Female Reproductive System: Anatomy & Function
advertisement

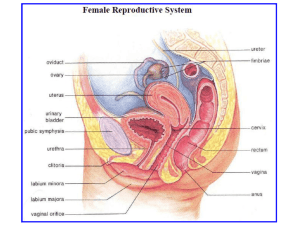
Female Reproductive System Components Paired ovaries Paired oviducts or Fallopian tubes Uterus Vagina Functions Produces female germ cells, ova (singular, ovum) Produces female sex hormones, estrogen, and progesterone Receives sperm Site of fertilization Transports female germ cells, sperm, and conceptus Houses and nourish conceptus during pregnancy Expels fetus at parturition Ovary Flattened, ovoid, paired glands - Exocrine function. Maturation and release of oocytes, deve' .nng female germ cells - Endocrine function. Secretion of estrogen and progesterone Subd ivisions 1. Cortex - Covered with a serosa - Germinal epithelium. Simple cuboidal epithelium (mesothelium) - Tunica albuginea Underlying, dense connective tissue. The exact contents depend on age of the ovary and the stage of the ovarian Cycle including: - Follic!es: Spheres of epithelial cells surrounding an oocyte. - Corpus luteum: Formed from the wall of the ovulating follicle after the oocyte is ovulated. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen and is present during the second half of the ovarian cycle. - Atretic follicles: Degenerating follicles that are not ovulated - Corpus albicans: Degenerating corpus luteum 2- Medulla Inner region composed of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves Follicles - Primordial follicle: Is the only follicle present until puberty - Primary follicles: 1- Primary unilaminar follicle 2- Primary multilaminar follicle - Secondary follicle - Mature (Graafian) follicle. - Atreticfollicles ' Corpus Luteum The corpus luteum is large, spherical, infolded body functional during the second half of the ovarian cycle . @ Functional stage: - The corpus luteum is formed by differentiation of the granulose and theca interna celts in the Graafian follicle before and after ovulation. It composed of: - Granulosa lutein cells. - Theca lutein cells. Secretes progesterone and estrogen - Degenerating stage. Corpus albicans - Consists of a white mass of scar tissue composed of much collagenous material and scattered fibroblasts - Results from the degeneration of the corpus luteum Oviduct The oviducts are paired, i2-cm-Iong tubes that have four subdivisions. - lnfundibuhun. Funnel-shaped, free end with finger-like fimbria embracing the ovary - Ampulla. Thin walled, lateral two-thirds; fertilization occurs here near its junction with the isthmus - Isthmus. Thicker walled, medial one-third - Intramural (interstitial). Within uterine wall; lumen is continuous with uterine lumen. Structure: Mucosa Shows gradations from infundibulum to intramural subdivisions - Exhibits complex mucosal folds - Epithelium. Simple columnar composed of ciliated cells, that are most abundant in thelnfundibulum, and secretory cells, that are most abundant in the intramural portion - Muscularis n1ucosae is lacking. Submucosa is continuous with lamina propria, forming a continuous connective tissue layer. - Muscularis externa has poorly defined inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers, which are thinnest in the infundibulum and thickest in the intramural portion. - Serosa. Covers the outer surface except in the intramural portion Uterus Cl'OSS Anatomy - A single, pear-shaped, ·and pear-sized organ - Subdivisions - Fundus. Domed portion above entrance of oviducts - Corpus or body. Major portion of the uterus - Isthmus. Constricted portion at j unction of cervix and body Cervix Located above and within the vagina, defining supravaginal and vaginal portions Vagina Structure Mucosa - Epithelium.Stratified squamous nonkeratinized· that accumulates glycogen; no glands are present. - lamina propria. Rich with numerous blood vessels and elastic fibers. - Muscularis mucosae is lacking. - Rugae (folds) allow for expansion. - Submucosa is continuous with the lamina propia, forming a single connective tissue layer. Muscular layer - Inner circular and aliter longitudinal smooth muscle layers intertwine .. - skeletal muscle surrounds the vaginal orifice. - adventitia of loose connective tissue Schematic representation of the female reproductive system