Chapter 12 Assignment Answers
advertisement

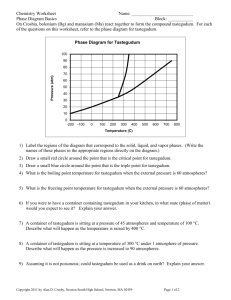
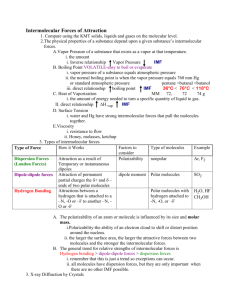
Chapter 12 Assignment Answers 18. Particles are closer together in solids than in liquids because of intermolecular attractions. 23. Because the adhesive forces between water molecules and the silicon dioxide in glass are greater than the cohesive forces between water molecules, the water rises along the inner walls of the cylinder. 24. The cohesion between mercury atoms is stronger than the adhesion between mercury and glass. 27. The addition of energy increases the kinetic energy of the particles, which reduces the intermolecular forces between the particles. As energy is removed, the kinetic energy of the particles decreases and intermolecular forces increase. 28. Freezing occurs when a liquid becomes a solid and energy is released. Melting requires an input of energy to convert a solid to a liquid. 29. A substance undergoes deposition when it goes from the vapor phase to the solid phase without going through the liquid phase. A substance undergoes sublimation when it goes from the solid phase directly to the vapor phase without going through the liquid phase. 30. In both processes, the substances become a vapor. During sublimation, the substance goes from the solid phase directly to the vapor phase. During evaporation, particles in a liquid gain enough energy to enter the vapor phase. 31. The combinations of temperature and pressure under which a given substance exists as a solid, liquid and/or gas. 32. Triple point: the temperature at which the three phases of a substance can coexist; critical point: the pressure and temperature above which a substance cannot exist as a liquid. 33. liquid 34. the one in which no KE is lost. 35. It is directly proportional to their temperature. 38. Gases have low density, can be compressed, will expand to fill all available space, and can undergo diffusion & effusion. 51. A temporary dipole forms when one molecule is close to another molecule, and the electrons repel each other creating a greater electron density in one part of the molecule. Permanent dipoles are found in polar molecules in which some regions of the molecule are always partially positive & partially negative. 53. A hydrogen bond involves a large difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen atom and the atom it is attached to (O, N, or F), making the bond extremely polar. 63. Capillary action results from the opposing forces of adhesion & cohesion. Adhesive forces between water molecules & the molecules in the glass of the capillary tube are stronger than the cohesive forces holding water molecules together, so water moves up the walls of the capillary tube. 68. Stronger intermolecular forces result in higher viscosity because the forces hold the particles together too tightly for them to flow easily. 69. Surface tension increases with strength of interparticle forces. Water molecules are held together by strong hydrogen bonds, resulting in higher surface tension; the weaker dispersion forces between benzene molecules result in lower surface tension. 77. The temperature at which the crystal lattice of a solid disintegrates and it becomes a liquid. 78. Boiling point is the temperature at which vapor pressure, exerted by liquid molecules escaping from the surface of a sample, equals the atmospheric pressure on the surface of the liquid. 79. Then water vapor in the air comes in contact with a cool object, it condenses on the object. 82. Melting does not require as much energy because the particles in a solid do not have to move far apart or gain much movement to form a liquid. 90. a. 100 o C b. 78.5 o C c. 94 o C