Atomic Structure & Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet
advertisement

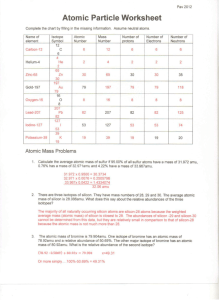
Atomic Particle Worksheet Complete the chart by filling in the missing information. Assume neutral atoms. Name of element Carbon-12 Helium-4 Zinc-65 Gold-197 Oxygen-16 Isotope Symbol 12 C 6 Atomic Number Mass Number Number of protons Number of Electrons Number of Neutrons 6 12 6 6 6 𝟒 𝟐𝑯𝒆 2 4 2 2 2 𝟔𝟓 𝟑𝟎𝒁𝒏 30 65 30 30 35 𝟏𝟗𝟕 𝟕𝟗𝑨𝒖 79 197 79 79 118 8 16 8 8 8 16 O 8 Lead-207 𝟐𝟎𝟕 𝟖𝟐𝑷𝒃 82 207 82 82 125 Iodine-127 𝟏𝟐𝟕 𝟓𝟑𝑰 53 127 53 53 74 Potassium-39 𝟑𝟗 𝟏𝟗𝒁𝒏 19 39 19 19 20 Atomic Mass Problems 1. Calculate the average atomic mass of sulfur if 95.00% of all sulfur atoms have a mass of 31.972 amu, 0.76% has a mass of 32.971amu and 4.22% have a mass of 33.967amu. (0.9500 x 31.972amu) + (0.0076 x 32.971amu) + (0.0422 x 33.967amu) = 32.06amu 2. There are three isotopes of silicon. They have mass numbers of 28, 29 and 30. The average atomic mass of silicon is 28.086amu. What does this say about the relative abundances of the three isotopes? The isotope with a mass number of 28 is the most abundant isotope because the atomic mass of is closest to 28. 3. The atomic mass of bromine is 79.904amu. One isotope of bromine has an atomic mass of 78.92amu and a relative abundance of 50.69%. The other major isotope of bromine has an atomic mass of 80.92amu. What is the relative abundance of the second isotope? 79.904amu = (0.5069 x 78.92amu) + (x x 80.92amu) x = 49.31% Nuclear Decay Reactions Complete the following nuclear equations and state the type of nuclear decay. Po _______ 24 He 1. 210 84 2. 8 5 3. _______ 4. 14 6 206 82𝑃𝑏 – B 48 Be _______ 234 91 𝟎 +𝟏𝜷 Pa e 0 1 C _______ e 5. ______ 81 37 𝟏𝟒 𝟕𝑵 Rb 3681Kr + X-ray photon O 157 N ______ 6. 15 8 7. 58 28 8. 226 88 9* 1 0 10. 238 92 Ni e _______ 0 1 Ra 222 86 – positron emission 𝟐𝟑𝟒 𝟗𝟎𝑻𝒉 0 1 Rn ______ 𝟎 −𝟏𝜷– electron capture 𝟎 +𝟏𝜷 – positron emission 58 27 Co – electron capture 𝟏 𝟏𝒑 U _______ 24 He – beta and gamma decay – beta decay 𝟒 𝟐𝑯𝒆– n _____ 10 e alpha decay alpha decay – beta decay 𝟐𝟑𝟒 𝟗𝟎𝑻𝒉 – alpha decay Complete the following nuclear equations. 9 4 Be 24 He _____ 01n F 178 O _____ ( 𝟏𝟏𝑯) H _____ 24 He 01n energy ( 𝟑𝟏𝑯) ( 𝟏𝟐𝟔𝑪) 20. 18 9 ( 𝟐𝟑𝟗 𝟗𝟑𝑵𝒑) 21. 2 1 ( −𝟏𝟎𝜷) 22. 27 14 30 Al ______ 14 Si 11H ( 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆) 23. ______ 2 He Ba ______ 10 e ( 𝟏𝟒𝟏 𝟓𝟕𝑳𝒂 ) 24. 32 15 16. ______ 2 He 8 O 1 p ( 𝟏𝟒𝟕𝑵) 25. 142 61 17. ______ ( 𝟏𝟖𝟓 𝟕𝟗𝑨𝒖) 26. 14 7 ( 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆) 27. 13 6 Cf n ( 𝟐𝟑𝟖 𝟗𝟐𝑼) 28. 239 94 11. 12. ______ Cu 13. 66 29 14. 27 13 15. 141 56 66 30 239 94 Pu 10 e Zn ______ 4 18. 241 95 17 181 77 1 Ir 24 He Am _____ 237 93 Np 19. ______ 6 C 12 246 98 Si 10 e ______ 4 210 81 Tl The alpha decay of iridium-174 𝟏𝟕𝟒 𝟕𝟕𝑰𝒓 2) 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆+ The beta decay of platinum-199 𝟏𝟗𝟗 𝟎 𝟕𝟖𝑷𝒕 −𝟏𝜷 3) + 𝟏𝟗𝟗 𝟕𝟗𝑨𝒖 Positron emission from sulfur-31 𝟑𝟏 𝟏𝟔𝑺 4) 𝟏𝟕𝟎 𝟕𝟓𝑹𝒆 +𝟏𝟎𝜷 + 𝟑𝟏 𝟏𝟓𝑷 Krypton-76 undergoes electron capture 𝟕𝟔 𝟑𝟔𝑲𝒓 + 𝟎 −𝟏𝒆 𝟕𝟔 𝟑𝟓𝑩𝒓 ( 𝟐𝟏𝟒 𝟖𝟑𝑩𝒊) P ______ 10 e ( 𝟑𝟐 𝟏𝟔𝑺) Pm _____ 142 60 Nd ( −𝟏𝟎𝜷) N _____ 146 C 11 p ( 𝟏𝟎𝒏) C 01n ______ ( 𝟏𝟒𝟔𝑪) Pu 24 He 11H 2 01n ______ ( 𝟐𝟒𝟎 𝟗𝟓𝑨𝒎) Using your knowledge of nuclear chemistry, write the equations for the following processes: 1) ( 𝟐𝟕 𝟏𝟓𝑷) Half Life Problems 1) A certain isotope has a half-life of 6.00 hours. How much of a 5.00g sample will be left after 24 hours? 