Political Economy of Corporate Governance/ Accounting Failures
Shyam Sunder, Yale School of Management
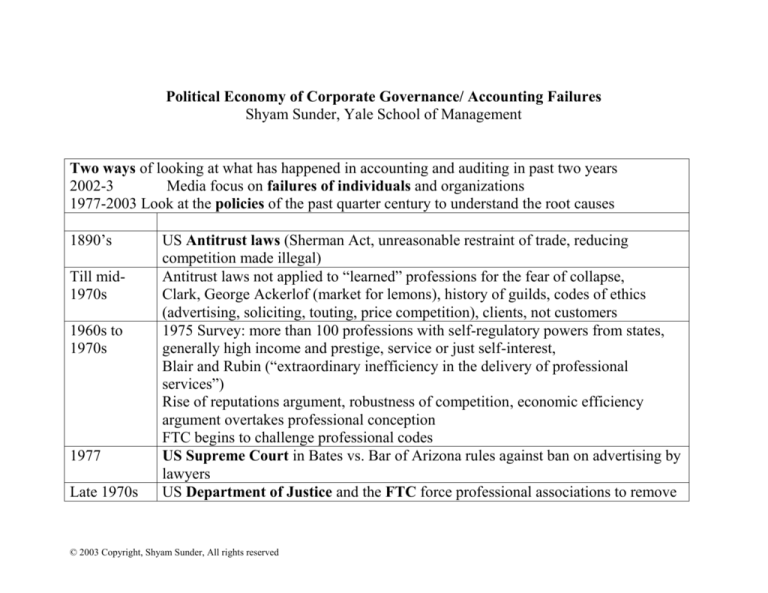
Two ways of looking at what has happened in accounting and auditing in past two years
2002-3
Media focus on failures of individuals and organizations
1977-2003 Look at the policies of the past quarter century to understand the root causes
1890’s
Till mid1970s
1960s to
1970s
1977
Late 1970s
US Antitrust laws (Sherman Act, unreasonable restraint of trade, reducing
competition made illegal)
Antitrust laws not applied to “learned” professions for the fear of collapse,
Clark, George Ackerlof (market for lemons), history of guilds, codes of ethics
(advertising, soliciting, touting, price competition), clients, not customers
1975 Survey: more than 100 professions with self-regulatory powers from states,
generally high income and prestige, service or just self-interest,
Blair and Rubin (“extraordinary inefficiency in the delivery of professional
services”)
Rise of reputations argument, robustness of competition, economic efficiency
argument overtakes professional conception
FTC begins to challenge professional codes
US Supreme Court in Bates vs. Bar of Arizona rules against ban on advertising by
lawyers
US Department of Justice and the FTC force professional associations to remove
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
anticompetitive provisions from their “codes of ethics”
1979
AICPA’s new Code of Ethics: allows advertising, solicitation of competitors’
clients and employees
Early 1980s Sharp drop in the price of audit services due to competitions, disappearing profits in
audit firms
Special problems of observing the quality of audit service
Early 1980s New business model of audit firms to maintain profitability:
New production function: shift from substantive to analytical tests
New product Mix: Use audit relationships to sell more consulting (consulting as a
consequence, not cause, of the collapse)
New internal compensation: Transfer between audit/consulting partners
New labor market policy: Cut wages of new hires
Early 1980s Growth of university accounting majors and CPA candidates stops
Mid-1980s
Many business and audit failures and law suits (S&Ls), auditors pay hundreds of
millions in settlements, worries about profitability resume
Later-1980s Goal to change the legal environment of auditors
Federal: Switch from joint-and-several to proportionate liability
State: Switch to Limited Liability Partnerships, 150 hour (five-year) qualification
for CPAs to reduce supply
1988-90-92- Large scale organized contributions to elections from auditors
94
1993
FASB’s attempt to write a standard for executive option accounting is beaten back
by business and Congress (role of CT senator)
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
1994
1995
1999
2001-3
US Supreme Court (Central Bank vs. First Interstate Bank of Denver) rules that
corporate advisors cannot be held liable to third parties for aiding and abetting
fraud
Private Securities Litigation Reform Act gives proportionate liability to auditors
plus a gift under pressure from the Silicon Valley: safe harbor for forward looking
(speculative) information
SEC misdiagnoses audit problems (consulting as the cause); attempts to have
auditors divest consulting; is beaten back with support from Congress, settles for
disclosure of fees
Accounting and audit failures surface in the wake of economic slow down and
stock market drop
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
Number of Settlements of Claims Against Auditors
Frequency by Time Period
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
1960-1964 1965-1969
1970-1974
1975-1979
1980-1984
Time Period
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
1985-1989
1990-1995
Unknown
Amounts of Settlements Against Auditors
500,000,000
400,000,000
300,000,000
Total
200,000,000
100,000,000
0
19
67
19
72
19
75
19
78
19
81
19
84
19
87
19
90
19
93
19
96
Amount of Settlements
Total Amount of Settlements
Year
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
Accountants’ Contributions to Political Campaigns
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
Accountants’ Contributions to Political Campaigns
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
Why Accounting/Auditing Collapsed? A Policy Story
Shyam Sunder, Yale School of Management
June 2003
Two ways of looking at what has happened in accounting and auditing in past two years
2002-3
Media focus on failures of individuals and organizations
1977-2003
Look at the policies of the past quarter century to understand the root causes
1890’s
US Antitrust laws passed
Till midAntitrust laws not applied to professions for the fear of collapse, “market for
1970s
lemons”
1960s to
Rise of reputations argument, robustness of competition
1970s
1977
US Supreme Court in Bates vs. Bar of Arizona rules against ban on advertising by
lawyers
Late 1970s
US Department of Justice and the FTC force professional associations to remove
anticompetitive provisions from their “codes of ethics”
1979
AICPA’s new Code of Ethics: allows advertising, solicitation of competitors’ clients
and employees
Early 1980s Sharpe drop in the price of audit services due to competitions, disappearing profits in
audit firms
Early 1980s New business model of audit firms to maintain profitability:
Production: shift from substantive to analytical tests
Product Mix: Use audit relationships to sell more consulting
Compensation: Transfer between audit/consulting partners
Labor Market: Cut wages of new hires
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved
Early 1980s
Mid-1980s
Growth of university accounting majors and CPA candidates stops
Many business and audit failures and law suits (S&Ls), auditors pay hundreds of
millions in settlements, again worries about profitability
Later-1980s Goal to change the legal environment of auditors
Federal: Switch from joint-and-several to proportionate liability
State: Switch to Limited Liability Partnerships
1988-90-92- Large scale organized contributions to elections from auditors
94
1993
FASB’s attempt to write a standard for executive option accounting is beaten back
by business and Congress
1994
US Supreme Court (Central Bank vs. First Interstate Bank of Denver) rules that
corporate advisors cannot be held liable to third parties for aiding and abetting fraud
1995
Private Securities Litigation Reform Act gives proportionate liability to auditors
plus a gift under pressure from the Silicon Valley: safe harbor for forward looking
(speculative) information
1999
SEC misdiagnoses audit problems (consulting as the cause); attempts to have
auditors divest consulting; is beaten back with support from Congress, settles for
disclosure of fees
2001-3
Accounting and audit failures surface in the wake of economic slow down and stock
market drop
© 2003 Copyright, Shyam Sunder, All rights reserved












