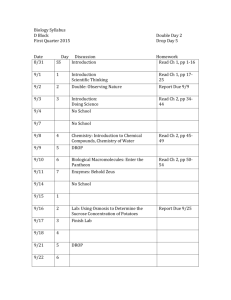
CV and publications
advertisement

JOHN LAWRENCE MARON ADDRESS Division of Biological Sciences, University of Montana, Missoula, MT 59812, Phone: 406-243-6202, Fax: 406-243-4184, e-mail: john.maron@mso.umt.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. U.C. Davis, Ecology. M.S. University of North Dakota, Biology. B.S. U.C. Davis, Renewable Resources 1996 1983 1980 PROFESSIONAL POSITIONS Organismal Biology and Ecology Program Director, Division of Biological Sciences, University of Montana Professor, Biological Sciences, University of Montana. Associate Professor, Biological Sciences, University of Montana. Assistant Professor, Biological Sciences, University of Montana. Assistant Professor, Botany Department, University of Washington. Adjunct Assistant Professor, Zoology, University of Washington. Postdoctoral Fellow, With Dr. Susan Harrison, U.C. Davis. Museum Scientist, Bodega Marine Reserve, U.C. Davis. Assistant Museum Scientist, Bodega Marine Reserve, U.C. Davis. Fall 2009-Present 2009-Present 2004-2009 2002-2004 1998-2002 1999-2002 1997-1998 1996-1997 1987-1997 TEACHING Population Biology, University of Montana (one of two instructors) Terrestrial Plant Ecology, University of Montana. Rocky Mountain Flora, University of Montana. Plant-Consumer Interactions, University of Montana. Conservation Biology, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Introductory Biology, University of Montana (one of four instructors). Trends in Plant Ecology, University of Montana (one of two instructors) Advanced Ecology, University of Washington (one of four instructors). General Ecology, University of Washington (one of three instructors). Plant-Consumer Interactions, University of Washington. Introduction to Plant Ecology, University of Washington. Sub-Tropical Field Ecology, Universidad de Cordoba, Argentina. Field Ecology, U.C. Bodega Marine Lab. (one of two instructors). 2009 2002-2004, 2006-2008 2005, 2007, 2009 2004, 2008 2006 2003 2003 2001 2001 1999 1998-2001 1992 1985-1991 RESEARCH GRANTS Current NSF, “Indirect effects of apex predators in a grassland ecosystem.” $578,295. (Co-PI. D. Pearson). NSF, “The role of soil microbes in plant invasions: inhibition at home and facilitation away?” $625,000. (Co-PI: R. Callaway). 1 2010-2014 2006-2010 USDA, Managed Ecosystems program, “Assessing the indirect effects of top predators on the diversity, productivity and health of grassland systems,” $300,000. (Co-PI: D. Pearson). 2005-2009 Previous BLM, “Effects of top predators on grassland communities,” $11,000. NSF, “Interacting effects of native plant diversity and resource availability on community invasibility and invader impact,” $368,998. (Co-PI: M. Marler). NSF ROA, “Interacting effects of native plant diversity and resource availability on community invasibility and invader impact,” $19,898. (Co-PI: P. Kittelson). USDA McIntire-Stennis program, “Effects of top predators on the management of grassland-forest ecotones in western Montana,” $89,942. BLM, “Effects of top predators on grassland communities,” $11,000. NSF, “Foxes and seabirds: the role of top-down processes in controlling marine subsidies to a terrestrial ecosystem,” $332,701. (Co-PIs: J. Estes and D. Croll). NSF, “Dissertation Research: Population dynamics of an invasive plant: Cynoglossum officinale in its native and introduced ranges,” $12,000 (written by: Jennifer Williams) National Parks/ESA Research Fellowship, “Assessing trophic control of Aspen demography across spatial and temporal scales in the Rocky Mountains.” $150,000. (PI: