Supplementary Figures and Legends (doc 1618K)
advertisement

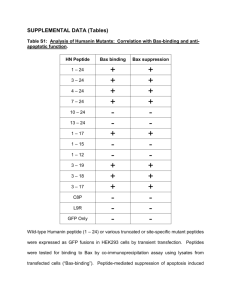
Legends to supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Bax potential trypsin cleavage sites. Amino acid sequence (a) and 3D structure (b) of human Bax. Its 9 -helices are underlined, potential trypsin cleavage sites are depicted in red, and probable accessible sites in oligomerized Bax are marked with an arrow (R34 or R37). 2D2 (amino acids 3-16) and polyclonal (amino acids 43-61) anti-Bax antibodies’ epitopes are respectively outlined in yellow and in green. The 3D structure of Bax was produced using the UCSF Chimera package from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco (supported by NIH P41 RR-01081).1 Supplementary Figure 2 Tr-Bax formation requires tBid and is inhibited by Bcl-xL. PC/CL 60/40 liposomes were incubated with recombinant Bax (100 nM) and various concentrations of tBid (0, 1, 5, 10 and 100 nM) (a) or with tBidmIII-2 (10 nM) (b). Binding of Bax and of tBid to the liposomes was assessed by immunoblotting (- trypsin) as was the degree of Tr-Bax formation (+ trypsin). (c) Similarly, PC/CL liposomes were incubated with recombinant Bax (100 nM) and tBid (10 nM) and various concentrations of Bcl-xL (0, 10, 25 and 50 nM), and Bax and tBid binding and Bax oligomerization were assayed. Blots show duplicates and are representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 3 Tr-Bax can be completely degraded by trypsin. tBid-induced Bax oligomerization assays were performed in vitro with PC/CL 60/40 liposomes. Samples were digested with (a) various trypsin concentrations (from 0.0017 to 17 mg/ml) or (b) various incubation times (from 30 to 240 min) and analyzed by immunoblotting. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 4 Only oligomeric Bax is resistant to trypsin digestion. In vitro Bax activation assays with 100 nM Bax and 10 nM tBid were performed with PC/CL 60/40 liposomes. After the ultracentrifugation, Bax was extracted from the liposomes with CHAPS and run on a size exclusion chromatography column (a). Individual Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 1 fractions were then digested with trypsin (b). Alternatively, after the ultracentrifugation, samples were digested with trypsin and then loaded on the column (c). All samples were analyzed by immunoblotting. Supplementary Figure 5 CHAPS-solubilized oligomerized Bax is also partially resistant to trypsin digestion. Bax (100 nM) was activated by tBid (10 nM) using PC/CL 60/40 liposomes, extracted from the liposomes with CHAPS (2%) and incubated with trypsin (0.17 mg/ml) for 1 or 2 hours. Tr-Bax formation was analyzed by immunoblotting and showed digestion of Bax to a slightly smaller trypsin-resistant Bax fragment (*), probably linked to a partial unfolding of the protein in the presence of detergents. Result is representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 6 Cholesterol inhibits Bax oligomerization. tBid-induced Bax activation was examined in vitro with PC/CL/CHO liposomes with a low CL content (20% w/w). The binding of tBid and Bax to the liposomes, as well as the resistance of Bax to trypsin digestion were examined by immunoblotting. Result is representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 7 Crude mitochondria isolated from untreated and U18666Atreated cells show a similar contamination by other intracellular organelles. (a) 48h after incubation with U18666A, mitochondria were isolated from HeLa cells and analyzed by immunoblotting for contaminations with endosomes (Rab5), TGN (GS28), lysosomes (Lamp1), ER (Calnexin) and peroxysomes (SKL and Catalase). Blots are representative of more than three independent experiments. (b) For each experiment, band intensities were quantified and normalized by the intensity of the SLP-2 band, and Control to U18666A ratios were calculated. Values are means of more than three independent experiments +/- SEM. Using a paired Student’s t-test, differences were not significant. Supplementary Figure 8 U18666A added to HeLa mitochondria does not delay tBidinduced MOM permeabilisation. Mitochondria were isolated from HeLa cells and incubated with various concentrations of U18666A for 10 minutes. tBid (20 nM) was Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 2 then added, a 10 minute incubation was carried out at room temperature, and the samples were spun. Smac and Cytochrome c release were assayed in the supernatants by immunoblotting. The blot is representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 9 U18666A-treatment does not increase the resistance of cells to mitochondria-independent apoptotic stimuli. 293T cells were incubated with U186666A for 36 hours and incubated with FasL in presence of cycloheximide. Cell death was analyzed after 28 hours by Annexin-V and PI staining. The percentage of unstained cells is displayed. Values represent means of more than six independent experiments +/- SEM. **: p < 0.009. References 1. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC et al. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 2004; 25: 1605-12 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 3 Supplementary Figure 1 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 4 Supplementary Figure 2 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 5 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Figure 4 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 6 Supplementary Figure 5 Supplementary Figure 6 Supplementary Figure 7 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 7 Supplementary Figure 8 100 % live cells 80 ** 60 40 20 0 C U Supplementary Figure 9 Lucken-Ardjomande et al. Supplementary information 8