24 hours / 6.00 hours = 4.00 = n initial= (5.00 g)(1/2)4.00 = (5.00 g)(1/16) = 0.3125 g = 0.313 g 2) A certain isotope has a half-life of 3.25 hours. How much of a 10.0kg sample will be left after 3 days? 3.25 hours / 24 hours = 0.135416667 days 3 days / 0.135416667 days = 22.15384615 = n final= (10.0 g)(1/2)22.15384615 = 0.000002143 g = 0.00000214 g 3) Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years. How long will it take for a 1.00kg sample to be reduced to 0.25kg of carbon-14? (0.25 kg) / (1.00 kg) = 0.25 = (1/2)n n=2 2.0 = TE / 5,730 years TE = (2.0)(5,730 years) = 11, 460 years = 11,000 years 4) A certain isotope of Uranium has a half-life of 4.3 billion years. How long will it take for a 2.7g sample to be reduced to 0.0844g? (0.0844 g) / (2.7 g) = 0.0312592593 = (1/2)n n = ln(0.0312592593) / ln (1/2) = 4.999572598 4.999572598 = TE / 4.3x109 years TE = (4.999572598)(4.3x109 years ) = 2.149816217x1010 years = 2.1x1010 years 5) A 0.40g sample of thorium-228 is reduced to 0.05g in 5.7 years. What is the half-life of thorium-228? (0.05 g) / (0.40 g) = 0.125 = (1/2)n n = ln(0.125) / ln(1/2) = 3 3 = 5.7 years / T T = 5.7 years / 3 = 1.9 years = 2 years 6) A sample of radon-222 is found to have decreased from 266g to 8.5g in 19 days. Calculate the halflife of radon-222. (8.5 g) / (266 g) = 0.0319548872 = (1/2)n n = ln(0.0319548872) / ln(1/2) = 4.967819594 4.967819594 = 19 days / T T = 19 days / 4.967819594 = 3.824615536 days = 3.8 days 7) An isotope with a half-life of 8 hours was received exactly 24 hours before it was to be used. At the time of use, the quantity of the isotope was 16.5g. How much of the isotope was there upon delivery to the lab? 24 hours / 8 hours = 3 = n 16.5 g =(1/2)3 x mi = (16.5 g) / (1/8) = 132 g 8) How long will a 12.4g sample of a radioisotope take to decay to 1.55g if its half-life is 1.2 days? (1.55 g) / (12.4 g) = 0.125 = (1/2)n n =3 3.00 = TE / 1.2 days TE = (3.00)(1.2days) = 3.6 days Induced Transmutation Reactions Write the following reactions from the given information 1. Alpha particle bombardment of einsteinium-253 (one of the products is a neutron). 𝟐𝟓𝟑 𝟗𝟗𝑬𝒔 2. 𝟐𝟓𝟔 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝑴𝒅 Induced transmutation of uranium-238 into californium-246 by bombardment with carbon-12. 𝟐𝟑𝟖 𝟗𝟐𝑼 3. + 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟏𝟎𝒏 + + 𝟏𝟐 𝟔𝑪 𝟐𝟒𝟔 𝟗𝟖𝑪𝒇+ 4 𝟏𝟎𝒏 One induced transmutation reaction of uranium-235 with a neutron results in the release of three neutrons and the production of two new nuclides. One of the nuclides is xenon-138. Write the equation with both reactants and all three products. 𝟐𝟑𝟓 𝟏 𝟗𝟐𝑼+ 𝟎𝒏 3 𝟏𝟎𝒏+ 𝟏𝟑𝟖 𝟗𝟓 𝟓𝟒𝑿𝒆+ 𝟑𝟖𝑺𝒓 4. Bombardment of uranium-235 with a neutron can generate tellurium-135, 3 neutrons, and one other product. Write the complete reaction for this transmutation. 𝟐𝟑𝟓 𝟏 𝟗𝟐𝑼+ 𝟎𝒏 3 𝟏𝟎𝒏+ 𝟏𝟑𝟓 𝟗𝟖 𝟓𝟐𝑻𝒆+ 𝟒𝟎𝒁𝒓 5. The first radioactive nucleus produced in the laboratory was phosphorus-30. Another product of this reaction was a neutron. This was accomplished through alpha bombardment. Write the complete transmutation reaction including original isotope. 𝟒 27 𝟐𝑯𝒆+ 13 Al 𝟑𝟎 𝟏 𝟏𝟓𝑷+ 𝟎𝒏 6. When sodium-23 combines with hydrogen-2, an alpha particle is produced along with a new nuclide. Write the complete equation for this fusion reaction. 23 11 Na + 21 H 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟐𝟏 𝟏𝟎𝑵𝒆