Organism - Bakersfield College

Supergroup
/Clade
Organisms
Excavata
- excavated groove in one side of cell
1. Diplomonads
- two equal sized nuclei
- ex. Giardia – cause of amoebic dysentery
2. Parabasala
- undulating membrane (smooth wavelike motion)
- ex. Trichomonas vaginalis - STD
3. Euglenozoa
- spiral or crystalline rod inside flagella
i. Phylum: Kinetoplastida
ex. Trypansoma – African Sleeping Sickness
ii. Phylum: Euglenophyta
ex. Euglena
Pictures
Trichomonas vaginalis Trypansoma sp.
Euglena sp. Giardia – amoebic dysentery
Supergroup
/Clade
Chromalveolata
- group may have originated from secondary endosymbiosis
- contains some of the most photosynthetic organisms on Earth
Organisms 1. Alveolata
– air sacs beneath plasma membrane
i. Phylum: Dinoflagellata
- armor of cellulose plates
ex. Ceratium
sp. –
cause of red tides and Peridinium
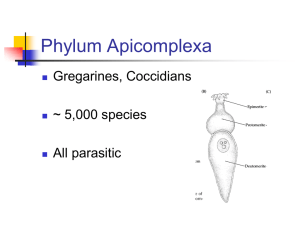
ii. Phylum: Apicomplexa
- apical complex of organelles
ex. Plasmodium sp. - Malaria
iii. Phylum: Ciliophora
- cilia for locomotion & feeding
ex. Paramecium & Stentor
2. Stramenopila
- hairy and smooth flagella
i. Phylum: Bacillariophyta
- glassy, two-part wall
- ex. diatoms ( dia = through and tom = to cut in half)
ii. Phylum: Phaeophyta
- all multicellular; some with alternation of generations
- brown algae and kelp beds
iii. Phylum: Chrysophyta
- golden algae
iv. Phylum: Oomycota
- hyphae that absorb nutrients
- ex. water molds, white rusts and downy mildews (usually found on plant tissues)
Pictures
Peridinium
The dinoflagellates are the cause of red tide: a very poisonous bloom that is hazardous to the health of many vertebrates (animals with backbones). Some are responsible for the unpleasant odors or taste in drinking water.
They have two flagella – one in each groove.
Pictures con’t.
Plasmodium
is the causative agent of malaria. The
Anopheles
mosquito is the vector of this protist. Please look up and study the life cycle of
Plasmodium
.
Paramecium Salmon infected with Saprolegnia (an
oomycete)
Porous cell wall of a diatom. Mixed diatoms
The picture above shows how diatoms (cell walls) are used to make filters. The picture to the left shows how they mine for diatomaceous earth.
Kelp beds are one of the most productive ecosystems on
Earth. They can be 100 feet tall and extend six miles outward.
Algin is a mucilaginous intercellular material found in the cell walls of members in the phylum Phaeophyta. It is used as a stabilizer, emulsifier for foods and paints; it is also used as a coating for paper. Other examples are shown in the picture to the right.
The above pictures are Laminaria , a common rockweed
(phylum Phaeophyta).
Supergroup/ clade
Organisms
Archaeplastida
- red and green algae (plus land plants)
- include key photosynthetic organisms that form the base of food webs in some aquatic communities i. Phylum: Rhodophyta
- phycoerthyrin pigment ii. Phylum: Chlorophyta
- plant-like chloroplasts (homologous) iii. Phylum: Charophyceae
- direct common ancestor to the land plants
Pictures
Miscellaneous Members of Rhodophyta are usually small, delicate marine or freshwater organisms. They often grow attached to rocks or algae at very deep depths. They manufacture the pigments phycoerythrin (red) and phycocyanin (blue), which allows them to photosynthesize in deep waters. Carrageenan is a component (a galactan) of their cell walls that is used in industry as a jelling agent (toothpaste, agar, ice cream, shaving cream etc.). Nori is often used to wrap sushi. Some species have calcium carbonate in their cell walls
coralline algae that are used to build coral reefs.
Pictures con’t.
Spirogyra- note spiral chloroplasts dotted with dark pyrenoid starch storage granules
.
Ulva
Conjugation in Spirogyra.
Miscellaneous
Volvox
Members of this phylum are mostly fresh water; some are found in salt water and snow. They are believed to be the ancestor (the Charophytes) to modern day land plants. They possess chlorophylls a & b and carotenoids. The green algae store food as starch and have cell walls made of cellulose; all of which are true for plants.
Supergroup/ clade
Rhizaria
- amoebas with threadlike pseudopodia (extensions that can bulge from any portion of a cell; used for movement and capture of prey)
Organisms i. Phylum: Foraminifera
Pictures
- porus shells with radiating pseudopodia ii. Phylum: Radiolaria
- pseudopodia radiating from central body of organism
Radiolarians
Foraminifera
Supergroup/ clade
Unikonta
-
amoebas with lobe – or tube – shaped pseudopodia (plus animals and fungi)
Organisms i. Phlym: Gymnamoeba
- soil-dwelling, freshwater, or marine
- ex. Amoeba sp. ii. Phylum: Entamoeba
- parasites
- ex. Entamoeba sp
Pictures
Amoeba proteus
Entamoeba sp.