Regents Physics
advertisement

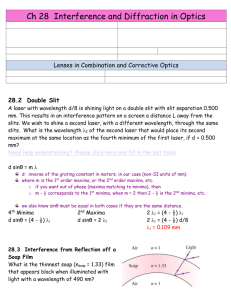
Name_______________________________________ Physics Paul D. Schreiber H.S. Practice Test 9 Light Waves/Color/Diffraction A) In the diagram below list the colors that could be added to produce white light. Sin θ = X= nλ L d 1 1 1 f = do + d i M = hi = - di ho do B) In the diagram below that shows a red wavelength incident on a double slit, label the central maximum as “0”. Mark maxima 1 and 2 on each side. Then show the location of the variables L, d, and x. C) There is a 4.00cm tall letter “T” that is 40.0cm in front of a convex lens (object distance) with a focal length of 20.0cm. a. Calculate the image distance. b. Calculate the image height. c. Calculate the magnification. D) Light passes through a diffraction grating with slit spacing of 1.7 x10-4m and hits a screen 9.00m away. The distance from the central maxima (bright spot) to the second maxima is 7.0cm. a. Calculate the wavelength. b. Calculate the frequency. c. What is the color? MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle clearly the letter of the best answer for the multiple choice questions below. 1. Reflection, refraction, and the formation of images by mirrors and lenses has been successfully described by the A. wave model of light. B. ray model of light. C. particle model of light. D. none of the given answers 2. The principle on which mirrors work is A. refraction. B. polarization. C. dispersion. D. reflection. 3. An image formed when the light rays do not actually pass through the image location, and would not appear on paper or film placed at that location is referred to as a A. real image. B. virtual image. 4. If the image distance is positive, the image formed is a A. real image. B. virtual image. 5. The principle on which fiber optics is based is A. refraction. B. polarization. C. dispersion. D. total internal reflection. 6. A object A. B. C. D. 7. Choose the best answer. The phenomenon depicted on Pink Floyd's Dark Side of the Moon album cover (light passing through a prism) is referred to as A. reflection B. refraction C. scattering D. diffraction E. dispersion F. polarization G. interference H. total internal reflection 8. When a light wave enters into a medium of different optical density, A. its speed and frequency change. B. its speed and wavelength change. C. its frequency and wavelength change. D. its speed, frequency, and wavelength change. 9. What principle is responsible for the fact that certain sunglasses can reduce glare from reflected surfaces? A. refraction B. polarization C. diffraction D. total internal reflection is placed between a convex lens and its focal point. The image formed is virtual and erect. virtual and inverted. real and erect. real and inverted. 10. On a clear day, the sky appears to be more blue toward the zenith (overhead) than it does toward the horizon. This occurs because A. the atmosphere is denser higher up than it is at the Earth's surface. B. the temperature of the upper atmosphere is higher than it is at the Earth's surface. C. the sunlight travels over a longer path at the horizon, resulting in dispersion and more scattering. D. none of the given answers