Donghai Zheng - East Carolina University
advertisement

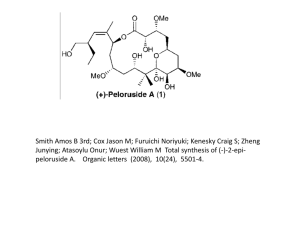
CURRICULUM VITAE Donghai Zheng Human Performance Lab Department of Exercise and Sport Science East Carolina University, Greenville, NC 27858 (252)-744-3465 (Office), (252)-757-1238 (Home) zhengd@ecu.edu CURRENT POSITION Senior Research Associate; East Carolina University, Department of Exercise and Sport Science, School of Health and Human Performance. EDUCATION AND CREDENTIALS PhD, Bioenergetics, 2006 Mentor: Dr. G. Lynis Dohm East Carolina University, Greenville, NC MS, Computer Science, 2003 East Carolina University, Greenville, NC MA, Exercise Physiology. 1995 East Carolina University, Greenville BA, Biology/Physiology. 1986. Nanjing University, Nanjing, China PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE April 2007 – Present Senior Research Associate Dept. of Exercise and Sport Science East Carolina University, Greenville NC July 2002-Mar.,2007 Visiting Instructor & Research Associate Dept. of Physiology/Exercise and Sport Science East Carolina University, Greenville NC May,95 - May, 2002 Research Technician III Dept. of Biochemistry, School of Medicine East Carolina University, Greenville NC Aug.,92-May,95 Graduate Research Assistant Human Performance Lab East Carolina University, Greenville, NC July,86-Aug.,92 Research Associate Dept. of Biochemistry and Physiology Jiangsu Research Institute of Sports Science Nanjing 210014, China PROFESSIONAL MEMBERSHIP American Physiological Society RESEARCH AND TEACHING EXPERIENCE Metabolism and Exercise • Insulin signaling pathway, insulin receptor and IRS1 phosphorylation in muscle and myocyte from insulin resistant patients (obese and diabetic). • Mechanism of regulation of Glut4 gene expression in response to exercise, Immobilization/denervation, fiber type and agents such as AICAR, hormones using rats, transgenic mice and human subject models. • Fatty acid uptake and oxidation regulation in muscle and cultured myocyte. • Energy expenditure, oxygen consumption and cardiac function in response to exercise training. Obesity, Diabetes and Exercise • Obese gene, uncoupling protein gene expression regulation by exercise and hormones in mice, rats and human models. • Glucose transport, fatty acid oxidation regulation in muscle from obese and diabetic animal models, obese and diabetic patients, exercise and after weight loss. Teaching Experience Exercise Physiology (EXSS 3805, East Carolina University), Spring 2004 PUBLICATION 1. W. Jiang, D. Zheng, Y. Li, N. Ding, L. Sheng, S. Ji: Maximal Oxygen Uptake, Anaerobic Threshold and Cardiac Function in Athletes of Different Span of Training Years. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology (in Chinese). 5(3): 260-265, 1989 2. W. Jiang, D. Zheng: Cardiac Function at and Above Anaerobic Threshold in Athelets. Chinese Sports Medicine (in Chinese). 8(3): 135-138, 1989 3. W.Jiang, W.Bai, N.Ding, D.Zheng, L.Sheng, S.Ji: Individual Characteristics of Aerobic Capacity in Oarsmen. Sports, Medicine and Health. 1990 Elsevier Science Publishers BV. pp707-712 4. W. Jiang, D. Zheng, N. Ding, S. Ji: The Effect of Different Training Cycle on Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacity of 2000 Meters Oarswoman. Sports Science (in Chinese). 12 (5): 53-55, 1992 5. W. Jiang, F. Ying, Z. Chen, N. Ding, D. Zheng, S. Ji: Using the Test of "LHRH-A" to Observe the effect of Hypothalamus on Pituitary--Gondad and Pituitary—Adrenal After Intensive Exercise. Sports Science (in Chinese). 14(2): 66-71, 1994 6. J.A.Houmard, M.D.Weidner, P.L.Dolan, N.Leggett-Frazier, K.E.Gavigan, M.S.Hickey, G.L.Tyndall, D.Zheng, A.Alshami, G.L.Dohm: Skeletal Muscle GLUT4 Protein Concentration and Aging in Humans. Diabetes. 44(5):555-560, 1995 7. M.S.Hickey, M.D.Weidner, K.E.Gavigan, D.Zheng, G.L.Tyndall, J.A.Houmard: The Insulin Action-Fiber Type Relationship in Humans Is Muscle Group Specific. American Journal of Physiology. 269 (1 pt 1):E150-154, 1995 8. T.Hortobagyi, D.Zheng, M.Weidner, N.J.Lambert, S.Westbrook, J.A.Houmard: The Influence of Aging on Muscle Strength and Muscle Fiber Characteristics With Special Reference to Eccentric Strength. Journal of Gerontology: Biological Sciences. 50A(6): B399-B406, 1995 9. D.Zheng, J.P.Jones, S.J.Usala, G.L.Dohm: Differential Expression of ob mRNA in Rat Adipose Tissues in Response to Insulin. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 218: 434-437, 1996 10. D.Zheng, M.H.Wooten, Q.Zhou, and G.L.Dohm: The Effect of Exercise on ob Gene Expression. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 225:747-750, 1996 11. J.A.Houmard, D.S.O’Neill, D.Zheng, M.S.Hickey, and G.L.Dohm: Impact of Hyperinsulinemia on Myosin Heavy Chain Gene Regulation. Journal of Applied of Physiology. 