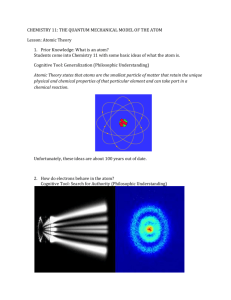
Name: Hour: Date: Abiotic Limiting Factor Limiting factor resulting
advertisement

Name: Hour: Date: Alpha particle Limiting factor resulting from something nonliving: shortage of a resource (food, water, space) Weather /disasters: temp, rain, hurricane, wind Organisms that result in the extinction of other species because they out compete native species for resources The largest radioactive particle that can be given off by an atom; can be easily stopped with paper Anemometer Tool used to measure wind speed for windmills Anthracite The cleanest burning coal; produces the most energy when burned Abiotic Limiting Factor Alien species (invasive/exotic) Atomic mass This growth occurs in a population when its numbers continue to increase by the same value (Example: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 etc.) Number of protons and/plus the number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus Atomic power Energy trapped inside a nucleus of an atom Background rate of extinction This is the # of organisms that will become extinct due to natural causes, not human beings Biodiversity The variety of different species on in a given area; benefits of protecting include: medicine, Arithmetic industry, agriculture, ethics, aesthetics & recreation Biomass fuel Biotic limiting factor Biotic potential Environmental Science – Final Exam: Spring Semester Notecards Use of yard clippings, manure, or left-over crops as a source of energy Limiting factor resulting from another organism: competition: 2 or more organisms fighting for a resource (parasitism, predation) When populations grow at a geometric rate, the fastest rate at which a population can grow; limited by reproductive potential Page 1 Dependent variable Maximum number of organisms that an ecosystem can support for any length of time; determined by the limiting resource (food/water) This part of a nuclear power plant keeps the rate of fission regulated so the reactor does not blow up like a bomb Factor that depends on a populations size; for example a disease infecting one tree could lead to destruction of nearby trees (small vs. large forest) Factor that has the same impact on a population regardless of its size; for example: volcanic eruptions, fire, habitat destruction in general This value is always plotted on the Y-axis of a population graph Electricity The "flow" of electrons; when electrons move between atoms, a current of electricity is created Electron The negative part of an atom; electric current is the movement/flow of this particle Carrying capacity Control rods Density-dependent factor Density-independent factor Emergent plants Plants that have roots attached to the ground and have leaves and stems extending above the water’s surface; Ex: cattails An area where fresh water meets salt water Estuary Eutrophication Fission Fossil fuel Fusion Gamma radiation Environmental Science – Final Exam: Spring Semester Notecards Water pollution may cause this – when a pond or lake eventually fills in and dries up; Excess nitrogen and phosphorous effect lakes usually by The process of splitting an atom’s nucleus to obtain energy; how nuclear power plants get their power Formed hundreds of millions of years ago; Coal, Oil (Petroleum) & Natural Gas (Main use of coal in our country is for electricity production) The combination of two small nuclei to form a larger nucleus; reaction in which 2 atoms of hydrogen combine to form an atom of helium High frequency photons; the most dangerous radioactive particle; penetrates most materials Page 2 Geothermal power This type of growth is shaped like the letter “J” when graphed; (Ex: 4, 12, 36, 108, 324); occurs in nature when there is no competition or predator energy found from the heat in the earth's crust (earth’s core) (Global) population growth Birth rate minus death rate Habitat destruction The number one cause of species extinction Half-life The time required for half of a radioactive atom to decay Heating & Industry The main use of natural gas in the United States Hydric soil A type of soil found in wetlands; waterlogged and low in oxygen Geometric (also called exponential or logarithmic) Hydroelectricity Hydrophytes Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Isotope Kilowatt-hours Lag Phase Environmental Science – Final Exam: Spring Semester Notecards Use of water as an energy source; involves a penstock Plants that are adapted to living in very wet soil; common in wetland areas Relationship that exists when two members of DIFFERENT species compete for a resource; one hunts the other or is faster & eats all the food Relationship that exists when two members of the SAME species compete for a resource; plants compete for light or wolves for rabbits Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons; Different isotopes have different atomic masses; Ex: 235 or 238 Ex:Element-24 has 10 protons & 14 neutrons How electric companies measure (charge us for) the energy we use This occurs when there is little growth in a population because its members are "getting used to" a new environment Page 3 Limnology The study of biotic and abiotic features of fresh bodies of water (lakes, ponds and streams) Littoral Community The shallowest part of a pond, closest to the shore; a lot of plant/animal growth Methane Neutron Non- renewable energy Another name for natural gas; a by-product when bacteria break down wastes in a landfill, can be burned to generate heat and electricity This subatomic particle has NO charge; In a nuclear reactor, these particles are fired at atoms to split their nuclei Fossil fuels: coal, oil, natural gas pH Scale alternative energy technology that uses the temperature difference between layers of water to generate electricity A U-shaped body of water formed when a wide meander from the main stem of a river is cut off to create a lake Neutral = 7, acid = less than 7 base = higher than 7. Most lakes have pH 6.5-9 Petroleum oil fossil fuel is taken to a refinery and split into different products when heated OTEC (ocean thermal energy conversion) Oxbow Lake convert sunlight into electricity Photovoltaic cells Profundal Community The deepest part of a lake; little or no sunlight and low oxygen; has bacteria & fungi The positive part of an atom Proton Radioactivity When an unstable atom breaks down, releasing energy and atomic sub-particles Rainfall most influential factor determining the kinds of plants living in a wetland Environmental Science – Final Exam: Spring Semester Notecards Page 4 Secchi disc S-shaped curve instrument is used to measure total suspended solids in a lake (T.S.S.: rock/soil erosion, algae, decaying plants/animals) Populations controlled by density dependent factors: has a Lag Phase, Exponential Phase and Carrying Capacity two main air pollutants causing acid rain sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide Time This unit should always be written on the X-axis when making a graph of population growth Transportation The main use of petroleum oil in the United States Tributary A smaller river or stream which feeds into a larger river or stream Uranium Fuel used in a nuclear power plant Volts The force that "pushes" electrons; how much force each electron is under Watts The unit of energy calculated by multiplying amps times volts Wetland Functions Wind energy Environmental Science – Final Exam: Spring Semester Notecards Trapping and filtering, reducing flood risk, buffering erosion, habitat for organisms, recreational area Use a yaw motor and nacelle; use windmills to create electricity; disadvantage: difficult to transport energy from source to use Page 5