Igneous Rock Exam: Physical Geology Questions & Answers
advertisement

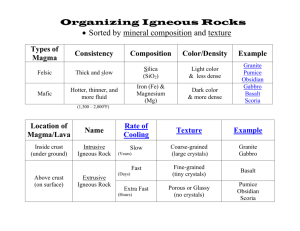
Physical Geology Igneous Rock Exam Name _____________________ Date ____________ © E. Fermann, 2007 MULTIPLE CHOICE [1 point each] 1. What is meant by “extrusive” and “intrusive”? a. Igneous rocks that cooled at the surface (volcanic) and interior to the surface (plutonic) of the Earth, respectively. b. Sedimentary rocks that cooled at the surface (volcanic) and interior to the surface (plutonic) of the Earth, respectively c. Metamorphic rocks that cooled at the surface (volcanic) and interior to the surface (plutonic) of the Earth, respectively d. All of these 2. Magma is _________. a. completely or partially molten material, which on cooling solidifies to form an igneous rock b. completely or partially molten material, which on cooling liquefies to form a lava tube c. an igneous rock, which on melting becomes completely or partially lava d. a lava fountain that completely or partially cools and solidifies to form molten rock 3. For igneous rocks, crystal size is interpreted to imply which of the following? a. how the magma felt during cooling b. time allowed for cooling of the magma/lava c. temperature of the magma d. chemistry/composition of the magma 4. Which of the following correctly describes the Hawaiian lava flows of aa and pahoehoe? a. Both are basaltic, pahoehoe contains more volatiles than aa b. Both are basaltic, pahoehoe contains fewer (less) volatiles than aa c. Both are volatile rich, pahoehoe is felsic and aa is mafic d. Both are felsic, pahoehoe is mafic and aa is mafic e. One is mafic, one has volatiles...and, Oh God! I don't know! 5. The immediate cause of the 1980 eruption of Mt. St. Helens seems to have been a. the formation of a bulge on the north side of the mountain b. a re-awakening of a long dormant hot spot under the volcano c. a build-up of pressure under the mountain d. an earthquake-triggered landslide that opened the side of the mountain. 6. .Quartz and olivine do not commonly occur in the same rock. What is the most probable reason for this? a. the two minerals form in different environments b. the two minerals compete for available silica, and one always 'wins' c. their x-tal structures are not compatible d. both minerals are bigoted, each thinking it is better than the other, and therefore refusing to x-tallize near one another. 7. The rock called GABBRO is a. intrusive and felsic b. intrusive and basaltic c. soft and fuzzy d. extrusive and felsic e. extrusive and mafic 8. Which of the following is an intermediate igneous rock? a. granite b. rhyolite c. diorite d. peridotite e. basalt 9. Andesite occurs most frequently a. on mid-oceanic island chains b. at continental margin volcanoes c. along continental rift zones d. along mid-oceanic ridges e. on stable platforms 10. The largest volcanoes on the Earth are a. composite volcanoes b. shield volcanoes c. cinder cones d. spatter cones e. strato-volcanoes 11. Which one of the following rocks is an ultramafic? a. rhyolite b. peridotite c. basalt d. diorite e. gabbro 12. The geothermal gradient __________. a. is the change in temperature with depth b. averages 20 to 30 degrees C per kilometer in the upper crust c. varies with depth d. is all of the above 13. The term 'granitic' means a. mafic and extrusive b. mafic and intrusive c. mafic, but not necessarily intrusive or extrusive d. felsic, but not necessarily intrusive or extrusive 14. A slowly cooled magma will most likely result in a rock with which one of the following textures? a. phaneritic b. pyroclastic c. glassy d. aphanitic e. porphyritic SHORT ANSWERS (point value is assigned after each question) 15. Define (one the answer sheet) the other four textures from question 14 (you get to leave one of them blank) [2 each for a total of 8] a. Phaneritic: b. Pyroclastic: c. Glassy: d. Aphanitic: e. Porphyritic: 16. The intrusive equivalent of the igneous rock basalt is ____. [1 pt] 17. The large circular depression occupied by Crater Lake is called a(n) ______ [1 pt] 18. The clinkery, sharp edged, chunky lava produced by the Hawaiian volcanoes is called _____ [1 pt] 19. The adjective that describes the composition of the rock in the upper mantle is _____ [1 pt] 20. The specifc name of the rock of the upper mantle is _____ (maybe two choices) [1 pt] 21. Ship Rock and Devil's Tower are erosional remnants of the cores of past volcanoes. These erosional remnants are called _____ (a 2 word answer is possible) [1 pt] 22. Two gases commonly exsolved from erupting magma are _____ and _____ [2 pts] 23. The fiery cloud eruption of Mt. Pelee that destroyed St. Pierre is known by its French term, _____. [1 pt] 24. Deadly mudflows created created when ash and loose earth on the side of an erupting composite cone are saturated by melted snow and ice are called _____. [1 pt] 25. How do temperature, pressure, and the amount of volatiles help control the melting of a magma? (answer this in the table on the answer page) [2 each for a total of 6] X 26. Identify (Place the appropriate letter in the boxes) the locations of the following igneous intrusions. There may be more than one location for some answers. [7 pts] a) dike b) sill c) lacolith d) batholith 27. What are the items identified with the letterX? [1 pt] 28. Where did they come from? [2 pts] 29. Are they solid or liquid? [1 pt] 30. How will the partial melting of these ‘things’ affect the composition of the magma they are in? [2 pt] 31. In the boxes above, identify the most likely locations for any of the following (use as many as you need) [4 pts] a. Basaltic volcanism b. Andesitic volcanism c. Granitic volcanism 32. Describe (with some detail) what accumulates in the subduction zone (composition, where it comes from, etc) [2 pts]