M. Kauffman). NSF, “Dissertation Research: Wildlife poaching, seed dispersal, and the functional similarity of mammalian frugivores in Thailand,” $8,242 (written by: Jedediah Brodie) NSF REU, “Interacting effects of native plant diversity and resource availability on community invasibility and invader impact,” $6,000. BLM, “Effects of top predators on grassland communities,” $5,000. BLM, “Effects of top predators on grassland communities,” $5,000. Montana Weed Trust, “Interacting effects of native plant diversity and resource availability on community invasibility and invader impact,” $14,633. (Co-PI: M. Marler). NSF, “Invasion and subsequent biological control of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum): rapid evolution of herbivore resistance?” $100,000. Missoula Weed Board, “Interacting effects of native plant diversity and resource availability on community invasibility and invader impact,” $6,000. (Co-PI: M. Marler). NSF REU, “Invasion and subsequent biological control of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum): rapid evolution of herbivore resistance?” $6,000. NSF REU, “Interacting effects of insect herbivory and rodent 2 2008-2009 2004-2009 2005-2009 2005-2008 2007-2008 2000-2007 2005-2007 2004-2007 2005-2006 2006 2005-2006 2004-2005 2003-2004 2000-2004 2002-2003 2002-2003 granivory on plant population dynamics,” $7,000. NSF, “Interacting effects of insect herbivory and rodent granivory on plant population dynamics,” $283,051. (Co-PI: E Simms). NSF REU, “Interacting effects of insect herbivory and rodent granivory on plant population dynamics,” $5,000. Royalty Research Fund, University of Washington, “Do biological control targets evolve resistance/tolerance to biological control agents?” $32,500. 2001-2002 1997-2002 2000-2001 2000-2001 FELLOWSHIPS/AWARDS/HONORS Catalunya PIV Fellowship, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona 2005-2006 PROFESSIONAL SERVICE Editorial Board, American Naturalist Review Panel Member, NSF, Ecology External “Frontiers in Ecology” Workshop, NSF Review Panel Member, NSF, Dissertation Improvement Grants External Workshop, NSF, Project NEON 2007-present 2006 2006 2002 2000 INVITED SEMINARS Estación Biológica de Doñana (EBD-CSIC), Sevilla, Spain “Darwin Lecture Series”, Fundation La Caixa, Madrid, Spain Guelph University Washington State University Miami University Colorado State University U.C. Davis Indiana University Fire Sciences Lab, U.S. Forest Service, Missoula University of Vermont Institute for Plant Sciences, University of Zurich Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research Université de Fribourg Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona “Eminent Ecologist Series”, Michigan State University UFZ Research Institute, Halle, Germany Plant protection meeting, Leysin, Switzerland CABI Bioscience, Delemont Switzerland University of Toronto Mississauga University of Toronto Idaho State University University Nevada Reno Cedar Point Biological Station, University of Nebraska Cornell University Bodega Marine Laboratory, U.C. Davis 3 2009 2009 2008 2008 2008 2007 2007 2007 2007 2006 2006 2006 2005 2005 2005 2005 2005 2005 2005 2005 2004 2004 2003 2003 2003 U.C. Santa Cruz University of Montana Native Plant Society, Seattle Chapter Duke University Smithsonian Environmental Research Center, Edgewater Bodega Marine Laboratory, U.C. Davis Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Simon Fraser University U.C. Santa Cruz University of Toronto Sonoma State University 2002 2001 2001 2001 2001 2000 2000 2000 1997 1996 1995 INVITED CONFERENCES AND WORKSHOPS ESA workshop, “Are invasives different?” Invasive Species in Natural Areas Conference Symposium on Insect-Plant Interactions (#13) Vice-Presidential Symposium, American Society of Naturalists. Project Baseline Workshop. Joint U.S.