Chapter Objectives
advertisement

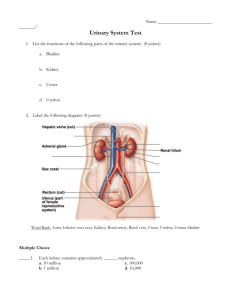
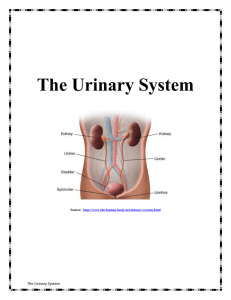
Chapter 15 Urinary System Chapter Objectives Upon completion of the chapter the participant will be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name and label on a diagram the organs of the urinary system. Describe the functions of the urinary system. Describe the process of filtering, re-absorption and secretion as it pertains to the urinary system. Analyze, define and spell the terms related to the urinary system. Successfully complete the exercises provided at the end of the chapter. The urinary system consists of a number of structures, each of which has a specific function or functions. Renal Cortex Renal Medulla Right Kidney Left Kidney Vena Cava Aorta Right & Left Ureter Urinary Bladder Prostate gland (males) Urethra Urethral meatus Revised 2005-09-13 -167- The components are: Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Kidneys (ren/o, nephr/o) Bean shaped, fist sized organs that lie on either side of the lumbar spine. Their position is retroperitoneal which means they lie behind the peritoneal membrane. Each kidney is covered with tissue that is referred to as the renal capsule. Under the capsule layer is the renal cortex (cortic/o) and below that is the renal medulla (medull/o) Blood flows into each kidney through the renal artery and out of the kidney through renal vein. Cortex Pyramids of Medulla Renal Pelvis Capsule Ureter While the blood is going through the kidney fluid and elements can be reabsorbed and the remaining product forms urine to be eliminated from the body. The functioning unit of the kidney is the nephron and that is the area where all Revised 2005-09-13 -168- the filtering occurs. An important part of the nephron is the glomerulus (glomerul/o). It is here that you find all the small capillaries that allows substances to move back and forth through the thin membrane. Urine that is to be secreted by the kidneys is stored in the renal pelvis (pyel/o). Ureters (ureter/o) Narrow tubes that connect the kidney with the bladder. Urine is moved along each tube by peristalsis. This is the same muscle activity that moves food through the digestive system. Urinary Bladder (cyst/o, vesic/o) A hollow muscular organ that acts as a reservoir for urine until it is to be eliminated from the body. When the bladder has a sufficient amount of urine present in it, the muscle fibers in the walls will contract giving you the urge to go to the bathroom. This process of passing urine is referred to as micturition. The end of the bladder has a sphincter that holds the urine in the bladder until there is an adequate amount present for elimination. Urethra (urethr/o) A tube which extends from the lower end of the bladder to the outside of the body. The external end of the urethra is referred to as the urethral meatus (meat/o) The male urethra is approximately 8 inches long while the female is 1.5 inches. In males the neck of the urethra is surrounded by one of the reproductive glands, the prostate gland. This was discussed in the previous chapter. Urine Production in the Kidney In each kidney are about one million nephrons. These structures are responsible for producing urine. In general terms they do this by filtering out excess electrolytes and waste products from the blood. This is done by the network of capillaries contained in the glomerulus. The capillary walls allow water, electrolytes and waste products to leave the blood and enter Bowman’s Capsule which surrounds the glomerulus. The filtrate then moves through the long system of twisted tubes called the renal tubules. As the filtrate moves through the tubes there is a constant exchange of substances occurring. When the end of the tubules is reached the remaining solution is urine (ur/o). Revised 2005-09-13 -169- Word Parts for the Urinary System Roots calic/o, calyc/o catheter/o corpor/o cortic/o cyst/o, vesic/o glomerul/o lith/o meat/o medull/o nephr/o, ren/o olig/o py/o pyel/o spad/o ureter/o urethr/o urin/o, ur/o calyx, calyx something inserted body cortex, outer layer bladder glomerulus stone opening, passageway middle or inner portion kidney scanty, few pus renal pelvis draw off ureter urethra urine, urinary organs Suffixes -cele -chrome -ectasis -emia -lithasis -osis, -pathy -pexy -ptosis -lysis -tripsy -uria hernia color enlargement, stretching blood presence of stones abnormal condition, disease surgical fixation drooping, dropping down breakdown, destruction crush urine, urination Prefixes anepiinparapolyretro- Revised 2005-09-13 without upper, above no, not beside many backward -170- Term Analysis