Bio 3.1
advertisement

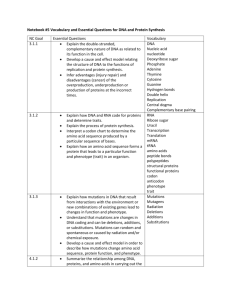
Unit Details Bio 3.1 (9/25 thru 10/8) Grade Level/Course Conceptual Strand Evolution and Genetics High School/Biology Common Core Essential State Standards NC Science Essential Standard(s) Bio 3.1 Explain how traits are determined by the structure and function of DNA. Clarifying Objectives Clarifying Objectives Number Standard Bio 3.1.1 Explain the double-stranded, complementary nature of DNA as related to its function in the cell. Bio 3.1.2 Explain how DNA and RNA code for proteins and determine traits. Bio 3.1.3 Explain how mutations in DNA that result from interactions with the environment (i.e. radiation and chemicals) or new combinations in existing genes lead to changes in function and phenotype. Essential Questions and Big Ideas Big Ideas DNA has a specific structure that allows it to replicate itself and provides the code for protein synthesis. Proteins must be made at the correct time and in the correct amount in specific cells. DNA and RNA provide the code for Essential Questions 1. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 2. Develop a cause and effect model relating the structure of DNA to the functions of replication and protein synthesis. 3. Infer the advantages and disadvantages of overproduction, underproduction, and production of proteins. 4. What is the process of protein proteins in a specific set of steps. There are 3 types of RNA that help with protein synthesis. A codon chart is used to determine the amino acids that would code for specifc mRNA codons. Proteins are consist of amino acids linked by peptide bonds to form polypeptides that are then put together. Proteins have specific functions within a cell or organism. Mutations are changes to the DNA that can cause changes to the amino acid sequence and its resulting protein and phenotype. 5. 6. 7. 8. synthesis? What are the 3 types of RNA? Interpret a codon chart. How do amino acid sequences build proteins and control phenotypes? How do mutations affect DNA, its resulting proteins and phenotypes? Vocabulary Objective 3.1.1 Academic DNA Vocabulary Performance Explain RNA Develop Nucleic acid Infer Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Complementary base pairing Double helix DNA Replication Protein Genetic code Gene expression Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine 3.1.2 mRNA Explain tRNA Interpret rRNA protein synthesis transcription Translation Codon Anticodon Peptide bond Polypeptide chain Structural protein Functional Protein Amino acid Phenotype 3.1.3 Mutation Understand Mutagen Develop Deletion Substitution Addition Heritable change