-Indian Forum on Invasive Plants. NCEAS Working Group- Natural Enemies Hypothesis. NSF Workshop-Model Systems in Community Ecology . USDA Conference on Biological Control of Weeds. University of Minnesota Symposium- Evolutionary Consequences of Invasions by Exotic Species. ESA Symposium-Phenotypic Change in Introduced Organisms. U.C. Bodega Marine Laboratory colloquium- Use of Model Systems in Ecological and Evolutionary Research. NCEAS Workshop- Spatial and Temporal Population Dynamics. 2009 2008 2007 2007 2007 2006 2004, 2005 2004 2004 2002 2000 1997 1996 PUBLICATIONS (Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals; 69 total) Williams, J.L, H. Auge, and J.L. Maron. In Press. Effects of disturbance and herbivory on invasive plant abundance at home and abroad. Ecology. Bricker, M., D. Pearson and J.L. Maron. In Press. Small mammal seed predation limits the recruitment and abundance of two perennial grassland forbs. Ecology. Maron, J.L., C.C. Horvitz and J.L. Williams. 2010. Using experiments, demography and population models to estimate interaction strength based on transient and asymptotic dynamics. Journal of Ecology 98: 290-301. Colautti, R.I., J.L. Maron and S.C.H. Barrett. 2009. Common garden comparisons of native and introduced plant populations: latitudinal clines can obscure evolutionary inference. Evolutionary Applications 2: 187-199. Johnson, M.T.J., A. Agrawal, J.L. Maron and J-P. Salminen. 2009. Heritability, covariation and natural selection on 24 traits of common evening primrose (Oenothera biennis) from a field experiment. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 22: 1295-1307. 4 Brodie, J., O.E. Helmy, W.Y. Brockelman and J.L. Maron. 2009. Bushmeat poaching reduces the seed dispersal and population growth rate of a mammal-dispersed tree. Ecological Applications 19: 854-863. Seifert, E.K., J.D. Bever and J.L. Maron. 2009. Evidence for the evolution of reduced mycorrhizal dependence during plant invasion. Ecology 90: 1055-1062. Brodie, J., O.E. Helmy and W.Y. Brockelman and J.L. Maron. 2009. Functional differences within a guild of tropical mammalian frugivores. Ecology 90:688-698. Maron, J.L. and M. Marler. 2008. Field based competitive impacts of invaders on natives at varying resource supply. Journal of Ecology 96: 1187-1197. Williams, J.L., H. Auge, and J.L. Maron. 2008. Different gardens, different results: Native and introduced populations exhibit contrasting phenotypes across common gardens. Oecologia 157: 239-248. Maron, J.L. and M. Marler. 2008. Effects of native species diversity and resource additions on invader impact. American Naturalist 172: S18-S33. Kittelson, P.M., J.L. Maron and M. Marler. 2008. Native diversity and invader impact: an exotic alters the leaf traits of two natives. Ecology 89: 1344-1351. Maron, J.L. and M. Marler. 2007. Native plant diversity resists invasion at both low and high resource levels. Ecology 88: 2651-2661. Maron, J.L., S. Elmendorf and M. Vilà. 2007. Contrasting plant physiological adaptation to climate in the native and introduced range. Evolution 61: 1912-1924. Morris, W.F., R.A. Hufbauer, A.A. Agrawal, J.D. Bever, V.A. Borowicz, G.S. Gilbert, J.L. Maron, C.E. Mitchell, I.M. Parker, A.G. Power, M.E. Torchin, D.P. Vázquez. 