Earthquake Epicenter Triangulation Worksheet
advertisement
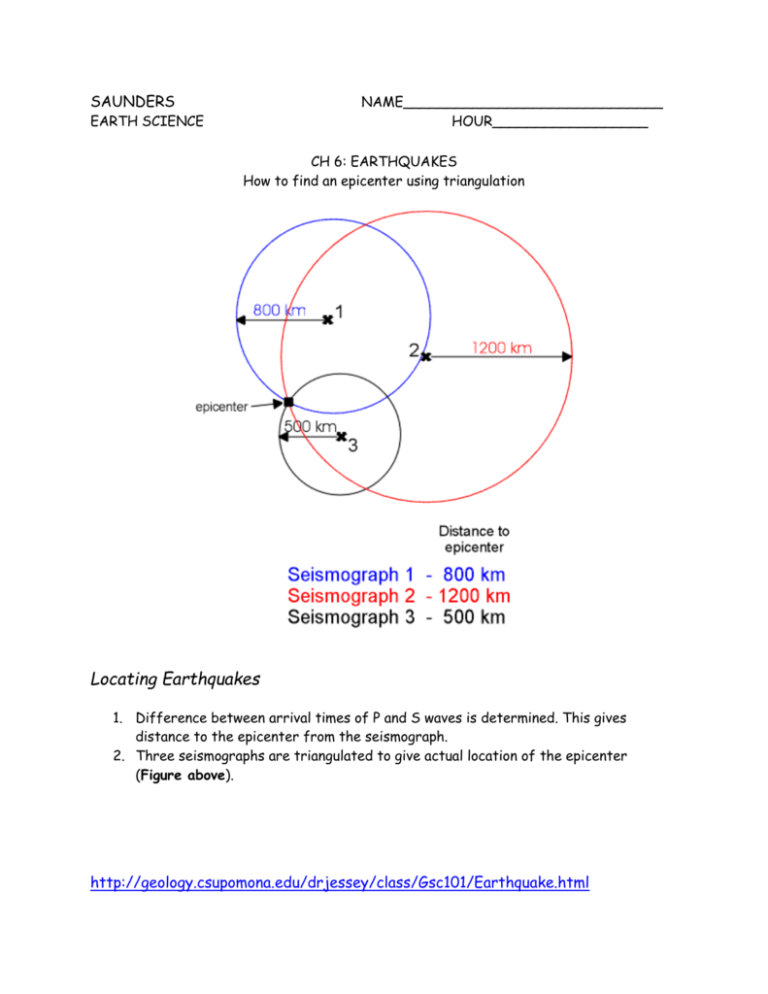
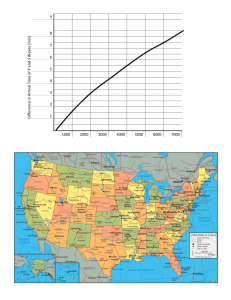
SAUNDERS NAME______________________________ HOUR__________________ EARTH SCIENCE CH 6: EARTHQUAKES How to find an epicenter using triangulation Locating Earthquakes 1. Difference between arrival times of P and S waves is determined. This gives distance to the epicenter from the seismograph. 2. Three seismographs are triangulated to give actual location of the epicenter (Figure above). http://geology.csupomona.edu/drjessey/class/Gsc101/Earthquake.html SAUNDERS EARTH SCIENCE NAME______________________________ HOUR__________________ CH 6: EARTHQUAKES Practice with Triangulation: Locating an earthquake epicenter In the 6.2 Notes, you learned that seismologists determine the distance to the earthquake epicenter using the difference between S and P wave arrival times. To locate the epicenter of the earthquake, seismologists use the distance data from 3 different seismographs, and then draw circles that distance away from the station. Where they intersect, that’s the epicenter!! (or close to it) An earthquake was recorded at Stations A, B, and C shown on the map below. Station A reported that the epicenter of the quake was 1500 km from the station. Station B reported a distance of 3500 km. Station C reported a distance of 5000 km. Using a ruler, compass, and the scale below of ¼ inch = 500 km, locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake on this map. ¼ inch = 500 km An earthquake was recorded at Stations A, B, and C shown on the map below. Station A reported that the epicenter of the quake was 2500 km from the station. Station B reported a distance of 5000 km. Station C reported a distance of 6750 km. Using a ruler, compass, and the scale below of ¼ inch = 500 km, locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake on this map. ¼ inch = 500 km SAUNDERS EARTH SCIENCE NAME______________________________ HOUR__________________ CH 6: EARTHQUAKES Practice with Triangulation: Locating an earthquake epicenter In the 6.2 Notes, you learned that seismologists determine the distance to the earthquake epicenter using the difference between S and P wave arrival times. To locate the epicenter of the earthquake, seismologists use the distance data from 3 different seismographs, and then draw circles that distance away from the station. Where they intersect, that’s the epicenter!! (or close to it) An earthquake was recorded at Stations A, B, and C shown on the map below. Station A reported that the epicenter of the quake was 2000 km from the station. Station B reported a distance of 2000 km. Station C reported a distance of 4500 km. Using a ruler, compass, and the scale below of ¼ inch = 500 km, locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake on this map. ¼ inch = 500 km An earthquake was recorded at Stations A, B, and C shown on the map below. Station A reported that the epicenter of the quake was 5500 km from the station. Station B reported a distance of 4000 km. Station C reported a distance of 1000 km. Using a ruler, compass, and the scale below of ¼ inch = 500 km, locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake on this map. ¼ inch = 500 km