BIOL 2306 – Living Planet (hybrid)
advertisement

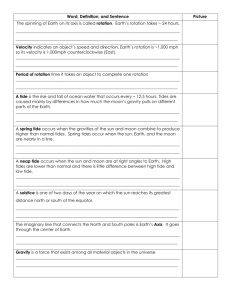
BIOL 2306 – Living Planet (hybrid) CONCEPTS FOR EPISODE 9 – Margins of the Land I. Tides – periodic changes in sea level due to gravitational pull of the moon and sun on water. A. High tides occur when earth, moon and sun are aligned B. Low tides occur when moon and sun are at right angles to each other; because the sun pulls the water in one direction and the moon pulls it in another direction, the total pull is lessened. C. Effects on organisms 1. variable salinity 2. variable temperature 3. variable O2 content 4. variable moisture 5. physical damage from wave force 6. variable susceptibility to predation II. Major types of coastal ecosystems A. rocky shore – underwater seaweed beds and tide pools B. sandy beach -- burrowers C. intertidal mud flat – nutrient-rich D. tidal estuary -- network of tidal creeks and salt marshes -- salinity is intermediate between salt and fresh water -- nursery grounds for shrimp, fish, birds III. Marine algae (seaweeds) A. body regions 1. blade – broad flat surface resembling leaf 2. holdfast – rootlike structure that attaches to solid surface 3. stalk – narrow region connecting blade and holdfast 4. air bladders – function as floats in some large seaweeds (example: kelp), keeping blade on surface of water during high tide so it can photosynthesize B. three main types 1. red algae - small, lacy - warm waters - deepest-occurring seaweeds because able to absorb blue light which penetrates deepest in water 2. green algae - small - variable - ancestors of plants 3. brown algae - largest seaweeds (giant kelps) - cool waters