Review - Ms. Anderson`s Room 280
advertisement
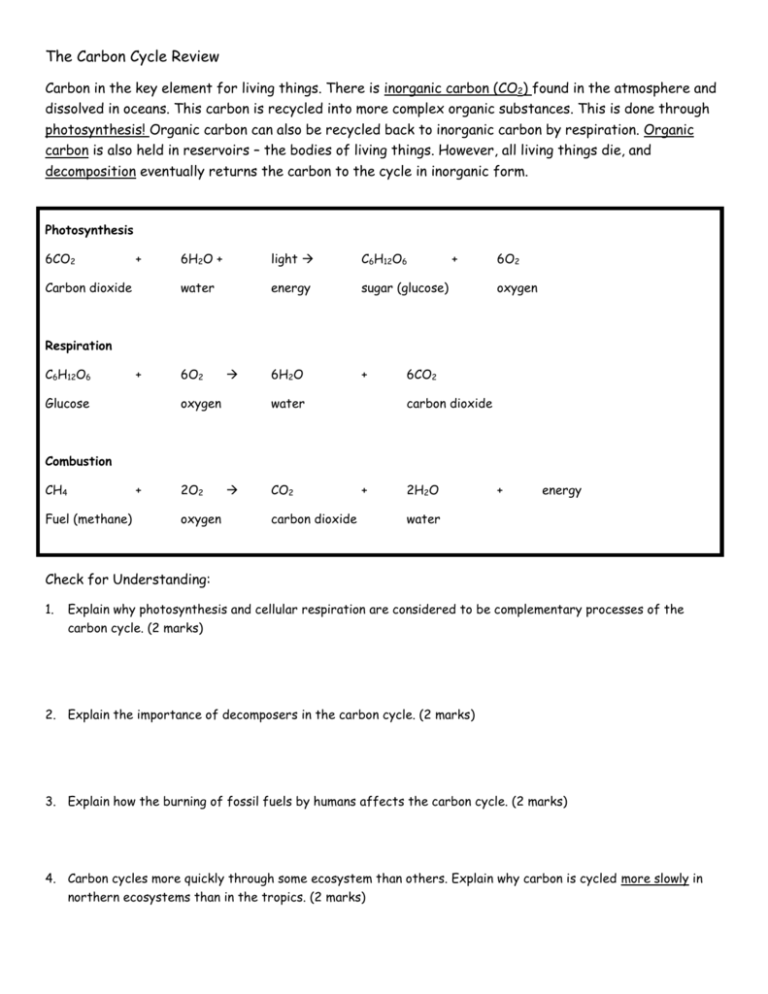
The Carbon Cycle Review Carbon in the key element for living things. There is inorganic carbon (CO2) found in the atmosphere and dissolved in oceans. This carbon is recycled into more complex organic substances. This is done through photosynthesis! Organic carbon can also be recycled back to inorganic carbon by respiration. Organic carbon is also held in reservoirs – the bodies of living things. However, all living things die, and decomposition eventually returns the carbon to the cycle in inorganic form. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + Carbon dioxide 6H2O + light C6H12O6 water energy sugar (glucose) 6H2O + + 6O2 oxygen Respiration C6H12O6 + Glucose 6O2 oxygen water 6CO2 carbon dioxide Combustion CH4 + Fuel (methane) 2O2 oxygen CO2 + carbon dioxide 2H2O + energy water Check for Understanding: 1. Explain why photosynthesis and cellular respiration are considered to be complementary processes of the carbon cycle. (2 marks) 2. Explain the importance of decomposers in the carbon cycle. (2 marks) 3. Explain how the burning of fossil fuels by humans affects the carbon cycle. (2 marks) 4. Carbon cycles more quickly through some ecosystem than others. Explain why carbon is cycled more slowly in northern ecosystems than in the tropics. (2 marks)