extraction of nanoparticle iron (iii), silica and calcium sulphate from
advertisement

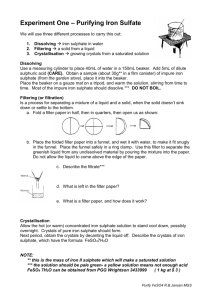
Extraction OF NANOPARTICLE IRON (III), SILICA AND CALCIUM SULPHATE FROM ELECTRIC ARC SLAG Muhammad Zamir Othman, Zaiton Abdul Majid* and Nor Aziah Buang Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science Universiti Technologi Malaysia *Email: zaiton@kimia.fs.utm.my Industrial waste material such as electric arc (EA) slag usually contains precious metal oxides and is classified as a scheduled waste. The EA slag is commonly used as a cement replacement material. Research has also shown the potential of utilizing EA slag in the treatment of phosphate containing wastewater and acidic wastewater. This research reports on a novel method of extraction of iron oxide catalyst from slag. Our group has successfully used this catalyst in the production of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The extraction process breaks down the perovskite structure of EA slag into nanoparticle size using top down principle. Besides the iron oxide, the extraction method also produced precious side products namely, silica and calcium sulphate. The slag used in this study was obtained from Antara Steel. It was ground and sieved before treating it with ammonium nitrate followed by sodium hydroxide and further heating at high temperature. The filtrate collected in ammonium nitrate and sodium hydroxide extraction process were further treated to produce silica and calcium sulphate. The treated slag was characterized using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM), Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDX), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer (FT-IR), and BET Surface Analyzer. The silica produced was characterized using X-ray Diffraction (XRD), FT-IR, FESEM-EDX and BET surface analyzer while the calcium sulphate produced was characterized using FESEM-EDX. The results obtained showed that nanoparticle iron was successfully extracted from the EA slag with a surface area of 72.51 m2/g. The EDX analysis showed high percentage of iron in the treated slag. Amorphous silica was successfully produced with a surface area of 133 m2/g and >90% purity . The XRD diffractogram illustrates clearly the existence of amorphous silica. This was further supported with the morphology of the amorphous silca as shown by FESEM. In addition, 99% of microsize calcium sulphate was successfully produced. FESEM analysis suggests that the calcium sulphate obtained is of high purity and have well crystalline structure of plane and rod like shaped. With this novel and simple extraction process, high yield and purity of iron oxide, silica and calcium sulphate were successfully extracted from EA slag.