2007. Direct and interactive effects of enemies and mutualists on plant performance: a meta-analysis. Ecology 88:1021-1029. Agrawal, A.A., D.D. Ackerly, F. Adler, B. Arnold, C. Cáceres, D. Doak, E. Post, P. Hudson, J. Maron, K. Mooney, M. Power, D. Schemske, J. Stachowicz, S. Strauss, M. Turner, and E. Werner. 2007. Frontiers in population and community ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 5:145-152. Maron, J.L. 2006. The relative importance of latitude matching and propagule pressure in the colonization success of an invasive forb. Ecography 29:819-826. Amsberry, L.K. and J.L. Maron. 2006. Effects of herbivore identity on plant fecundity. Plant Ecology 187: 39-48. Kauffman, M. and J.L. Maron. 2006. Influence of density-dependence and seed bank dynamics in habitat-specific population dynamics of bush lupine, Lupinus arboreus. American Naturalist 168:454-470. Maron, J.L. and E. Crone. 2006. Herbivory: effects on plant abundance, distribution, and population growth. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 273:2575-2584. Callaway, R.M. and J.L. Maron. 2006. What have exotic invasions taught us over the past twenty years? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 21: 369-374. Mitchell, C.E., A.A. Agrawal, J.D. Bever, G.S. Gilbert, R.A. Hufbauer, J.N. Klironomos, J.L. Maron, W.F. Morris, I.M. Parker, A.G. Power, E.W. Seabloom, M.E. Torchin, D.P. Vázquez. 2006. Biotic interactions and plant invasions. Ecology Letters 9: 726-240. Maron, J.L., J.A. Estes, D.A. Croll, E.M. Danner, S.C. Elmendorf, and S. Buckalew. 2006. An introduced predator transforms Aleutian Island plant communities by disrupting spatial subsidies. Ecological Monographs 76:3-24. 5 Maron, J.L. and M. Kauffman. 2006. Habitat-specific consumer impacts on plant population dynamics. Ecology 87:113-124. Croll, D.A., J.L. Maron, J.A. Estes, E.M. Danner, and G.V. Byrd. 2005. Introduced predators transform subarctic islands from grassland to tundra. Science 307:1959-1961. Vilà, M., J.L. Maron and L. Marco. 2005. Evidence for the enemy release hypothesis in Hypericum perforatum L. Oecologia 142:474-479. Hierro, J., J.L. Maron and R.M. Callaway. 2005. A biogeographical approach to plant invasion biology: The importance of studying exotics in their introduced and native range. Journal of Ecology 93:5-15. Maron, J.L., M. Vilà, and J. Arnason. 2004. Loss of natural enemy resistance among introduced populations of St. John’s Wort, Hypericum perforatum. Ecology 85:3243-3253. Maron, J.L., M. Vilà, R. Bommarco, S. Elmendorf and P. Beardsley. 2004. Rapid evolution of an invasive plant. Ecological Monographs 74:261-280. Umbanhowar, J., J.L. Maron and S.P. Harrison. 2003. Density dependent foraging behaviors in a parasitoid lead to density dependent parasitism of its host. Oecologia 137:123-130. Vilà, M., A. Gómez and J.L. Maron. 2003. Are alien plants more competitive than their native conspecifics? A test using St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum). Oecologia 137:211-215. Callaway, R.M., A. Sala, E. Crone, J. Maron. 2003. Plant ecology textbooks: a new contender. American Journal of Botany 90:960-964. Rudgers, J.A. and J.L. Maron. 2003. Facilitation between coastal dune shrubs: a non-nitrogen fixing shrub facilitates establishment of a nitrogen-fixer. Oikos 102:75-84. Karban, R., J. Maron, G.W. Felton, G. Ervin and H. Eichenseer. 2003. Herbivore damage to sagebrush induces resistance in wild tobacco: evidence for eavesdropping between plants. Oikos 100:325-332. Maron, J.L., J.K. Combs and S.L. Louda. 2002. Convergent demographic effects of insect herbivory on related thistles in coastal vs. continental dunes. Ecology 83:3382-3392. Karban, R. and J.L. Maron. 