Latin V
advertisement

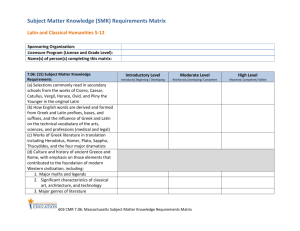
Latin V Approved February 2011 1 Plautus’ Menaechmi with Grammar Review Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standards: 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How does comedy reflect culture? Learning Goals: Students will: Identify the characteristics of Roman comedy. Apply their understanding of Roman comedy to the study and analysis of Plautus’ Menaechmei Improve their ability to read authentic Latin texts. Determine grammatical difficulties and address them as needed. Discuss and write about the Latin text citing specific passages. Read and discuss historical fiction to deepen their understanding of the Roman world. 2 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Translation of Latin versions of Aesop’s Fables ? Discuss grammatical and syntactical elements and translation choices Create and participate in text specific vocabulary activities Synopsis based tactile activities Vocabulary, grammar and translation quizzes and tests, written analysis of translated text Synopses quizzes Latin: Our Living Heritage: Book III Review Latin Grammar by John K. Colby Latin: Three and Four Years by Charles I. Freundlich Review and Test Preparation Guide for the Intermediate Latin Student by Sally Davis Beyond Latin One by LeaAnn A. Osburn A Funny Think Happened on the Way to the Forum A Web of Latin Verb Synopses (University of Tennessee, Knoxville) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html Whittaker’s Words (Notre Dame) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html No Dictionaries www.nodictionaries.com running vocabulary from the text Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 3 Classical Essay Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standard(s): 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How does the classical tradition live on? Learning Goals: Students will: Discuss how to interpret an essay question and find evidence to support different conclusions. Demonstrate their knowledge of the ancient world and connect it to contemporary life. Cite ancient sources. Develop a well-reasoned essay suitable for publication. 4 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Participate in classroom discussion. Research topics in the library and using internet resources. Participating in the editing and revising process. Modeling of how sources are cited. Essays (submitted as entries in the writing contest sponsored by the Classical Association of New England) library Internet classroom library Internet Perseus Project (administered by Tufts University) http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/ varies with the topic chosen Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Access and process information Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 5 Reader’s Choice (author and text vary from year to year based on the interest and expertise of the class) Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standards: 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How does literature reflect the culture that created it? Learning Goals: Students will: Identify the characteristics of different Roman genres. Apply the understanding of genre characteristics to the study of selected texts. Improve their ability to read authentic Latin texts. Determine grammatical difficulties and address them as needed. Discuss and write about the Latin text citing specific passages. Discuss the context in which the text was written and read. 6 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Translation of selected text. Discuss grammatical and syntactical elements and poetical word choices. Create and participate in text specific vocabulary activities. Analysis of cultural context of text. Vocabulary, grammar and translation quizzes and tests, written analysis of translated text. Responsive and analytical essays based in the text. vary depending on the text selected, authors include Caesar, Seneca, Ovid, Vergil, Lucretius The Phaedra of Seneca edited by Gilbert and Sarah Lawall and Gerda Kunkel De Rerum Natura edited by Bonnie A. Catto Ecce Romani III Caesar’s De Bello Gallico by Andrew C. Aronson Petronius: Selections from the Satyricon edited by Gilbert Lawall Whittaker’s Words (Notre Dame) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html No Dictionaries www.nodictionaries.com running vocabulary from the text Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 7 Catullus Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standards: 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How does poetry reflect human experience? Learning Goals: Students will: Identify the characteristics of Roman poetry genres. Improve their ability to read authentic Latin texts. Determine grammatical difficulties and address them as needed. Discuss and write about the Latin text citing specific passages. Discuss the context in which Catullus’ poems were written and read. 8 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Translation of selected poems of Catullus. Discuss grammatical and syntactical elements and poetical word choices. Create and participate in text specific vocabulary activities. Analysis of poems in English. Vocabulary, grammar and translation quizzes and tests, written analysis of translated text. Responsive and analytical essays based in the text. Catullus: Expanded Edition by Henry V. Bender and Phyllis Young Forsyth Catulli Carmina I-XI by Gilbert Lawall Whittaker’s Words (Notre Dame) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html No Dictionaries www.nodictionaries.com running vocabulary from the text Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 9 Horace Satire 1.9 (The Boor) Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standards: 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How does satire encourage deeper reflection on a topic? Learning Goals: Students will: Develop close reading skills for deeper understanding of text. Improve their ability to read authentic Latin texts. Discuss and write about the Latin text citing specific passages. Discuss how cultural context enriches understanding of a text. 10 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Translate Horace’s Satire 1.9 Discuss grammatical and syntactical elements Participate in text specific vocabulary activities Explore relevant elements of Roman daily life Vocabulary, grammar and translation quizzes and tests, written analysis of translated text Horace: Satire 1.9: The Boor by Margaret A. Brucia and Madeleine M. Henry Forum Romanum online scavenger hunt (Archer School for Girls; Los Angeles, California & VROMA) hhtp://www.vroma.org/~forum/ people.umass.edu/glawall/ecceteach.html Whittaker’s Words (Notre Dame) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html No Dictionaries www.nodictionaries.com running vocabulary from the text Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 11 Latin Special Project Essential Understandings: 1. Communicate in languages other than English. 2. Gain knowledge and understanding of other cultures. 3. Connect with other disciplines and acquire information. 4. Develop insight into the nature of language of culture. 5. Recognize how Latin grammar and syntax transform in the Classical period. 6. Connect how the development of Latin leads to a transformation into the Romance languages. 7. Gain an understanding of the products and perspectives expressed through the Latin literature of the time period. Content Standards: 1.1 Students read, understand and interpret Latin or Greek. 1.2 Students use orally, listen to and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. 2.1 Students demonstrate understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greek or Romans. 2.2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. 3.1 Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their knowledge of classical languages. 3.2 Students expand their knowledge through the Latin and Greek and the study of ancient culture. 4.1 Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. 4.2 Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world. 5.1 Student use their knowledge of Latin and Greek in a multilingual world. Essential Question: How do you develop a deep understanding of a topic? Learning Goals: Students will: Research a topic of their choice in the Roman world. Read a related Latin text on that topic. Create reading resources for a selection of their related Latin text. Present their research and Latin passage to peers. Learn from and evaluate peers’ projects and utilize reading resources for a variety of Latin texts. 12 Suggested Strategies Suggested Assessments Suggested Resources Suggested Tech Integration Content Vocabulary Lifelong Learning/21st Century Skills Discuss grammatical and syntactical elements and translation choices. Participate in the editing and revising process, both guided and unguided. Journal their learning process and progress. Research specific topics using a variety of resources. Develop targeted vocabulary lists and grammatical ntoes. Create a presentation that includes a learning activity for peers. Participate both in their own presentations and in those by peers. Journal entries. Presentation. English translation of Latin text. Participation in and evaluation of peer presentations Final reflection on project. vary with individual student project choices Whittaker’s Words (Notre Dame) http://archives.nd.edu/words.html No Dictionaries www.nodictionaries.com Internet research Student Presented PowerPoint related movies, et cetera vary with individual student project choices specific to student’s translation piece Productive Habits of Mind Quality work Access and process information Communicate effectively Read critically Collaborate and cooperate Core Ethical Values 13