File
advertisement

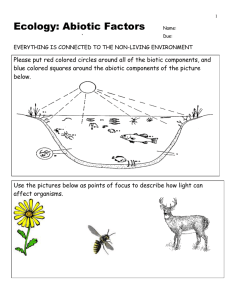
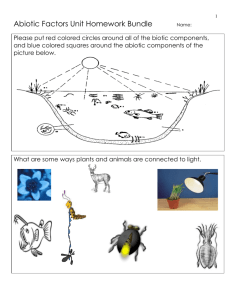
1 Ecology: Abiotic Factors Name: ANSWER KEY Due: EVERYTHING IS CONNECTED TO THE NON-LIVING ENVIRONMENT Please put red colored circles around all of the biotic components, and blue colored squares around the abiotic components of the picture below. Living = Red Circles : All fish, Insects, Larvae, Zooplankton, Phytoplankton, Grasses, Weeds, and Microscopic Life. Non-Living = Blue Squares: The Sun, the air, the water without microbes, the soil without microbes. 2 Use the pictures below as points of focus to describe how light can affect organisms. Intensity: How bright it is (lumens). How long it lasts? Length of day, seasonal changes. Quality / type of light. Examples include if the day is sunny vs. cloudy, summer vs. winter, and morning and evening vs. the middle of the day. Phototropism – Moving toward the light Many insect can display photokinesis – Moving toward the light. Many insects also see light in the UV Spectrum. Why is this turtle sitting on a log? Explain using some terms discussed in class. The turtle has general cold bloodedness and must heat up before it can become active. By sunning itself it’s warming its core temperature. It can also escape predators by falling off the log into the safety of the water. Many mammals are crepuscular, in that they are most active during the dawn and dusk / low light conditions. Animals are also effect by the time / duration of light, seasonal changes for feeding, mating, migrations. Mammals see in the visible light spectrum Snakes can see prey in the Infrared Spectrum. 3 Use the picture below to describe some of the advantages and disadvantages to having warm and cold bloodedness? Cold-blooded Advantages -You do not get as many infections as warm blooded creatures. -A single meal can go a long way because you don’t have to constantly stay warm. Cold-blooded Disadvantages -You can’t be active in the cold weather. -Limited environments on earth. Warm-blooded Advantages -Active during the winter and cold periods. Warm-blooded Disadvantages - Warm-blooded bodies provide an nice warm environment for viruses, bacteria and parasites to live in. -Warm-blooded require a lot of energy to maintain high metabolism. Please describe the difference between a physical and behavioral adaptation based on how you thermo-regulate on a cold winters day. Physiological: The functions of the body. Physiological adaptations to temperature. These you generally cannot control, your body does them automatically. Behavioral: Actions or reactions of an organism to the environment. You can control these reactions. 4 Describe how you have a range of tolerance when it comes to temperature. Please use the words below in your discussion of this topic. Hypothermia Hyperthermia Hypothermia - A decrease in the core body temperature to a level at which normal muscular and brain functions are impaired. Your body cannot become to cold Hyperthermia: Having a body temperature that is to high, cause heart failure, among other problems and death. Your body cannot become to warm. Warning! Two Part Question. Please add desert plants and animals to the scene below. Provide text to around your sketches that describe how these organisms are adapted to survive this deserts high temperature, and low moisture. Adaptations of plants to survive with minimal water include. •Using stomata: Structures that can close to keep water in when dry. •Thick waxy cuticles to keep water in (succulents, cacti) •Small leaves, or absence of leaves. •Water storage tissues. •Deep roots How animals have adapted to low water availability? •Body covering can limit water loss. – Skin vs. scales, insect chitin vs. feathers. • Body tissue that retain water. • Some small animals can absorb water from the air in morning (dew), then go underground. – Rare desert frogs and some insects. • Eat prey items that are full of water. • Have really dry feces. • Come out only at night. Nocturnal. • Seek shade, and live underground. 5 Please tell me about this organisms and its relationship to the non-living environment. This is the pillbug (Aramadillidium vulgare) It is connected to the non-living environment because it breathes oxygen through gills. It cannot survive in dry areas. It also does not prefer sunlight or very warm temperatures that cause evaporation. What are the positives and negatives of wind? Please write a short paragraph explaining your answer. • Wind brings weather, especially precipitation. Water evaporates over ocean, wind carries water over land where it falls. • Wind can also cause erosion of soil, and will dry out areas much faster. • Eroded soil can be redistributed to an area that needs it. • Wind can be very damaging to plants and animal populations. • Wind also increases the intensity of wild fires. • Animals and plants use wind in many ways. 6 Please describe how plants and animals utilize wind using the pictures below. Animals use wind… Plants use wind To smell. To pollinate. Water, prey items, Pollination: The predators, etc. transferring of pollen To fly with minimal (plants sex cells) from effort. one plant to another. To move. To disperse seeds. To dry out and also to cool down. Please describe the type of seed dispersal below. Wind Water Animal 7 Tension Animal Fire (Opens Cone) Please describe Island Biogeography theory based on the map below. Please describe using text which Island will most likely exhibit the following. 