LabDx-11-02
advertisement

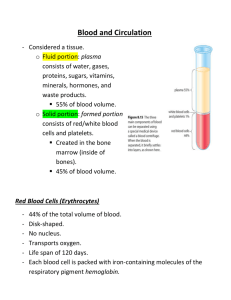
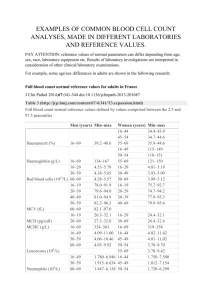
Lab Dx 11-2-98 HO- article “Psychoneuroimmunology: Brain and Immunity” – he read it to us. 11-4-98 www.goask.alice.columbia.edu/0556.html White cell disorders: Leukemia – cancer of WBC’s -abnormal growth of disorganized WBC’s (these cells don’t work) -impair production of RBC’s, platelets, and normal WBC’s -large #’s of WBC’s lead to pale blood -impaired function of organs (liver , spleen, lymph nodes, brain, abdomen-GI) -undergo mass effect (space occupying process) -brain can only stand so much pressure before it stops -blood vessels only stand so much pressure before they bleed -leukemia uses up nutrients (esp. B12) -acute vs. chronic forms -fulminant -classified by type of WBC’s -acute- can be fatal in weeks if not treated -6-7 new cases of acute leukemia per 100,000 people per year Acute leukemia- very immature WBC’s (blasts) -2 cell forms: lymphoblasts and myeloblasts -monoclonal theory – one cell mutates then divides (marrow and blood) uncontrollably until billions of it -symptoms: -gumbleeding (due to dec. platelets) -enlarged lymph nodes (cell proliferation) -anemia -headaches (from hypoxia) -frequent bruising Lymphadenopathy- 4 types: -immune stimulus -infection -neoplasm -miscellaneous (ex. CT) -anemia- myelophthisic (normocytic) diagnosis- marrow aspiration or biopsy treatment- chemotherapy, transfusions – platelets etc. Chronic Leukemia- 2 forms: lymphocytic and myelogenous 4 per 100K people per year. Many out live their chronic leukemia. Incurable. Most patients more than 50. Treatment: transfusions, antibotics, chemotherapy, radiation therapy Chronic Myeloid (2 new per 100K/year)- prolonged fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss -chronic phase can last for several years -symptoms similar to acute form treatment – chronic phase = chemotherapy -acute phase – bone marrow transplant chronic form average survival rate about 3 years from date of diagnosis (20% live more than 10 years) bleeding – purprua – hard to stop bleeding from a small cut fatigue recurrent infections CBC – usually not more than 100k WBC’s/ platelets show thrombocytopenia / RBC’s show microcytic, normocytic (acute forms) (chronic form = no cap on counts may see 800K-1mil WBC’s) may see bone destruction- collapsed VB’s. 5% of acute cases present with joint pain or knee pain (esp. in kids) distal femur -osteosarcoma in kids = knee pain Femur = fastest growing site in skeleton. Why the knee pain is a concern (good place for cancers) www.mic.ki.se/diseases._____ www.medstudents.com.br/hemat/hematb.htm Multiple myeloma = most common primary neoplasm of the skeleton(M/C malignant neoplasm of skeleton = metastatic carcinoma) -starts in the marrow -whole marrow goes bad at once -plasma cell is the target – produces antibodies (IgG, IgA) -probably a single clone is responsible *NBQ- IgG elevation is the prime immunoglobulin Symptoms: skeletal destruction, back pain is earliest complaint (mimics mechanical LBP), anemia, hypercalcemia, renal failure (kidney stones may be first sign of MM) lead to signs of edema Hypercalcemia leads to fatigue, general muscular weakness Hypocalcemia leads to irritability to muscle spasms and seizures MM- median age (61) black males (4 new cases/100K/year) Etiology – radiation exposure, benzene and other organic solvents, herbicides, insecticides, may be a genetic predisposition (increased risk for farmers, woodmakers, oilworkers) Clinical – bone lesions (punched out skull- lots of diploic marrow) bone pain, lytic lesions, IL-6 and osteoclastic activation factors, low bone density leads to fractures, imitates osteoporosis Often they die from infections (pneumonia, pyelonephritis), protein flooding the kidneys stresses them. Anemia in 80% of pt.'s with MM (normocytic, normochromic with fatigue). Neurological symptoms – radiculopathy , deficits, and compression Hypercalcemia- lethargy, dizziness, depression MM- diagnosis – marrow aspiration more than 10% are plasma cells -in bone , urine, or serum -order: CBC, UA, Ig electrophoresis, marrow aspiration (bone scans usually negative) Treatment of symptomatic MM: Nelphalan, Prednisone (shut down marrow by obliterating stem cells to slow down the tumor)