doc - Chemical Education Projects

Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes and Alkynes
Grzegorz Filipczyk
Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh
June 2006
OVERVIEW
In this exercise you will use the CAChe program to model key structures of the intermediate carbocations in electrophilic addition to alkenes and alkynes. The minimum energy of each of the possible intermediate carbocations will be used to predict the products. Begin this exercise by using what you already know about electrophilic addition reaction to answer question 1.
Q1: What product would you expect in each of the following reactions?
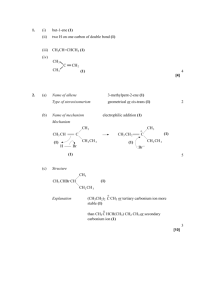
H
Q1a
C + H Cl
H
2
C CH
3
CH
3
Q1b
C
CH
3
CH
3
+ H Cl
+ H Br
Q1c
H
2
C
Q1d HC C CH
3
+ H Br
MODELING
For each of the reactions make models of two possible carbocations formed in the first step of the addition reaction.
Building the Structures
1.
Open the Workspace/Editor and build a molecule (carbocation). Be sure to choose the correct hybridizations for each carbon atom and add + charge to the appropriate one.
2.
Select Beautify/Comprehensive .
3.
Select File/Save as and save the molecule as for example “Carbocation 1”
(see Table 1).
4.
Select Experiment/New . Experiment window will appear. Choose Property of: chemical sample, Property: optimized geometry, Using: AM1 geometry.
Click on Start . When the operation is done, close the experiment windows.
5.
Built and optimize the geometry of the other molecules in the same manner as for the first one.
Project Leader
1.
Open the ProjectLeader (under Program Files in the CAChe folder).
2.
Double click on the first blank cell in the column labeled “ Chemical
Sample
”. In the dialog box that appears, locate the folder your molecules are stored in. Highlight one of the molecules which you have saved before. Click on Open . The name of the file appears in the first cell of Project Leader. Add the remaining molecules in the same way, each to the new cell in that first column.
3.
Double click on the gray cell of Column B. Choose Property of the chemical sample, kind of property : conformation minimum energy, kind of procedure : Hf at AM1 geometry, OK.
4.
Right click on the cell with letter B in the Column B. Choose Evaluate/Cell from the pop-up menu. Results will appear in the spreadsheet as they are calculated.
REPORT
Write the results of your calculations in the Table 1.
Table 1. Minimized Structures and Their Energies for Question 1.
Minimized Structure Filename Conformation
Minimum E
(kcal/mole)*
Q1a-1
Q1a-2
Q1b-1
2
Q1b-2
Q1c-1
Q1c-2
Q1d-1
Q1d-2
* Numbers in parenthesis are relative energies.
Q2: In each reaction, what is the most stable carbocation?
The most stable carbocations are:
Q3: Based on the results of the calculations collected in the Table 1 draw the product of the addition of X to the most stable carbocation in reactions a, b, c , d.
Compare the results with your answers to the Q1. Are these the expected products?
3
Product for reaction 1a Product for reaction 1b
Product for reaction 1c Product for reaction 1d
Q4: Predict the structure of the alcohol formed in the following addition reaction which would be acid catalyzed in practice:
C
2
H
5
+ H OH
C
H
2
C CH
3
Q5: For the following reaction of 1,3-butadiene with HBr draw three possible carbocations two of which are a pair of resonance structures. What do you predict to be the main product of the addition of one equivalent of HBr to 1,3-butadiene?
+ HBr
The possible carbocations are:
Using CAChe, draw these three carbocations that might be formed in the first step of the addition reaction. Name them “Q5-1”, “Q5-2” and “Q5-3”.Optimize the geometry. Copy and paste the models to the space below.
Using ProjectLeader calculate the minimum energies as described above. Write the results of the calculations in Table 2. Comment on what you calculate.
4
Table 2. Minimized Structures and Their Energies for Question 5.
Filename Conformation
Minimum E
(kcal/mole)*
Minimized Structure
Q5-1
Q5-2
Q5-3
Q6: Based on the calculations what is the main product of the second step of the addition reaction? Draw the structure below. Is it the expected product (see your answers to Q5)?
5
Q7. Predict the major product(s) formed in the following reactions
H
3
C C
3
H
7
Q7a C C + HBr
H
3
C
H
3
C
C
3
H
7
F
Q7b C C + HBr
H
3
C
H
3
C
F
I
Q7c C C + HBr
H
3
C I
Q8. Freehand draw the structures of the carbocations that give rise to the products you predicted for Q7.
Q7a Q7b Q7c
6
Q9. As described above, calculate the two carbocations possible for each reaction
(put the results of the calculations in the Table 3). Do your calculations agree with your predictions?
Table 3. Minimized Structures and Their Energies for Question 7.
Minimized Structure Filename Conformation
Minimum E
(kcal/mole)*
Q7a-1
Q7a-2
Q7b-1
Q7b-2
Q7c-1
Q7c-2
7