1) Most migrations and fewest extinctions. 2) Fewest migrations and most extinctions, 3) Describing using multiple arrows were island hopping may occur. 1) The Island right next to the mainland will have the most migrations and fewest extinctions. 2) The farthest away and smallest island will have the most extinctions and fewest and migrations. 3) Draw arrows from the first islands to the next island and so on down the chain. 8 Are forest fires good? Please answer this question in the space below. Fire: Some seeds require a fire event or very hot temperature after they have been dispersed to germinate. Fire ecology: A branch of ecology that focuses on the origins of wildland fire and its relationship to the environment that surrounds it, both living and non-living. Fire Dependence: This concept applies to species of plants that rely on the effects of fire to make the environment more hospitable for their regeneration and growth. Forest fires are a very destructive force that can destroy trees, property, and can be deadly to animals and people. They however, have an important role in the forest ecosystem. Forest fires can aid in seed dispersal, renew forests, and play an important role in the ecosystem. In the space below, please label the hydrologic (water) cycle. A strong answer will contain most of the word bank below. •Condensation •Evaporation •Precipitation •Percolation •Transpiration •Sublimation •Infiltration Storage •Ground Water Storage •Freshwater discharge •Surface run-off. •Ocean 9 Evaporation – Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. Precipitation – Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. Sublimation – Solid state turns directly to a gas state skipping liquid phase. Transpiration – Water released by plants into air. Non-living to the living, and back again. Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Percolation: The slow movement of water through the soil. Groundwater discharge: Water that has been underground seeps back into the oceans, or into rivers or lakes. 10 Please describe the oxygen carbon dioxide balance based on the picture below. Be very specific, using the equations for both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Oxygen is released from the plant during photosynthesis. The oxygen is used by living organisms in cellular respiration. Carbon Dioxide is released by the Pillbug in the process. This carbon dioxide is then taken in by the plant for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis – Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars – carbon based). 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cellular Respiration: Processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + released energy. Please write out the equation for photosynthesis in the boxes below. 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O Which of the following is the correct equation for photosynthesis? 11 • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • D) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O • E) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Please write out the equation for cellular respiration in the boxes below. C6H12O6 + 6O2 = Released energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O. Which of the following is the correct equation for cellular respiration? • A) B) • C) • D) C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C12H6O6 + + + + 6H2O = Released energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O. 6O2 = Released energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O. 6O2 = Released energy + 6O2 + 6H2O. 6O2 = Released energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O. • E) C6H12O6 + 6CO2 = Released energy + 6O2 + 6H2O. Describe how humans are interfering with the natural balance of the carbon and nitrogen cycle? When human burn fossil fuels they release carbon that has been trapped away under the earth for hundreds of millions of years. This new carbon increases the Earths natural greenhouse effect and warms the planet. Humans burn coal and gasoline which releases nitrogen into the atmosphere and causes acid rain. 12 Describe how nitrogen is fixed and then broken down as part of the nitrogen cycle below. Fixed Lightning can fix nitrogen. Bacteria in the soil can fix nitrogen. Broken Down Bacteria can break nitrogen down. Nitrogen Cycle: The circulation of nitrogen; nitrates from the soil, absorbed by plants, eaten by animals that die and decay returning the nitrogen back to the soil. 13 Please describe acid rain in the space below. Make reference to the pH scale in and around the boxes. Burning of coal and from cars release nitrogen and sulfur compounds into the air. The compounds mix with air and the clouds. Precipitation (rain, fog, snow) that has a low pH is acid rain. 1 2 Acidic 3 4 5 6 7 8 Neutral 9 10 11 12 13 14 Basic Please draw arrows showing how phosphorus travels through the living and non-living world in the phosphorus cycle. 