Science Introduction
advertisement

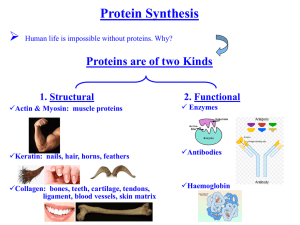
7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk Chapter 4 - Genetics: The Science of Heredity Engage – Discover Activity – Page 131 Objectives: 1. Explain what forms the genetic code. 2. Describe how a cell produces proteins. 3. Identify how mutations can affect an organism. 4-4 The DNA Connection A. The Genetic Code 1. The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits. 2. Genes and DNA Each chromosome contains thousands of genes. 1 gene may contain several hundred to a million or more bases. 4-4 Page 1 of 3 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk 3. Order of Bases The sequence of bases in a gene forms a code that tells the cell what proteins to make.(ATGACGTAC) Proteins are made of amino acids. A group of 3 DNA bases = Specific Amino Acid ( EX. CGT = Alanine) B. How Cells Make Proteins 1. Protein Synthesis – The cell uses info. from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein. Occurs on ribosomes in cytoplasm. 2. Role of RNA – Messenger – carry genetic code from nucleus into cytoplasm. 3. Types of RNA – Messenger RNA – copies code from DNA 4-4 Page 2 of 3 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk Transfer RNA – carries amino acids to ribosomes and adds them to the growing protein. 4. Translating code – page 134-135 C. Mutations 1. Mutation – any change in a gene or chromosome. 2. Body cells not passed on. Sex Cells passed on. 3. Types of Mutations Single base may be substituted for another. Chromosomes do not separate correctly during meiosis. 4. Effects of Mutations Genetic variety Harmful mutations – Albino Deer Helpful mutations – Resistant bacteria to antibiotics. 4-4 Page 3 of 3