AS 434 Lab 1 Exercise (2002)
advertisement

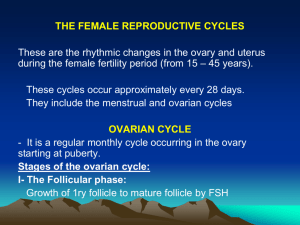
Lab Exercise 1 Animal Science 434 - Laboratory Exercise 1 – Questions This document is only the questions for lab 1. Student 1: Student 2: Student 3: Student 4: Date: Questions: 1. Draw a diagram of the cow or pig reproductive tract you are given in lab and identify the following structures. broad ligament mesovarium mesosalpinx mesometrium germinal epithelium tertiary follicle corpus luteum corpus albicans fimbria infundibulum ampulla isthmus uterotubal junction uterine horn uterine body endometrium myometrium perimetrium Bifurcation caruncles cervix internal cervical os external cervical os cervcal rings cervical canal fornix of the vagina vagina 2. What type of organism Trichomonas fetus is and what are its symptoms after it has infected cattle. 3. Trichomoniasis can be controlled by artificial insemination. What does this tell you about the disease and why would it be more common in beef rather than dairy cattle? 4. Visit one or more of the web sites listed in the other links section of the Trichomoniasis page and describe something you found that was not discussed in the AS 434 web site. 5. Aspirate the visible follicles on a bovine or porcine ovary as instructed by your TA and the lab procedure. Draw a picture of what one of the oocytes look like under a dissecting microscope. In case you do not find an oocyte, draw a picture of the one from the website. 6. What is the difference between a primary, secondary and tertiary follicle? Which of these follicle types can be seen without the use of a microscope? 7. Why is it unlikely to find a functional corpus luteum and a corpus hemorrhagicum at the same time in a normally cycling cow or pig? 1 Lab Exercise 1 8. Your textbook has a glossary. Using that glossary, define the following terms: a. Antrum b. Atresia c. fallopian tubes d. hilus e. labia f. necrosis g. stigma h. vestibule 9. Draw diagrams of the reproductive tracts of the sow, ewe, cow, mare and human along with the uterine shape classification of each (do not label parts of the tracts). What evolutionary pressure might have caused the development of different uterine shapes among mammals? In addition to the pig, what other species would you speculate might have a bicornuate shape to the uterus with long uterine horns? 10. List 3 differences between the reproductive tracts of a cow and sow. 11. What is the major morphological difference in a woman's reproductive tract as compared with the reproductive tracts of female farm animals? 12. What does the term ovulation fosa mean with regards to the mare? 2