glossary
advertisement

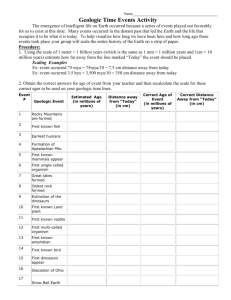
Glossahizzary Definitions provided by Dictionary.com Distribution/Range: The area over which a species is populated. The geographic range. Biodiversity: diversity among and within plant and animal species in an environment. K-Strategist Types of K-strategists Ecotone: the transition zone between two different plant communities, as that between forest and prairie. The edge of a forest has more biodiversity but provides less protection. Ecosystem: a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their environment. Population Density Effects: Dependent and Independent Controls Natural Population Curve: Irruptive, Stable, Irregular, Cyclic Biotic Potential: the capacity of a population of organisms to increase in numbers under optimum environmental conditions. Interspecific Competition: Predation: a relation between animals in which one organism captures and feeds on others. In this relationship, only the predator benefits. Extinction: When a species is no longer in existence, because it has died out. Background Extinction: The ongoing extinction of individual species due to environmental or ecological factors such as climate change, disease, loss of habitat, or competitive disadvantage in relation to other species. Background extinction occurs at a fairly steady rate over geological time and is the result of normal evolutionary processes, with only a limited number of species in an ecosystem being affected at any one time. Mass Extinction: The extinction of a large number of species within a relatively short period of geological time, thought to be due to factors such as a catastrophic global event or widespread environmental change that occurs too rapidly for most species to adapt. At least five mass extinctions have been identified in the fossil record, coming at or toward the end of the Ordovician, Devonian, Permian, Triassic, and Cretaceous Periods. The Permian extinction, which took place 245 million years ago, is the largest known mass extinction in the Earth's history, resulting in the extinction of an estimated 90 percent of marine species. In the Cretaceous extinction, 65 million years ago, an estimated 75 percent of species, including the dinosaurs, became extinct, possibly as the result of an asteroid colliding with the Earth. Fundamental Niche: Niche: the position or function of an organism in a community of plants and animals. Realized Niche: Habitat: the natural environment of an organism; place that is natural for the life and growth of an organism. Generalist Species: Migration: To move from one place to another. Fragmented Land: Land that has been disturbed by Roads or other man made obstacles, that break up an environment. Keystone Species: A species whose presence and role within an ecosystem has a disproportionate effect on other organisms within the system. A keystone species is often a dominant predator whose removal allows a prey population to explode and often decreases overall diversity. Other kinds of keystone species are those, such as coral or beavers, that significantly alter the habitat around them and thus affect large numbers of other organisms. Gestation: Being preggers Species Food Requirement: Secondary Consumer: Part of the food chain a carnivore that feeds only upon herbivores. Biome: a complex biotic community characterized by distinctive plant and animal species and maintained under the climatic conditions of the region, esp. such a community that has developed to climax. Organism: Any living thing TERMS TO DEFINE FOR GIULIA BECAUSE SHE IS A LOSER! Endangered Tropical Rainforest: True Desert: Boreal forest: Temperate deciduous forest: Temperate grassland: Gestation: Litter: K-Specialist: Carnivore: Scavenger: Prey: Threatened: Eradication: Territory: Population: Primary Consumers: Endangered Species Act '73: Conservation: Reintroduction: Management Policies: Environment: Economic Value: