Steps in titration and serial dilution
advertisement

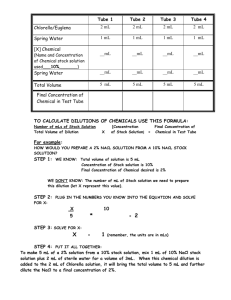
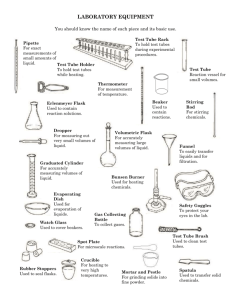
Steps in titration and serial dilution Teaching notes Some examination questions in Applied Science require students to recall the stages in the procedures they have carried out in class. This is a simple starter or revision activity to help students learn the steps. They cut out the slips of paper and rearrange them in the correct order. When working on practice questions, students can use the slips to help them decide which stages are the most important for their answer. Answers Titration 1. Fill burette with potassium manganate solution. 2. Crush iron tablets and find their mass. 3. Dissolve crushed tablets in acid. 4. Transfer crushed tablets and acid to a flask. 5. Add a known volume of distilled water to the flask. 6. Let out liquid from the burette until a faint pink-purple colour appears in the flask. 7. Record how much potassium manganate has been used. 8. Use graph to calculate how much iron is in the tablets. Serial dilution 1. Start with sterilised equipment. 2. Label 6 test tubes 1/10, 1/100 etc. 3. Aseptically transfer 9ml of sterile distilled water to each test tube. 4. Aseptically transfer 1ml of milk to first test tube (1/10. 5. Aseptically pipette 1ml from first tube into tube 2. 6. Repeat along the line of test tubes. 7. Streak labelled agar plates with 0.1ml from each tube. 8. Incubate plates at 25oC for 24 hours. 9. Count colonies of bacteria and multiply dilution factor by 10 to give estimate of number of bacteria. N.B. This is a revision activity and is not intended to be used as an experimental method. © www.teachitscience.co.uk 2012 19564 Page 1 of 3 Steps in titration and serial dilution Titration – to find the iron content of food supplements Task Cut up the stages used in titrations and arrange them in the correct order. Use graph to calculate how much iron is in the tablets. Crush iron tablets and find their mass. Transfer crushed tablets and acid to a flask. Fill burette with potassium manganate solution. Add a known volume of distilled water to the flask. Record how much potassium manganate has been used. Dissolve crushed tablets in acid. Let out liquid from the burette until a faint pink-purple colour appears in the flask. © www.teachitscience.co.uk 2012 19564 Page 2 of 3 Steps in titration and serial dilution Serial dilution – used to investigate the shelf life of milk Task Cut up the stages used in serial dilution and put them in the right order. Incubate plates at 25°C for 24 hours. Repeat along the line of test tubes. Streak labelled agar plates with 0.1ml from each tube. Aseptically transfer 9ml of sterile distilled water to each test tube. Start with sterilised equipment. Aseptically pipette 1ml from first tube into tube 2. Count colonies of bacteria and multiply dilution factor by 10 to give estimate of number of bacteria. Label 6 test tubes 1/10, 1/100 etc. Aseptically transfer 1ml of milk to first test tube (1/10). © www.teachitscience.co.uk 2012 19564 Page 3 of 3