2002. The fitness consequences of interspecific eavesdropping between plants. Ecology 83:1209-1213. Kittelson, P.M. and J.L. Maron. 2001. Fine scale genetically-based differentiation of life-history traits in the perennial shrub, Lupinus arboreus. Evolution 55:2429-2438. Maron, J.L. and M. Vilà. 2001. Do herbivores affect plant invasion? Evidence for the natural enemies and biotic resistance hypotheses. Oikos 95:363-373. Maron, J.L. and R.L. Jefferies. 2001. Restoring enriched grasslands: effects of mowing on species richness, productivity and nitrogen retention. Ecological Applications 11:1088-1100. Maron, J.L. and E.L. Simms. 2001. Rodent limited establishment of bush lupine: Field experiments on the cumulative effect of granivory. Journal of Ecology 89:578-588. Maron, J.L., S. Harrison, and M.E. Greaves. 2001. Origin of an insect outbreak: escape in space or time from natural enemies? Oecologia 126:595-602. Maron, J.L. 2001. Intraspecific competition and subterranean insect herbivory: individual and interactive effects on bush lupine. Oikos 92:178-186. Harrison, S., K.J. Rice and J.L. Maron. 2001. Habitat patchiness promotes invasion by alien grasses (Avena fatua and Bromus hordeaceus) on serpentine soil in California. Biological Conservation 100:45-53. Alpert, P. and J.L. Maron. 2000. Carbon addition as a countermeasure against biological invasion by plants. Biological Invasions 2:33-40. 6 Polis, G.A., D.R. Strong, G.R. Huxel, A.L.W. Sears and J.L. Maron. 2000. When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 15:473-475. Maron, J.L. and S.N. Gardner. 2000. Consumer pressure, seed versus safe-site limitation, and plant population dynamics. Oecologia 124:260-269. Harrison, S., J.L. Maron and G. Huxel. 2000. Local extinction, colonization and large-scale patterns of fluctuation in five plants confined to serpentine seeps. Conservation Biology 14:769779. Kittelson, P.M. and J.L. Maron. 2000. Outcrossing rate and inbreeding depression in the perennial yellow bush lupine, Lupinus arboreus (Fabaceae). American Journal of Botany 87:652-660. Grosholz, E.D., G.M. Ruiz, C.A. Dean, K.A. Shirley, J.L. Maron and P.G. Connors. 2000. The impacts of a non-indigenous marine predator in a California bay. Ecology 81:1206-1224. Maron, J.L. and R.L. Jefferies. 1999. Bush lupine mortality, altered resource availability and alternative vegetation states. Ecology 80:443-454. Maron, J.L. 1998. Individual and joint effects of below- and above-ground insect herbivory on perennial plant fitness. Ecology 79:1281-1293. Maron, J.L. and S. Harrison. 1997. Spatial pattern formation in an insect host-parasitoid system. Science 278:1619-1621. Maron, J.L. and E.L. Simms. 1997. Effects of seed predation on seed bank size and seedling recruitment of bush lupine (Lupinus arboreus). Oecologia 111:76-83. Maron, J.L. 1997. Interspecific competition and insect herbivory reduce seedling survival in bush lupine, Lupinus arboreus. Oecologia 110:285-290. Jefferies, R.L. and J.L. Maron. 1997. An embarrassment of riches: anthropogenic deposition of nitrogen and community and ecosystem processes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 12:74-78. Strong, D.R., H.K. Kaya, A. Whipple, A. Child, S. Kraig, M. Bondonno, K. Dyer, and J.L. Maron. 1996. Entomopathogenic nematodes: natural enemies of root-feeding caterpillars on bush lupine. Oecologia 108:167-173. Maron, J.L. and P.G. Connors. 1996. A native nitrogen-fixing shrub facilitates weed invasion. Oecologia 105:302-312. Strong, D.R., J.L. Maron, and P.G. Connors. 