and Definition Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition calic/o, calyc/o caliceal calic = calyx -eal = pertaining to Pertaining to the calices of the kidney catheter/o catheterization catheter = something inserted -ion = process Process of inserting a tube into a body cavity, like the bladder, to remove fluid corpor/o extracorporeal corpor = body extra = outside -eal = pertaining to Pertaining to outside the body Cortic/o cortical cortic = cortex, outer layer -al = pertaining to Pertaining to the outer layer of the kidney. cyst/o vesic/o cystitis cyst = bladder -itis = inflammation Inflammation of the bladder cystoscope -scope = instrument used to visually examine Instrument used to visually examine the bladder vesicoureteral vesic = bladder ureter = ureter -al = pertaining to Pertaining to the bladder and ureters. Glomerulonephritis glomerul = glomerulus nephr = kidney -itis = inflammation Inflammation of the glomerulus of the kidney glomerulosclerosis -sclerosis = hardening Hardening of the glomerulus lith/o lithotripsy lith = stone -tripsy = crushing Crushing of kidney stones using sound waves meat/o meatotomy meat = meatus -tomy = process of cutting Process of cutting into the urinary meatus medull/o medullary medull = medulla -ary = pertaining to Pertaining to the medulla nephr/o, ren/o nephrolithiasis nephr = kidney -iasis = condition lith = stones Kidney stones glomerul/o Revised 2005-09-13 -171- Word Part pyel/o ureter/o urethr/o Revised 2005-09-13 Term Term Analysis Definition nephrolithotomy -tomy = Surgical incision Process of removing stones through a surgical incision into the kidney nephropathy -pathy = disease Disease of the kidney nephropexy -pexy = surgical fixation Surgical fixation of the kidney nephroptosis -ptosis = drooping Drooping of the kidney hydronephrosis hydro = water -osis = condition Conition where there is accumulation of fluid in the kidney nephroblastoma -blast = immature -oma = tumor Tumor of the kidney made up of underdeveloped material renal ren = kidney -al = pertaining to Pertaining to the kidneys pyelogram pyel = renal pelvis -gram = record Record of the ureter and kidney, particularly the renal pelvis pyelonephritis nephr = kidney -itis = inflammation Inflammation of the kidney and the renal pelvis ureteral ureter = ureter -al = pertaining to Pertaining to the ureter ureterectasis -ectasis = stretching Stretching of the ureter ureterostenosis -stenosis = narrowing Narrowing of the ureter ureterostomy -stomy = permanent new opening Cystourethrography cysto = bladder urethr = urethra -graphy = process of recording Creation of a permanent new opening into the ureter Process of recording an image of the bladder and urethra using X-Ray transurethral trans = across -al = pertaining to -172- Performed across or through the urethra Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition utethroplasty -plasty = surgical repair Surgical repair of the urethra urin/o urinary urin = urine -ary = pertaining to Pertaining to urine ur/o uremia ur = urinary tract, urine, urination -emia = blood Accumulation of urine in the blood because of kidney dysfunction urogram -gram = record Record of the urinary tract urologist -logist = one who specializes One who specializes in the urinary system dialysis dia = through -lysis = separate, breakdown Mechanical replacement of kidney function with a machine. Blood passes through the machine and the waste products are separated out and the blood returns to the patient. urinalysis urin = urine -lysis = apart Laboratory test analysis of urine anuria an = no, lack of -uria = urine, urination No urine formation bacteriuria bacteri = bacteria Bacteria in the urine dysuria dys = painful, difficult Painful urination hematuria hemat = blood Blood in the urine nocturia noct = night Frequent urination at night oliguria oligo = deficient, scanty py = pus Decreased urination -lysis -uria pyuria Pus in the urine in- incontinence in = no, not -continence = to stop No control of excretion functions such as urination poly- polyuria poly = many -uria = urine Excretion of large amounts of urine Revised 2005-09-13 -173- Word Part Term polycystic kidneys Term Analysis cyst = sac -ic = pertaining to Abbreviations: ADH: antidiuretic hormone BUN: blood urea nitrogen CRF: chronic renal failure C and S: culture and sensitivity ECSL: extracorporeal shockwave lithotriptor ESWL: extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy GU: genitourinary H2O: water I and O: intake and output IVP: intravenous pyelogram KUB: kidney, ureter, bladder UTI: urinary tract infection Revised 2005-09-13 -174- Definition Pertaining to kidneys with many cysts.