Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions Outline
advertisement

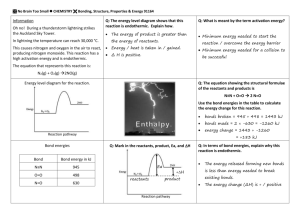
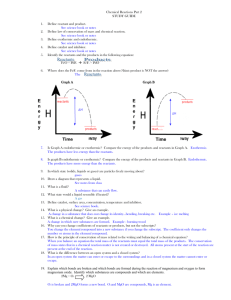
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions Outline I. Chemical reactions alter arrangements of atoms. A chemical reaction produces new substances by changing the way atoms are arranged. Bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds form between different atoms. A. Atoms interact in chemical reactions. 1. Physical changes may change some of the properties of a substance, but it is still the same substance i.e. liquid water changes to water vapor when boiled 2. Chemical changes: New substance is formed .i.e. wood burns to form smoke and ash; rust forms on iron; 3. Reactants and products Two types of substances are involved in all chemical reactions. a. reactants-the substances present at the beginning of a chemical reaction b. products-substances formed by the chemical reaction 4. Evidence of chemical reactions-obvious changes-substance looks different a. color change Brown rust on iron b. formation of a precipitate Two liquids that react may produce a solid product c. formation of a gas carbon dioxide gas produced when limestone reacts with an acid. d. temperature change This change can be inferred from the observation of a flame, but other temperature changes are not so obvious. Concrete feels warm before it hardens due to a chemical reaction. B. Chemical reactions can be classified. All reactions form new products, but the ways these products form can differ. 1. Synthesis -A new product is formed by the combination of simpler reactants; N2 + 2O2 2NO2 2. Decomposition- A reactant breaks down into simpler products, which can be elements or compounds. Electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction. 2H20 2H2 + O2 3. Combustion- One reactant is always oxygen and another reactant often contains carbon and hydrogen. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2 H2O C. The rates of chemical reactions can vary. Striking a match- quick reaction while iron rusting can take longer. Most chemical reactions take place when particles of reactants collide with enough force. Four factors (3 physical &1 chemical ) that greatly affect the rate at which reactant particle collide: 1. Concentration – turn up the valve releases more gas-burns faster 2. Surface area- breaking a substance down-log compared to kindling 3. Temperature-Adding energy makes particles move faster-reactants collide more often 4. Catalysts-Substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction but are not themselves consumed or changed in the reaction. an enzyme in your saliva, called amylase, starts off the breakdown of starch in food. II. The masses of reactants and products are equal. Many times, mass may seem to disappear, but it most likely has turned into a gas. When wood burns, for example, the carbon unites with oxygen to become carbon dioxide gas. A. Careful observations led to the discovery of the conservation of mass. The French chemist Antoine Lavoisier did a lot to confirm the law of the conservation of mass with his very careful observations of chemical reactions. In a number of chemical reactions, he demonstrated how all the mass of the reactants could be accounted for in the products. B. Chemical reactions can be described by chemical equations. 1.Chemical equations represent how atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction. 2.The reactants appear on the left side of the equation and the products on the right. 3. Since no atoms are lost or gained during a chemical reaction, there are the same number of each kind of atom on each side of the equation. 4. Every correct chemical equation is balanced. 5. To write a chemical equation, you need to know 3 things. a. The reactants and products in the reaction b. The atomic symbols and chemical formulas of the reactants and products in the reaction c. The direction the reaction proceeds Example : Reactants C + O2 Direction of reaction Products CO2 “Carbon reacts with oxygen to yield carbon dioxide.” C. Chemical equations must be balanced. They must follow the law of conservation of mass (matter). 1. Balancing chemical equations The same number of atoms must appear on both sides of a chemical equation. 2. Using coefficients to balance equations. a. Coefficients are numbers placed before the chemical formula to show how many molecules of each the substance are involved in the reaction . b. Multiply coefficients and subscripts. i.e. 2H2O contain 2x2 Hydrogen and 2x1 Oxygen c. Only coefficients can be changed to balance a chemical equation. Subscripts are part of the chemical formula for reactants or products and cannot be changed. Never change subscripts! 3. Using the conservation of mass A balanced chemical equation and the law of the conservation of mass can explain how many things can occur, such as how an automobile air bag can inflate using only a small amount of matter. See p84 III. Chemical reactions involve energy changes. A. Chemical reactions release or absorb energy. Whether a chemical reaction will release or absorb energy depends upon the energy in the bonds of the reactants and products. 1. The energy associated with the bonds in a compound is called its bond energy. 2. The bond energy for a bond between C and H is different from the bond energy for C and O. 3. Breaking chemical bonds, such as when the reactants of a reaction break apart, requires energy. 4. Forming chemical bonds, such as when products in a reaction are formed, releases energy. B. Exothermic reactions release energy. This occurs when more energy is released when the products form than is needed to break the bonds in the reactants. 1. The bond energies of the reactants are less than the bond energies of the products. 2. This energy difference between reactants and products is often released as heat. 3. Some energy must first be added to break bonds in the reactants. i.e. A small amount of energy is needed to start the combustion of methane, but the energy released by combustion is much greater. 4. Some exothermic reactions release energy as light. i.e. glow sticks and fireflies p.88 C. Endothermic reactions absorb energy. This occurs when more energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants than is released when the products form. 1. The bond energies of the reactants are greater than the bond energies of the products. 2. The energy difference is usually absorbed from the surroundings as heat. 3. This often causes a decrease in the temperature of the reaction mixture 4. The decomposition of water is an exothermic reaction that absorbs electrical energy to proceed. If the flow of electrical energy stops, the reaction stops. 5. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants absorb energy from sunlight to turn carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose (a type of sugar). (most imp endothermic reaction) 6. The energy added by the sunlight to process this reaction is stored in the bonds of the glucose molecule. D. Exothermic and endothermic reactions work together to supply energy. 1. Energy is released in an exothermic reaction, so energy is made one of the products. 2. Energy is absorbed in an endothermic reaction, so it is made one of the reactants. 3. If an exothermic reaction proceeds in the opposite direction, it becomes an endothermic reaction. 4. If an endothermic reaction proceeds in the opposite direction, it becomes an exothermic reaction. 5. A large amount of energy used on Earth comes from the Sun. The Sun's energy is stored by endothermic reactions in fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum, and then released by exothermic reactions, such as the burning of these fuels in furnaces and automobiles. The energy stored by plants in photosynthesis reactions is released by living things through a series of exothermic reactions. IV. Life and industry depend on chemical reactions. A. Living things require chemical reactions. 1. The glucose molecules produced by photosynthesis make up the basic food used for energy by almost all living things. 2. Living cells obtain energy from glucose molecules through a process called respiration, which is the "combustion" of glucose to obtain energy. 3. Respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis. It is the “combustion” of glucose. 4. Glucose molecules from the food you eat are stored in your body. The energy contained in them is released by respiration when you need it. (like running to class) Photosynthesis 6 CO2 + 6H2O+ energy Respiration C6H12O6 + 6 O2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy 5. Your body uses enzymes at various stages to speed up the process of respiration. B. Chemical reactions are used in technology. 1. An example, driving a car involves the combustion of gasoline. However, the combustion of gasoline makes harmful waste products. 2. Catalysts found in a car’s catalytic converter, can be used to eliminate some of the waste products or make them less harmful C. Industry uses chemical reactions to make useful products. 1. Electronic industry is extremely dependent on the semiconductor silicon, Si because it can precisely control conduction of electronic signals. 2. Various chemical reactions with this material and others have made it possible to make computer chips, cell phones and laser printers as well as many other electronic instruments.