86(6): 1828-1832, 1999 12. D.S. O’Neill, D. Zheng, W.K. Anderson, G.L. Dohm, and J.A. Houmard: Effect of endurance exercise on myosin heavy chain gene regulation in human skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology. 276 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 45): R414R419, 1999 13. R.N. Cortright, D. Zheng, J.P. Jones, J.D. Fluckey, S.E. Dicarlo, D. Grujic, B.B.Lowell, and G.L. Dohm: Regulation of Skeletal Muscle UCP-2 and UCP-3 Gene By Expression By Exercise and Denervation. American Journal of Physiology. 276. (Endocrinol. Metab. 39): E217-E221, 1999 14. T. Hortobagyi, L.Dempsey, D.Fraser, D.Zheng, G.Hamilton, J.Lambert, and L.Dohm: Changes in Muscle Strength, Muscle Fibre Size and Myofibrillar Gene Expression after Immobilization and Retraining in Humans. Journal of Physiology (Lond). 524 (Pt1):293-304, 2000 15. P.S.MacLean, D.Zheng, and G.L.Dohm: Muscle Glucose Transporter (GLUT4) Gene Expression During Exercise. Exercise and Sports Sciences Review. 28 (4), 2000 16. D. Zheng, P.S.MacLean, S.C.Pohnert, J.B.Kight, A.L.Olson, W.W.Winder, G.L.Dohm: Regulation of Muscle GLUT-4 transcription by AMP-activated protein kinase. Journal of Applied of Phsiology.. 91: 1073-1080, 2001 17. P.S. MacLean, D. Zheng, J.P. Jones, A.L. Olson, G.L. Dohm: Exercise-Induced Transcription of The Muscle Glucose Transporter (Glut4) Gene. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 292(2):409-14, 2002 18. M.W. Hulver, D. Zheng, C.J. Tanner, J.A. Houmard, W.E. Kraus,C.A. Slentz, M.K. Sinha,W.J. Pories, K.G. MacDonald, G.L. Dohm: Adiponectin is not altered with exercise training despite enhanced insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 283(4):E861-5, 2002 19. R.C. Noland, R.C. Hickner, M. Jimenez-Linan, A. Vidal-Puig, D. Zheng, G.L. Dohm, R.N. Cortright: Acute endurance exercise increases skeletal muscle uncoupling protein-3 gene expression in untrained but not trained humans. Metabolism. 52(2):152-8, 2003 20. J.P. Thyfault, M.G. Cree, D. Zheng, J.J. Zwetsloot, E.B. Tapscott, T.R. Koves, O. Ilkayeva, R.R. Wolfe, D.M. Muoio, and G.L. Dohm: Contraction of insulin resistant muscle alters metabolic flux and normalizes insulin action. Am J Physiol Cell 292: C729C739, 2007 21. J.J. Zwetsloot, E. B. Tapscott, D. Zheng, S.I. Itani, J.Kim, E.G. Fontenot, M. Leitges, B. B. Roman, R. McKinney, P.M. Buttrick, and G. L. Dohm: PKCbeta Regulates IRS1 Signaling in Transgenic Mice. (Manuscript submitted to Diabetes. 2007) 22. D. Zheng, J.P. Thyfault, J.E. DeVente, G.L. Dohm,: IRS1 Serine Phosphorylation Is Increased in Skeletal Muscle From Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Patients. (Manuscript in preparation). 23. D. Zheng, J.R. Berggren, J.E. DeVente, P. Shaver, G.L. Dohm: Inhibition of Protein Kinase C Reverses Insulin Resistance in Human Cultured Myotubes Caused by Free Fatty Acids but Not by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. (Manuscript in preparation). RECENT PRESENTATIONS AND PUBLISHED ABSTRACTS D. Zheng, J.P. Thyfault, J.M. Bennet, C.M. Isler, G.L. Dohm, J.E. DeVente: Serine phosphorylation is increased in skeletal muscle from gestational diabetes mellitus patients. FASEB Journal, 18, 451.14, 2004. J.P. Thyfault, E.B. Tapscott, R.R. Fish, D. Zheng, and G.L. Dohm. Acute muscle contraction restores insulin effect on glucose uptake in insulin resistant muscle. Integrative Biology of Exercise, 28.2, 2004. J.J. Zwetsloot, D. Zheng, W.J. Pories, K.G. MacDonald, and G.L. Dohm: Link between PKC and IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in obese human skeletal muscle. American Diabetes Association's 65th Annual Scientific Sessions. 2005. D. Zheng, J.P. Thyfault, J.E. DeVente, G.L. Dohm: TNF Alpha Increased IRS1 Serine 312 Phosphorylation is Associated with Decreased Insulin Sensitivity in Cultured Human Myotubes. (poster ) 2006 Keystone Symposia-- Diabetes Mellitus and the Control of Cellular Energy Metabolism. J.P. Thyfault, M.G. Cree, D. Zheng, J.J. Zwetsloot, E.B. Tapscott, T.R. Koves, R.R. Wolfe, D.M. Mouio, G.L. Dohm: Contraction of Insulin Resistant Muscle Alters Metabolic Flux and Normalizes Insulin Action. (poster ) 2006 Keystone Symposia-Diabetes Mellitus and the Control of Cellular Energy Metabolism. D. Zheng, J.R. Berggren, J.E. DeVente, P. Shaver, G.L. Dohm: Inhibition of Protein Kinase C Reverses Insulin Resistance Caused by Free Fatty Acids in Human Cultured Myotubes. (poster) American Diabetes Association's 66th Annual Scientific Sessions. 2006. E.B. Jensen, D. Zheng, R.A. Russell, A.L. Olson, G.L. Dohm: The Decline in Skeletal Muscle GLUT4 Expression in Response to Denervation is Regulated by MEF2 and GEF. (poster) American Diabetes Association's 66th Annual Scientific Sessions. 2006.