1996. Top down from underground? The underappreciated influence of subterranean food webs on above ground ecology. In Food Webs (G. A. Polis and K. O. Winemiller, eds.), pp 170-175. Chapman and Hall, New York. Strong, D.R., J.L. Maron, P.G. Connors, A. Whipple, S. Harrison, and R.L. Jefferies. 1995. High mortality, fluctuation in numbers, and heavy subterranean insect herbivory in bush lupine, Lupinus arboreus. Oecologia 104:85-92. Harrison, S. and J.L. Maron. 1995. Impacts of defoliation by tussock moths (Orgyia vetusta) on the growth and reproduction of bush lupine (Lupinus arboreus). Ecological Entomology 20:223229. Johnson, O.W., P.G. Connors, P.L. Bruner, and J.L. Maron. 1993. Breeding ground fidelity and mate retention in the Pacific Golden-plover. Wilson Bulletin 105:60-67. Connors, P.G., B.J. McCaffery and J.L. Maron. 1993. Speciation in golden-plovers, Pluvialis dominica and Pluvialis fulva: evidence from the breeding grounds. Auk 110:9-20. Myers, J.P., M. Sallaberry A., E. Ortiz, G. Castro, L.M. Gordon, J.L. Maron, C.T. Schick, E. Tabilo, P. Antas, and T. Below. 1990. Migration routes of New World sanderling (Calidris alba). Auk: 107:172-180. 7 Maron, J.L. and J.P. Myers. 1985. Seasonal changes in feeding success, activity patterns, and weights of non-breeding sanderlings, (Calidris alba). Auk 102:580-586. Maron, J.L. and J.P. Myers. 1984. An evaluation of two techniques for sexing wintering sanderlings (Calidris alba). Journal of Field Ornithology 55:336-342. Myers, J.P, J.L. Maron, and M. Sallaberry. 1984. Going to extremes: why sanderlings migrate to the neotropics. Ornithological Monographs 36:520-535. Myers, J.P., G. Castro, B. Harrington, M. Howe, J.L Maron, E. Ortiz, M. Sallaberry, C.T. Schick, and E. Tabilo. 1984. The Pan American Shorebird Program: a progress report. Wader Study Group Bulletin 42:26-30. Myers, J.P., J.L. Maron, E. Ortiz T., G. Castro V., M.A. Howe, R.I.G. Morrison, and B.A. Harrington. 1983. Rationale and suggestions for a hemispheric color-marking scheme for shorebirds: A way to avoid chaos. Wader Study Group Bulletin 38:30-32. Maron, J.L. 1982. Shell-dropping behavior of western gulls. Auk 99:565-569. PUBLICATIONS (Peer-Reviewed Book Chapters) Maron, J.L. and M. Vilà. 2008. Exotic plants in an altered enemy landscape: effects on enemy resistance. Pages 280-295 In: Specialization, Speciation and Radiation: the Evolutionary Biology of Herbivorous Insects (Kelley J. Tilmon, Ed.). University of California Press, Berkeley. MANUSCRIPTS IN REVIEW Bricker, M. and J.L. Maron. In Review. Seed predation lowers population growth rate in a longlived perennial forb (Lithospermum ruderale). Ecology. Maron, J.L., D.E. Pearson and R. Fletcher Jr. In Review. Large-scale predator removal has variable effects on a mid-latitude rodent community. Ecology Maron, J.L., M. Marler, J. Klironomos, and C. Cleveland. In Review. Soil pathogens contribute to the positive plant diversity-productivity relationship. Ecology. MANUSCRIPTS IN PREPARATION Maron, J.L. and D.E. Pearson. Effects of large-scale predator exclusion on deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus) foraging behavior. For Oikos. GRADUATE ADVISING Current Ph.D. students: Jennifer Palladini, Elliott Parsons, Sarah Pinto. MS students: Lauren Priestman Past Lindsay Amsberry, MS 2003, Jedediah Brodie, Ph.D. 2007, Jennifer Williams, Ph.D. 2008, Mary Bricker, Ph.D. 2009. Postdoctoral Fellows, Past Matthew Kauffman, Currently Assistant Co-Op Leader, USGS, University of Wyoming. Riccardo Bommarco, Currently Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden. 8