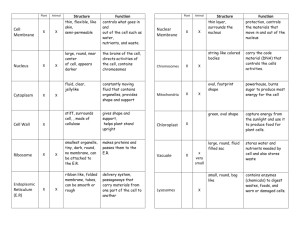
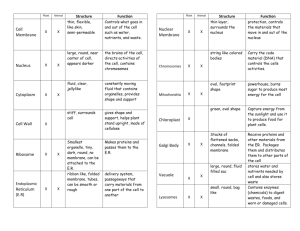
File
advertisement

Human Anatomy & Physiology Prefix & Suffix List 1st 4 ½ weeks Britt 1. append2. cardi3. cerebr4. cran5. 6. 7. 8. dorshomeo–logy meta- 9. nas10. orb11. pariet12. pelv13. peri14. pleur15. –stasis 16. super17. –tomy 18. endo19. adip20. chondr21. –cyt 22. epi23. –glia to hand something: appendicular – pertaining to the upper limbs and lower limbs heart: pericardium – membrane that surrounds the heart brain: cerebrum – largest portion of the brain helmet: cranial – pertaining to the portion of the skull that surrounds the brain back: dorsal – position toward the back of the body same: homeostaisis – maintenance of a stable internal environment the study of: physiology – study of body functions change/middle: metabolism, metatarsals – chemical changes that occur within the body or middle nose: nasal – pertaining to the nose circle: orbital – pertaining to the portion of skull that encircles an eye wall: parietal membrane – membrane that lines the wall of a cavity basin: pelvic cavity – basin-shaped cavity enclosed by the pelvic bones around: pericardial membrane – membrane that surrounds the heart rib: pleural membrane – membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage standing still: homeostasis – maintenance of a stable internal environment above: superior – referring to a body part that is located above another cutting: anatomy – study of structure, which often involves cutting or removing body parts within: endoplasmic reticulum – complex of membranous structures in the cytoplasm fat: adipose tissue – tissue that stores fat cartilage: chondrocyte – cartilage cell cell: osteocyte – bone cell over, above: epithelial tissue – tissue that covers all free body surfaces glue: neuroglia – cells that bind nervous tissue together Human Anatomy & Physiology Prefix & Suffix List 1st 4 ½ weeks Britt 1. append2. cardi3. cerebr4. cran5. 6. 7. 8. dorshomeo–logy meta- 9. nas10. orb11. pariet12. pelv13. peri14. pleur15. –stasis 16. super17. –tomy 18. endo19. adip20. chondr21. –cyt 22. epi23. –glia to hand something: appendicular – pertaining to the upper limbs and lower limbs heart: pericardium – membrane that surrounds the heart brain: cerebrum – largest portion of the brain helmet: cranial – pertaining to the portion of the skull that surrounds the brain back: dorsal – position toward the back of the body same: homeostaisis – maintenance of a stable internal environment the study of: physiology – study of body functions change/middle: metabolism, metatarsals – chemical changes that occur within the body or middle nose: nasal – pertaining to the nose circle: orbital – pertaining to the portion of skull that encircles an eye wall: parietal membrane – membrane that lines the wall of a cavity basin: pelvic cavity – basin-shaped cavity enclosed by the pelvic bones around: pericardial membrane – membrane that surrounds the heart rib: pleural membrane – membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage standing still: homeostasis – maintenance of a stable internal environment above: superior – referring to a body part that is located above another cutting: anatomy – study of structure, which often involves cutting or removing body parts within: endoplasmic reticulum – complex of membranous structures in the cytoplasm fat: adipose tissue – tissue that stores fat cartilage: chondrocyte – cartilage cell cell: osteocyte – bone cell over, above: epithelial tissue – tissue that covers all free body surfaces glue: neuroglia – cells that bind nervous tissue together 24. hist25. hyal26. inter27. macr28. neur 29. os30. phag31. pseud32. squam33. strat34. stria35. cut36. derm37. folic38. melan39. seb40. meat41. odont42. poie43. ax44. carp45. –clast 46. clav47. condyl48. corac- web, tissue: histology – study of composition and function of tissues resemblance to glass: hyaline cartilage – flexible tissue containing chondrocytes among, between: intercalated disk – band of gap junctions between the ends of adjacent cardiac muscle cells large: macrophage – large phagocytic cell nerve: neuron – nerve cell bone: osseous tissue – bone tissue to eat: phagocyte – cell that engulfs and destroys foreign particles false: pseudostratified epithelium – tissue with cells that appear to be in layers, but are not scale: squamous epithelium – tissue with flattened or scalelike cells layer: stratified epithelium – tissue whose cells are in layers groove: striated muscle – tissue whose cells have alternating light and dark cross-markings skin: subcutaneous – beneath the skin skin: dermis – inner layer of the skin small bag: hair follicle – tubelike depression in which a hair develops black: melanin – dark pigment produced by certain cells grease: sebaceous gland – gland that secretes an oily substance passage: auditory meatus – canal of the temporal bone that leads inward to parts of the ear tooth: odontoid process – toothlike process of the second cervical vertebra make, produce: hematopoiesis – process by which blood cells are formed axis: axial skeleton – upright portion of the skeleton that supports the head, neck, and trunk wrist: carpals - wrist bones break: osteoclast – cell that breaks down bone tissue bar: clavicle – cone that articulates with the sternum and scapula knob, knuckle: condyle – rounded, bony process a crow’s beak: coracoid process – beaklike process of the scapula 24. hist25. hyal26. inter27. macr28. neur 29. os30. phag31. pseud32. squam33. strat34. stria35. cut36. derm37. folic38. melan39. seb40. meat41. odont42. poie43. ax44. carp45. –clast 46. clav47. condyl48. corac- web, tissue: histology – study of composition and function of tissues resemblance to glass: hyaline cartilage – flexible tissue containing chondrocytes among, between: intercalated disk – band of gap junctions between the ends of adjacent cardiac muscle cells large: macrophage – large phagocytic cell nerve: neuron – nerve cell bone: osseous tissue – bone tissue to eat: phagocyte – cell that engulfs and destroys foreign particles false: pseudostratified epithelium – tissue with cells that appear to be in layers, but are not scale: squamous epithelium – tissue with flattened or scalelike cells layer: stratified epithelium – tissue whose cells are in layers groove: striated muscle – tissue whose cells have alternating light and dark cross-markings skin: subcutaneous – beneath the skin skin: dermis – inner layer of the skin small bag: hair follicle – tubelike depression in which a hair develops black: melanin – dark pigment produced by certain cells grease: sebaceous gland – gland that secretes an oily substance passage: auditory meatus – canal of the temporal bone that leads inward to parts of the ear tooth: odontoid process – toothlike process of the second cervical vertebra make, produce: hematopoiesis – process by which blood cells are formed axis: axial skeleton – upright portion of the skeleton that supports the head, neck, and trunk wrist: carpals - wrist bones break: osteoclast – cell that breaks down bone tissue bar: clavicle – cone that articulates with the sternum and scapula knob, knuckle: condyle – rounded, bony process a crow’s beak: coracoid process – beaklike process of the scapula