Natural & Artificial Selection Worksheet: Biology
advertisement

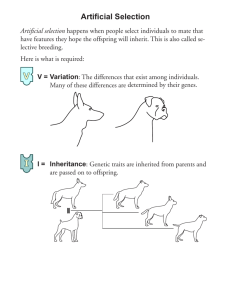
Natural Selection and Artificial Selection Natural Selection: the process that results when the ______________ of a ____________ of organisms ______ over many _____________. Individuals with certain ________ ___________survive specific local environmental conditions and _____ on their traits through ____________. For natural selection to occur you must have ________ within a _______. I.e. peppered moth When environment changes it exerts a _________ ___________ on a population. The pressure may result from predators, parasites, weather etc The individuals with ________ traits are selected for by their environment. They __________ the _______ in the environment. I.e. antibiotic resistant bacteria or plants that survive under dense trees in forest. Natural selection is ______________, has no will, purpose or direction. A trait that was __________ in one environment may not be if environmental conditions change. Over time the population numbers of individuals with favourable or unfavourable traits will change over generations to accommodate the new environment. Those individuals with the most __________ traits for that environment will be _________, their numbers will start to _______ over many generations and they will be considered to be the _______ or have the best _______ for their environment. Artificial Selection: I.e. dog and cat breeders and the use of biotechnology for crops and plants (food industry) The difference between natural and artificial selection is in natural selection the ____________ plays the role that ________ play in artificial selection. In natural selection the _____ ________ are affected since the individuals with the best fitness will pass on their traits while the others may die off or become extinct. Consequences of Artificial Selection When humans _____ and choose the ______ for ________, the individuals that result will not be the most ____ for the environment (i.e. British Bulldog: respiratory ailments and hip dysplasia) Plants that have been ___________ bred lack genetic diversity. Most agriculture is based on extensive plantings of the same desired varieties called ____________. What if a new disease arises or mutation? To reduce catastrophe gene banks have been assembled: bank contains populations of early ancestors with vast diversity