Russia and Central Asia Physical Worksheet Key
advertisement

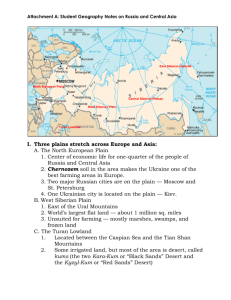
Russia and Central Asia Physical Characteristics Russia and Central Asia—Physical Features WS 1. How many times zones does Russia cover? 11 2. Which mountain range is usually considered the dividing point between Europe and Asia? The Ural Mountains 3. Where is the Volga River located? Western Russia; begins near Moscow and flows into the Caspian Sea 4. Is there more land on the European or Asian side of Russia? Asian side 5. Russia spans nearly 170 degrees of longitude, which is almost half the globe. How many total degrees of longitude are there? 180 --What is the name of the 0 degree longitude line? The Prime Meridian --What is the name of the 180 degree longitude line? The International Date Line 6. Name two reasons why it is difficult to govern a huge country like Russia. The expansive land area; the weak infrastructure; the diverse economies and cultures of the Russian people 7. What is permafrost? Where in Russia can it be found? Permanently frozen subsoil; Northern Russia in the Tundra (upper high latitudes) and the Subarctic Climate region (lower high latitude) 8. Where in Russia and Central Asia might you find a steppe region? What is the land like in a steppe? Southern Siberia and Central Asia in the land of the “Stans” (mostly Kazakhstan and western Uzbekistan; this area has a semi-arid climate and is predominantly grasslands used for nomadic farming 9. Where can you find deserts in Central Asia? In eastern Uzbekistan (Kyzyl-Kums), Turkmenistan (Kara-Kums), and Southeastern Kazakhstan (Muyun-Kums) 10.What is chernozem soil? Where can you find it? Nutrient rich, fertile (arable) soil or “black earth”; along the North European Plain in the Ukraine and western Russia within the Fertile Triangle 11.Where in Russia can you find a tundra climate? What is the land usually like in these areas? Northern Russia in the upper high latitudes close to the Arctic Circle 12.Which country in Europe, formerly known as the “breadbasket of the Soviet Union”, is famous for its black earth? The Ukraine 13.Is there a higher population on the European or Asian side of Russia? The European side 14.Which rebellious region of Russia can be found in the Caucasus Mountains? Chechnya within the Caucasus Mountains 15.Where do the Ural Mountains begin and end? The Kara Sea in the north and extend to the land just north of the Caspian Sea in the south 16.Where is the Aral Sea? Central Asia, in southwestern Kazakhstan and northwestern Uzbekistan 17.Where is Siberia? The Russian land area east of the Ural Mountains 18.Describe the population density in Siberia. Sparse (some village life-styles in the central uplands, some nomadic-herding in the southern parts; but, wages are high in Siberia for workers willing to brave the bitter cold climate) 19.Where in Russia and Central Asia might you find good farmland? Along the North European Plain, in the Fertile Triangle known for the rich, black soil chernozem 20.Name two reasons why it is difficult and expensive to develop the resources in Siberia. Cold climates, expansive land area, poor infrastructure, lack of capital and human resources 21.What river in Russia is the longest river in Europe? The Volga 22.Why is the Aral Sea polluted? The poor agricultural practices of the Soviet government (over-irrigation and irresponsible use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and nuclear weapons testing) 23.Where are the Caucasus Mountains? They span the land area between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea 24.Which body of water does the Ob River flow into? The Arctic Ocean 25.What is the climate like in much of Siberia? Bitter cold temperatures, tundra and subarctic climates 26.Which body of water does the Amur River flow into? The Pacific Ocean by way of the Strait of Tartar 27.Name three resources found in Siberia. Oil, coal, natural gas, iron ore, timber (taiga) 28.What types of resources can be found in and around the Caspian Sea? Oil and natural gas 29.Where in Russia might you find a taiga region? The lower high latitudes, in the subarctic climate region 30.Which lake in Siberia is the deepest freshwater lake in the world? Lake Baikal 31.Which river can be seen from the Kremlin in Moscow? The Volga 32.What is the world’s largest landlocked sea? The Caspian Sea (actually a salt water lake) 33.Which huge region in Russia is called “the sleeping land”? Siberia 34.Why was a canal built between the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea? Which larger sea can be reached if you can get to the Black Sea? The transportation of goods to the Mediterranean Sea and into the Atlantic Ocean 35.The Amur River forms part of the border between Russia and which Asian country? China 36.Name another river somewhere else in the world that forms part of a border between two countries. The Rio Grande between the U.S. and Mexico, the Danube between Bulgaria and Romania, the Jordan between Jordan and Israel 37.Why is the Aral Sea shrinking? Diversion of water from the Syr Darya and the Amur Darya, both feeder rivers to the Aral Sea, for the over-irrigation of the land area within Central Asia (Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan) to grow cotton as a cash crop; with the shrinking of the water body the salt concentration also increased 38.Which body of water separates Russia from Alaska? The Bering Strait