Felsic
advertisement
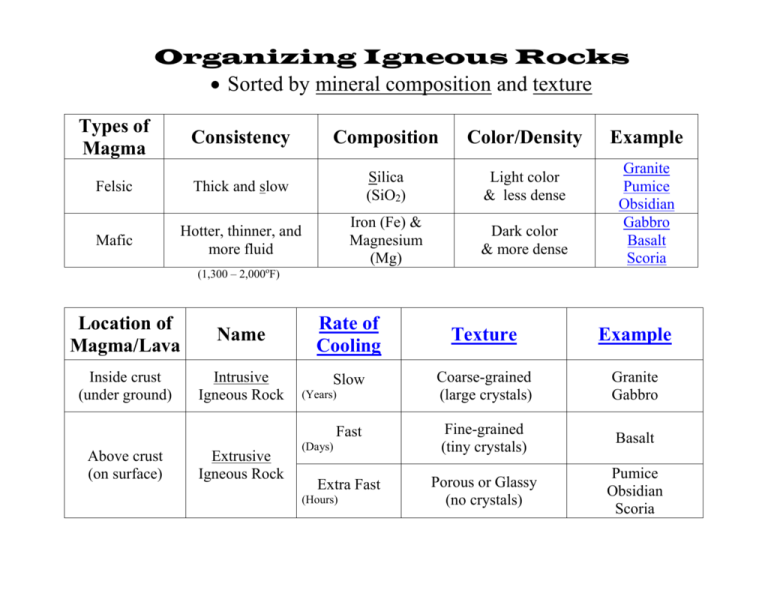
Organizing Igneous Rocks Sorted by mineral composition and texture Types of Magma Consistency Composition Color/Density Felsic Thick and slow Silica (SiO2) Light color & less dense Mafic Hotter, thinner, and more fluid Iron (Fe) & Magnesium (Mg) Dark color & more dense Example Granite Pumice Obsidian Gabbro Basalt Scoria (1,300 – 2,000oF) Location of Magma/Lava Name Rate of Cooling Texture Example Inside crust (under ground) Intrusive Igneous Rock Slow Coarse-grained (large crystals) Granite Gabbro Fast Fine-grained (tiny crystals) Basalt Extra Fast Porous or Glassy (no crystals) Pumice Obsidian Scoria Above crust (on surface) Extrusive Igneous Rock (Years) (Days) (Hours) “Volcanic landforms”- Igneous Intrusions A rock mass that forms when magma cools inside Earth’s interior. Also called a pluton Reaches Earth’s surface only after uplift and/or erosion. 1. Sills - A sheet of igneous rock that lies parallel to the layer it intrudes. Forced between rock layers. 2. Dikes - A sheet of igneous rock that cuts across rock layers vertically or a steep angle. Forced through (perpendicular) to rock layers. 3. Laccoliths - Dome shaped mass of igneous rock. Thick lava that does not flow easily pushes rock layers upward. 4. Volcanic Neck – the remnant of an extinct volcano. 5. Batholith - Largest of all plutons that form the cores of many of Earth’s mountain ranges. Exposed through uplift and erosion. 3D website 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. lava flow volcano magma pipe solidified lava flow sill dike laccolith batholith eroding laccolith volcanic neck