14 Please label the following pictures as olgiotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic, or eutrophication Emergent vegetation and some free floating aquatic plants Green + Algae + Eutrophic Crystal Clear High Mountain Lake Olgiotrophic Mesotrophic Green + Algae + Dead Organisms Eutrophication 15 Please describe Eutrophication below. Use the pictures as a resource in your response. Eutrophication Aquatic plants use Phosphorus and Nitrogen and grow out of control. Aquatic plants overpopulate and die. Bacteria break down dead plants and use oxygen in water (respiration). No oxygen left for fish / other aquatic life and they die. 16 Abiotic Factors Name:________________________ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16 18 20 23 17 19 21 22 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 Possible Answers: abiotic, acid, adaptation, biogeochemical, biogeography, biological, biotic, carbon, coldbloodedness, condensation, dispersal, eutrophic, eutrophication, evaporation, evapotranspiration, hibernation, hyperthermia, hypothermia, light, lightenergy, mesotrophic, moisture, nitrogen, oligiotrophic, percolation, phosphorus, photo, photosynthesis, physiological, pollination, precipitation, respiration, shivering, temperature, thermoregulation, tolerance, warmbloodedness, water Copyright Ryan Murphy 2010 3 - This is when water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid. 5 - Having a body temperature that is to high that may cause heart failure, among other problems and death 7 - Wind, water, animal, and tension are all types of seed _____________ 10 - Type of rain that has a lower pH from air pollutants. 11 - Processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. 1 - Being inactive during winter, and lower metabolism 2 - The circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms (biotic) and back again (abiotic). (___________ cycle) 4 - A common nutrient in nutrient pollution. 6 - A process whereby an organism becomes better suited to its habitat. 8 - This is when water is released by plants into air 9 - Process where muscles contract and relax 17 (Cellular ______________) 15 - This is when a substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). P H Y 16 - Prefix for the word light A O 18 - The slow movement of water through the D I S P soil A P H 20 - Island __________________ is the Pstudy of rates of colonization and extinction ofT O A R species on islands. T U 26 - The transferring of pollen (plants sex I S O cells) from one plant to another N 27 - Name for a lake or river with moderate productivity W B P O a L range L I Nof A T I O N 29 - AllA organisms have R I H ____________________ to the abiotic factors M E S O T R O P H I C O 30 - Of,B pertaining to, or produced by life or L T L L O O B I O T I C living organisms. O G S G 31 - Warm and cold abiotic factor O I Y I 32 - The of thermoregulation that D type C N O you can A T E M P E R A T U R E control E D L H 33 - The wettest of the seven abioticR factors N E M O I S T U R 34 - This nitrogen from the air, E cycle circulates S P to the soil, to organisms, theO R S L I G Hand T thenTback H E to R M S S I air. (_________ cycle) C O N D E N 35 - The brightest of the seven abiotic factors 36 - The ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries 37 - This is when water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation Name:________________________ Abiotic Factors when it is cold, this generates heat H 12 - Name for a lake or river with high C P R E C I P I T A T I O N productivityA B P13 E -RThe T H __________ E R M I A cycle is the E continuous B R movement of water on, above, and below the E R S A L O N of the Vsurface H N Earth A A14 C -I When D R E Scan’t P I R A T I O N organisms regulate their Pinternal V W C U I temperature O E V A P O R A T I O N O P H O T O 17 A decrease in the core bodyNtemperature to T R T L R Y atE which normal muscular and brain Ra level I D O P Afunctions N R areB impaired P E R C O L A T I O N N G L H I T 19 - 6CO2 +O6H2O +_________________ = S B I O G E O G R A P H Y +O6O2 C PC6H12O6 B U H B E I 21 - When I D T T I R oxygen is removed from a water R O E R E O M body by bacteria A G D O N T I T22 O -L Another E R A Nname C E for theP word E non-living I A I 23 - Maintaining O E C a warm HbodyR temperature O C S I G independent of environmental conditions. N H S C Y 24 - This is a life, Earth, change atoms, E A M T repeating event (_____________________ P H Y S I O L O G I C A L cycle)I E C O 25 - The A answer for this question N I T R is O biological G E N E26 G -UAL process A T I Othat N converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, S A T I O N using the energy from sunlight. 28 - Name for a lake or river with low productivity 18