors trained in inclusive county and local Romani language teachers education authorities, civil society 3. Training with teachers on curricular 60 school mediators trained 2. Agreements with areas 30 Romani language teachers trained participatory schools 4. Extracurricular activities with 120 persons participating in seminars children on school mediators MATERIAL RESOURCES 1200 teachers trained in 8 curricular 1. School equipment ACTIVITIES AT FAMILIY LEVEL areas and 4 extra-curricular areas 2. Didactic materials 1.Parental education sessions 5500 children involved in curricular 3. Training resource 2.Support groups for enhancing and extracurricular activities packages parents-school cooperation 50 educators trained for becoming 3. Working resources trainers in the field of parental (guides, CDs, movies) ACTIVITIES AT COMMUNITY LEVEL education 1. Mobilize community networks 1200 parents trained for improving HUMAN RESOURCES 2. Promote Roma role models their parental skills 1.Trainers 3. Train social workers 40 partnership public-private 2.Community organizers agreements signed 3. Researchers CROSS SECTORAL ACTIVITIES 200 training sessions in parental 4. Parental educators 1.Awarness raising on the importance education supported financially by 5. Local resources of education local authorities 6. Volunteers 2.Interinstitutional partnerships 1 study on the impact of the parental developed for addressing dropout education drafted 3. National conference on prevention 1 national network of Roma students of school absenteeism and dropout developed 100 visits of Roma role models organized 1 pedagogical kit on inclusive education drafted CONTEXT An estimated 400.000 children of compulsory school age not attending school regularly; A new educational law approved, promoting a 10 year free of charge compulsory education; An increase in poverty rates following the economic crisis, in parallel with significant cuts in public expenditure. OUTCOMES A decrease by 50- 60% of dropout and absenteeism in SAI communities More welcoming and friendlier schools Parents have better parental skills and parent –child communication is improved Communities are mobilized and act in an integrated manner to prevent school dropout Evidence-based recommendations are feeding public policies Inter-institutional cooperation is enhanced in SAI communities LOGIC MODEL SCHOOL ATTENDANCE INITIATIVE (SAI) 2013-2014 GOAL Prevent and reduce school dropout and increase school attendance with a focus on the most disadvantaged children INPUTS ACTIVITIES OUTPUTS OUTCOMES CONTRACTUAL RESOURCES 1. Partnership agreements with the MOE county and local authorities, civil society 2.UNICEF-ISE-ARACIP agreement 3. Partnership agreements with 75 participatory schools 4.Partnership agreements with 30 DGASPC, ISJ and CJRAE MATERIAL RESOURCES 1. Kit model 2.Working tools (guides, methodological guidelines, pedagogical kits, CDs, movies) 3.On line communication platforms 4. Micro grants ( 2000 $ per school) HUMAN RESOURCES 1.National Coordinators ( UNICEF) 2. National facilitators ( ISE) 3..Management county facilitators (CJRAE) 4.Implementation county facilitators ( CJRAE, DGASPC) 5.Local management (at school level) 6.Local implementation staff ( school staff and social worker) 6.Trainers ( national and county level) 7.Researchers 6.Parental educators 7.Roma role models 8. National Volunteers 9. Local volunteers ACTIVITIES AT SCHOOL LEVEL 1.Blended learning for school representatives in order to improve evidence based decision making process 2. Training with teachers on 7 curricular, transversal themes 3 and 3 extracurricular areas 3. Extracurricular activities with children 4 Activities with parents at school level, involving teachers, parents and students ACTIVITIES AT FAMILIY LEVEL 1.Parental education sessions ACTIVITIES AT COMMUNITY LEVEL 1. Mobilize community networks 2. Promote Roma role models in 50 schools 3. Train social workers on civic and social competencies 4.Develop a monitoring methodology for identifying children at risk of dropout in need of social support 4. Sensitize mayoralties for financing parenting education sessions CROSS SECTORAL ACTIVITIES 1.Awarness raising on the importance of education 2.Interinstitutional partnerships developed for addressing dropout 3. Studies on the impact of parenting education 150 school representatives participated in school management training 700 teachers trained in 7 curricular areas, 3 transversal and 3extra-curricular areas 2500 children involved in curricular and extracurricular activities 1900 parents involved in teachers/parents/students activities 600 monitoring visits organized at school level 152 monitoring visits 600 parents trained for improving their parental skills 1 study on the impact of the parental education drafted 70 social workers trained on social and civic competencies 30 county experts trained on applying monitoring methodology 1500 children at risk needing social support identified School aged children not enrolled in school identified 30 cross sectoral meetings addressing dropout 1 national network of Roma students 5000 children participant to the debate and movie presentation on What do you