Unit: Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement

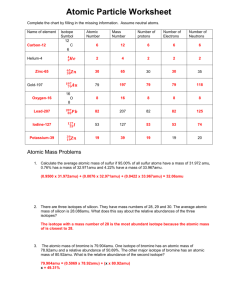
Practical Chemistry TEST Objectives/Notes: Unit 3: NUCLEAR Chemistry Define radioisotope and state why certain elements are radioactive. o Elements with atomic numbers greater than 83 are unstable and undergo decay. o An isotope that is unstable and thus radioactive, is call a radioisotope. o Isotope: atoms having the same atomic number but a different atomic mass. Recognize isotopes of an element and interpret isotopic notation. o Remember, isotopes have the same atomic number! (But different atomic mass.) o Isotopic Notation for carbon: 126C or C-14 (hyphen notation). List the common nuclear particles, and write their symbols. o Alpha, Beta, Positron and Gamma radiation (refer to Table O in Reference Table). o Know the identity of the numbers written as part of the symbol for these particles. o Also know their penetrating power: high, moderate, or low. Predict products of natural decay reactions. o Use Table N in the Reference Table to determine what particle emission occurring during natural decay of a radioisotope. o Identify the types of radioactive decay a sample undergoes. Write and balance nuclear reactions undergoing transmutation. o Understand the symbol notation. o Remember that the total charge/mass on the reactant (left) side of the “yields” sign () must equal the total charge/mass on the product (right) side of the equation. Distinguish between natural and artificial transmutation reactions. o Natural transmutation is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus in order to achieve stability. (ONE reactant on left side of sign). o Artificial transmutation occurs when the nucleus is bombarded with high-energy particles causing the change in the nucleus (TWO reactants on left side of sign). Define the difference between fission and fusion. o A fission reaction involves the splitting (or breaking up) of a heavy nucleus to produce lighter (lower atomic number) nuclei. o A fusion reaction involves the combining (or building up) of two light nuclei to produce a heavier (higher atomic number) nucleus. Define the term Half-Life and solve problems involving its terms. o The time it takes for half of the atoms in a given sample of an element to decay is called the half-life of the element. Each isotope has its own half-life. o Use Table N in the Reference Table to determine the half-life of a radioisotope. Describe the uses of radioactive isotopes. o Relating to Dating (organic: C-14; geological: U-238) o Tracers (P-31: plants; C-14: organic) o Medical treatments (thyroid: I-131; tumors: Co-60; Tc-99)