UN9F38~0
advertisement

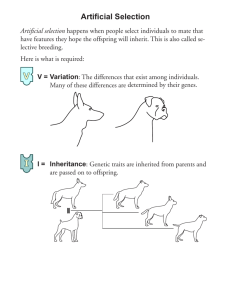
Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution Artificial Selection versus Natural Selection Section 7.2 Pages 305-311 Artificial Selection Selective pressure exerted by humans on populations to “improve” or modify particular and desirable traits Selective breeding in farm animals and crops (genetics) Breeding for selective qualities or purebred cats and dogs Natural Selection Process by which characteristics of a population (…not individuals…) change over many generations as organisms with heritable traits (i.e., passed down in genes) survive and reproduce passing the favourable traits to their offspring Darwin observed…. Every generation produces more offspring than can survive given the limitation of resources Individuals within a species vary in many ways…and some of the variation is inherited Individuals with traits that enabled them to survive would likely have more offspring with these favoured traits…and as such, the traits are passed on (Survival of the Fittest) Processes for change are slow, gradual and random “Evolution?” Darwin did not use the term “evolution.” Rather, he used the expression “Descent with Modification.” Why? Evolution implies progress. Darwin observed that evolution via Natural Selection has no set or predetermined direction. As well, it may not demonstrate progress. Factors needed for Natural Selection to occur Variation in characteristics Differences in survival and reproduction (i.e., fitness) Heritability of characteristics from parent to offspring Key Difference In Natural Selection, it is the environmental conditions that determine which individual traits in a population are selected for…there is no human pressure or involvement. Consequences of Artificial Selection Pro Crops – Increased nutritional value Con Crops – may not tolerate poor soil quality…limited locations to farm To protect against genetic disasters, gene banks have been established. Gene banks contain populations of early ancestors of modern plants. Our most important food plants come from wild ancestors with genetic combinations that allowed them to survive and reproduce successfully in their environments.