want to be when you grow up? A decrease by 50% of dropout and absenteeism in school by comparison to school year 2011-2012 CONTEXT An estimated 400.000 children of compulsory school age not attending school regularly; A new educational law approved, promoting a 10 year free of charge compulsory education; An increase in poverty rates following the economic crisis, in parallel with significant cuts in public expenditure. Welcoming and friendlier schools Parents have better parental skills and parent –child communication is improved Communities are mobilized and act in an integrated manner to prevent school dropout Children at risk of dropout have increased self esteem Evidence-based recommendations are feeding public policies Inter-institutional cooperation is enhanced in SAI communities Increased cooperation at local and county level ( DGASPCSPAS), SPAS-schools LOGIC MODEL SCHOOL ATTENDANCE INITIATIVE (SAI) 2014-2015 GOAL Prevent and reduce school dropout and increase school attendance with a focus on the most disadvantaged children INPUTS CONTRACTUAL RESOURCES 1. Partnership agreements with the MOE county and local authorities, civil society 2.UNICEF-ISE-ARACIP agreement 3. Partnership agreements with 32 participatory schools 4.Partnership agreements with 19 DGASPC, ISJ and CJRAE MATERIAL RESOURCES 1. Kit model 2.Working tools (guides, methodological guidelines, pedagogical kits, CDs, movies) 3.On line communication platforms 4. Micro grants ( 2000 $ per school) HUMAN RESOURCES 1.National Coordinators ( UNICEF) 2. National facilitators ( ISE) 3.Management county facilitators (CJRAE) 4.Implementation county facilitators (CJRAE, DGASPC) 5.Local management (at school level) 6.Local implementation staff (school staff and social worker) 6.Trainers ( national and county level) 7.Researchers 6.Parental educators 7.Roma role models 8. National Volunteers 9. Local volunteers ACTIVITIES OUTPUTS OUTCOMES ACTIVITIES AT SCHOOL LEVEL 1.Blended learning for school representatives in order to improve evidence based decision making process 2. Training with teachers on 7 curricular subjects and 9 transversal themes 3. Extracurricular activities with children 4 Activities with parents at school level, involving teachers, parents and students ACTIVITIES AT FAMILIY LEVEL 1.Parental education sessions ACTIVITIES AT COMMUNITY LEVEL 1. Mobilize community networks 2. Promote Roma role models in 32 schools 3. Apply a monitoring methodology for identifying children at risk of dropout in need of social support 4. Support the children identified at risk of school dropout CROSS SECTORAL ACTIVITIES 1.Awarness raising on the importance of education 2.Interinstitutional partnerships developed for addressing dropout 3. Studies on: impact of parenting on school culture; violence in school, transitions to upper cycles of education, resilience in disadvantaged schools, access to education of children with disabilities 64 school representatives benefitting from customized school management training 320 teachers trained in 7 curricular areas and 9 transversal themes 2000 children involved in curricular and extracurricular activities promoted in SAI 300 parents involved in teachers/parents/students activities 42 monitoring visits organized at school level (and 8 support visits per school delivered by county facilitators) 490 parents trained for improving their parental skills Studies on: impact of parenting on school culture; violence in school, transitions to upper cycles of education, resilience in disadvantaged schools, access to education of children with disabilities 32 social workers supported to apply the child monitoring methodology 19 county experts applying the child monitoring methodology No. of children at risk needing social support identified; for which a social inquiry was conducted; with a Plan of Services; who benefitted of social prestations following the social inquiry; referred to the DGASPC in order to prevent abuse – neglect – exploitation; referred to DGASPC in order to get registered with a degree of disability No. of school aged children not enrolled in school identified No. of children supported through the Community Support Network 64 courses organized to test the pedagogical kit; 3200 children participating in the courses; 64 meetings with parents; 320 parents participating in the meetings; A decrease by 50% of dropout CONTEXT An estimated 400.000 children of compulsory school age not attending school regularly; A new educational law approved, promoting a 10 year free of charge compulsory education; An increase in poverty rates following the economic crisis, in parallel with significant cuts in public expenditure. and absenteeism in school by comparison to school year 2011-2012 Welcoming and friendlier schools Parents have better parental skills and parent –child communication is improved Communities are mobilized and act in an integrated manner to prevent school dropout Children at risk of dropout have an increased self-esteem Evidence-based recommendations are feeding public policies Inter-institutional cooperation is enhanced in SAI communities Increased cooperation at local and county level ( DGASPCSPAS), SPAS-schools