Homeostasis review - Nanchang No. 2, Science 10 & Biology 11
advertisement

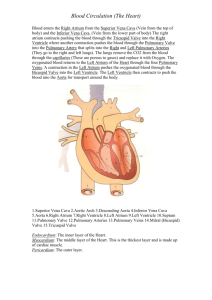
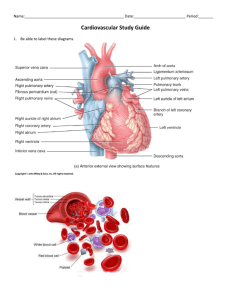
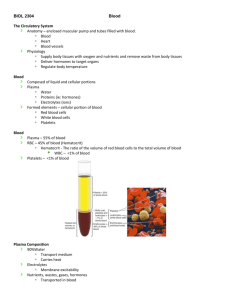
Semester II: Biology 11 exam Test Format (may change): PART A: Multiple Choice – Kingdom Animalia PART B: Multiple Choice – Maintaining dynamic equilibrium PART C: Multiple Choice – Population dynamics PART D: Short Answer PART E: Diagram labelling 10marks 23marks 32marks 15marks 5 marks 85marks Animalia Key terms and questions Heterotrophic Biology Zoology Notochord Omnivore Quadrupedal Aquatic Feeding Excretion Reproduction Eukaryotic Physiology Invertebrates Herbivore Detritivore Bipedal Sessile Respiration Response Multicellular Anatomy Vertebrates Carnivore Parasite Terrestrial Motile Circulation Movement What are some representative organisms of the different phyla? Homeostasis Key Terms & questions Homeostasis Receptors Stimulus Tropism Endotherm Control Centres (Regulators) Negative feedback Phototropism Ectotherm Effectors Positive feedback Gravitropism Circulatory System Key Terms Open Circulatory System Blood vessels Red blood cells (erythrocytes) Platelets Veins Right ventricle Valve Double loop Aorta Left Pulmonary veins Left Atrium Tricuspid Valve Pulmonary Valve Arteriosclerosis Stroke Closed Circulatory System Blood Heart Plasma White blood cells (leukocytes) Blood Vessels Artery Capillaries Right atrium Left atrium Left ventricle Pulmonary Systemic Inferior Vena Cava Superior Vena Cava Right Pulmonary Artery Left Pulmonary artery Right Pulmonary Veins Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Bicuspid (Mitral) valve Aortic Valve Angina Atherosclerosis Hypertension Heart attack Arrhythmia Respiratory System Key Terms Respiration Spiracles Nasal Cavity Larynx Inhalation Breathing Lungs Pharynx Bronchial tree Exhalation Alveoli Gills Countercurrent flow Trachea Bronchi, bronchioles Diaphragm Bronchitis 1.) What is Homeostasis and why is maintaining homeostasis important? Explain using an example. 2.) Using homeostasis examples compare and contrast positive feedback and negative feedbacks. 3.) You are running a Marathon (a race). You are 75% finished the race and begin to feel tired. What are two body systems that may be affected? What will the body systems do to maintain homeostasis and why? 4.) Making reference to both the Pulmonary Circuit and the Systemic Circuit explain why the heart is called a double loop. 5.) be able to label a diagram of the heart and respiratory system. Population Dynamics key terms (Ch. 14) & questions Population size Ecological density Carrying capacity Biotic potential Geometric growth Lag phase Delayed Density Dependence graph Population density Quadrat sampling Population dynamics Open population Exponential Growth Log phase Crude density Mark-Recapture Fecundity Closed population Logistic Growth Stationary phase Density-Dependent Factors • Intraspecific competition, Predation, Disease, Allee Effect, Minimum viable population size Density-Independent Factors Interspecific competition Realized Niche Commensalism Interference competition Resource partitioning Exotic Species Limiting Factor Community Ecological Niche Fundamental Niche Symbiosis Mutualism Parasitism Interspecific Competition Exploitative competition Defence Mechanisms (Passive vs. Active) 1.) You should be able to calculate population change. 2.) You should be able to calculate crude and ecological density. 3.) You should be able to estimate populations using quadrant sampling and mark and recapture techniques 4.) You should be able to read, interpret and produce population graphs. Population Dynamics key terms (Ch. 15) & questions Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) Ecological Footprint Bioremediation Eco-cities High-Throughput Economy Low-Throughput Economy 1. What is the world’s human carrying capacity? What are the limiting factors for humans on earth? 2.) What are the effects of human population growth? Which countries are growing? 3.) Why has human population grown? 4.) What are the pros and cons of GMO’s? 5.) What are the five R’s of waste reduction? 6.) How can we deal with global pollution? 7.) What is the difference between high throughput and low throughput economies? What are eco-cities? 8.) What is an ecological footprint? 9.) Be able to answer all questions from Activities 15.4.1 and 15.4.2 Test Preparation: 1.) Study your notes 2.) Review all handouts 3.) Review past quizzes, tests and assignments 4.) Review textbook and textbook questions/ assignments