Adult dog
advertisement

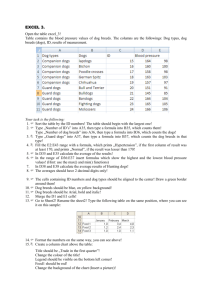
ADULT DOG - Neutered adult dog "The diet must help the adult dog remain in perfect health." INDICATIONS Adult dog, according to size of breed: Small breeds: from 12 months to 9 years Medium breeds: from 14 months to 8 years Large breeds: from 16 months to 7 years Giant breeds: from 18 months to 6 years Constipation Post surgery (general) COUNTER INDICATIONS Chronic kidney failure Liver failure Pancreatic failure INGREDIENTS Dehydrated meat (poultry) [for adult dog with salmon: dehydrated meat (poulty) and fish (minimum salmon content 4 %)], cooked cereals, animal fats, maize proteins, cooked soybeans, beet pulp, linseed, sea salt, fructo-oligosaccharides, chondroitin sulphate, chitosan, DL-methionine, minerals, trace elements and vitamins. With antioxidants: EC additives. NUTRITIONAL CHARACTERISTICS High protein contribution and their high quality, contribute to maintaining muscle mass. Moderate starch content guarantees good digestive tolerance. The reinforced contribution in soluble and insoluble food fibres contributes to satiety, stimulates intestinal transit and contributes to the balanced development of digestive bacteria in the gut. Richness in vitamin E and selenium, an anti-oxidant complex, protects against cell ageing. HEALTH BENEFITS Healthy skin and shiny coat – essential fatty acids Omega 6 and Omega 3 essential fatty acids are major components in the development and maintenance of healthy skin. They are responsible for the barrier function of the epidermis and regulate the quality of the sebaceous secretions that make a dog’s coat shine and look nice. With an optimal omega 6 to omega 3 ratio between 5 and 10, they help regulate the inflammatory cascade. Joint mobility – chondroitin sulphate + chitosan Chondroitin sulphate, a natural component of cartilage in the joints, helps maintain the elasticity and resistance properties of cartilage. Chitosan, a purified extract of the shell of crustaceans, increases the biovailability of ingested chondroitin sulphate by protecting it from attacks by acids and enzymes in the stomach and tehn by promoting absorption in the intestine. Urinary health – DL-methionine (controlled urinary pH) DL-methionine, a sulphur amino acid, contributes to the normal acidification of urine, maintaining urinary pH within the physiological norms and limiting the risk of disorders of the lower urinary tract. TYPICAL ANALYSIS Moisture ........................................................................................ 8 % Crude protein ............................................................................. 27 % Crude fat ..................................................................................... 19 % Minerals .................................................................................... 8 % Crude fibre ....................................................................................2.5 % Soluble fibres ............................................................................... 1 % Insoluble fibres ............................................................................ 7 % NFE .......................................................................................... 35.5 % Starch.......................................................................................... 26 % Calcium ...................................................................................... 1.5 % Phosphorus ............................................................................... 1 % Ca/P .............................................................................................. 1.5 Essential Fatty Acids ................................................................. 3.4 % ω6/ ω3 ratio ...................................................................................... 6 Chondroitine sulphate ......................................................... 215 mg/kg Chitosan …………………..................................................... 215 mg/kg DL Methionine + Cystine ........................................................... 0.8 % Metabolisable energy (FEDIAF formula) ......................... 380 kcal/100g PCR .................................................................................... 71 g/Mcal Average digestibility ................................................................ 90 % Urinary pH ............................................................................ 6.4 – 6.8 Vitamin A .......................................................................... 11000 UI/kg Vitamin D3 ......................................................................... 1100 UI/kg Vitamin E ............................................................................. 500 mg/kg