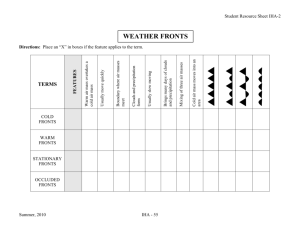
Winds, Air Masses, and Fronts Note
advertisement

Name: _____________________________________________________________________________ Period: __________________________ Winds, Air Masses, and Fronts Note Guide 1) What are winds? a) A wind is the horizontal movement of air from an area of __________ pressure to an area of ___________ pressure. b) _____________ are caused by differences in air pressure. 2) Convection Currents a) Form when an area of Earth’s surface is _____________________ by the sun’s rays. b) Air over the heated surface _____________________ and becomes ________________ dense. As the air becomes less dense, its air pressure ______________________________. c) _____________ dense air with a higher pressure flows underneath the ________________, less dense air =warm air rising 3) How do we measure wind speed? a) Winds are described by their _______________________ and _______________________. b) _______________________________________ are used to measure wind speed. 4) Wind direction a) The name of a wind tells you where the wind is coming _________________. b) For example: A west wind comes from the ______________ and blows toward the ______________. c) Wind direction is determined with a ________________ ___________________. d) The wind swings the wind vane so that one end points into the wind. 5) Wind direction represented on a map a) __________ _________________________ is shown by a line leading into a circle. b) The example below shows that the wind blew in from the ______________. 6) Wind speed represented on a map a) The wind speed is shown by the “____________________” on the wind direction line. b) One “feather” = _________________________. c) Half of a “feather” = ____________________. d) A circle within a circle = _____________, ________ ________________. e) A _________________ = 50 knots. f) 1 knot = 1.15 mph g) Feathers are also sometimes called “barbs” 7) Weather symbol example a) Example #1: What is the wind speed and direction in the image? b) Wind coming from the __________ at a speed of __________________. 8) Pressure and Wind a) ______________________ are lines joining places on a weather map that have the same _________ _________________________. b) Meteorologists use isobars on weather maps to observe atmospheric ___________________ changes over an area and to make predictions about wind _________________. c) Remember: Wind is a result of air pressure differences and wind blows from high to low pressure. d) The closer the isobars are = the ____________________ the wind speed. e) The further apart the isobars are = the ____________________ the wind speed. 9) Wind Chill Factor a) Wind blowing over your _________________ removes body heat. b) The stronger the wind, the more _____________________ is created from the air molecules hitting your body. c) This creates heat energy which is absorbed by the water near the surface of your skin, causing it to ________________________. d) This evaporation removes heat from your body and makes you feel ______________________. 10) Local Winds a) Local winds are winds that blow over _________________ distances. b) Local winds are caused by the _________________ ______________________ of Earth’s surface within a small area. c) Unequal heating often occurs along the shore of a large body of water. d) It takes _____________ energy to warm up a body of water than it does to warm up an equal area of land (water has a high specific heat). e) During the day the ___________________ warms up faster than the __________________ (unequal heating). f) At night, the ________________ cools faster than the ______________ (unequal heating). g) Land Breeze i.) Local wind that blows from the _______________ Sea Breeze ii.) Local wind that blows from an ______________ to a body of ____________ or _____________ to the during the night. _______________ during the day. 11) Global winds a) Global winds are winds that blow steadily from specific directions over ____________ distances. b) Global winds are created by the __________________ heating of Earth’s surface. c) ____________ air rises at the Equator and ________________ air sinks at the poles. 12) Jet Streams a) About 10 km above Earth’s surface are bands of high-speed winds called __________ _________________. b) Meteorologists use the location of some of the jet streams as an aid in ____________________ ____________________. c) Jet streams generally blow __________________ to ____________________. d) Jet streams form at the boundary of adjacent air masses with significant differences in _______________________ (polar region vs. Equator). e) Jet streams have a __________________________ shape. Part 2: Air Masses and Fronts 13) Air Masses a) A huge body of air that has a similar _______________________ (warm or cold), ____________________ (dry or wet), and __________ __________________________ (high or low), at any given height is called an __________ _______________. b) Four major types of air masses influence the weather in North America: i) ___________________________ ___________________________ ii) ___________________________ ___________________________ iii) ___________________________ ___________________________ iv) ___________________________ ___________________________ c) Types of air masses: i) Continental: ________________(_______________) ii) Mar: ______________ (_______________) iii) Tropical: ______________/_______________ iv) Polar: _______________ d) The area that the air mass forms over will determine its characteristics. i) For example: If the source region is an _____________________, the air mass will have a lot of _______________________. ii) For example: If the source region is _______________, the air mass will be ____________________. e) Putting it together i) Maritime Polar… _______________ and _________________ ii) _________________________ ____________________… Dry and cold iii) Maritime Tropical… _______________ and _________________ iv) _________________________ ____________________… Dry and warm f) Air masses and their origin Air Masses Origin ________________________ ________________________ Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic and Pacific Ocean Continental Tropical __________________________ and ___________________ ___________________ ________________________ ________________________ North Pacific and North Atlantic Continental Polar ___________________ and ___________________ ______________________ and _____________________ g) How air masses move i) ____________________________ ______________________________-push air masses west to east. ii) __________ _____________________ 14) Fronts a) The boundary where 2 unlike air masses meet is called a __________________. b) 4 types of fronts: i. _____________________ ii. _____________________ iii. _____________________ iv. _____________________ Storms and changeable weather often develop along fronts. c) Symbols for fronts (see side picture) d) Front symbols and direction i) Front symbols point in the _______________________ of _________________________. ii) Example: In the picture below, the warm, cold, and occluded fronts are moving _____________________ and the stationary front is not moving in any direction. iii) Draw a cold front moving east: iv) Draw a warm front moving south: v) Draw an occluded front moving northeast: e) Cold Fronts i) A cold front is when a fast-moving _____________ air mass takes over a ________________ air mass. ii) Possible weather: Clouds with possible thunderstorms with heavy rains or snow, ________________ weather on the way. f) Warm Fronts i) A warm front is when a ______________ air mass overtakes a slow-moving ______________ air mass. ii) Possible weather: Humid, light rain or snow for several days; warmer weather on the way. g) Stationary Fronts i) A stationary front is when cold and warm air masses ______________, and neither can ______________the other. ii) Possible weather: The air masses remain ________________ over an area, and may bring ___________days of clouds and precipitation. h) Occluded Fronts i) An occluded front is when a _____________ air mass is caught between two __________________ air masses. ii) Possible weather: Cloudy and _______________ or __________________. 14) Low Pressure and Weather a) If you look at a weather map, you will see areas marked with a letter ________ and the L stands for “_________ _____________________”. b) Low pressure systems lead to _________________ conditions that often bring _____________________. c) Here’s how it works: -Areas of __________ pressure are caused by massive amounts of air ___________________ from the ground into the atmosphere. -As the air molecules rise, they take their ______________ with them. -Air pressure is a ______________. -Force = ______________ x _________________________. -Less mass of air molecules left at ground level means _________ air pressure. -As this air rises it takes whatever water vapor it is holding along with it. -As altitude increases in the troposphere, the temperature _______________________. -Eventually the air mass reaches a temperature at or below the _________ _________________ and the water vapor ________________________. -___________________ ___________________ rises because colder air cannot hold as much water vapor. -This condensation forms clouds. -If there is enough water vapor in the air, it might also bring ___________________________. 15) High Pressure and Weather a) If you look at a weather map, you will see areas marked with a letter ________ and the H stands for “_________ _____________________”. b) High pressure systems lead to _________________ and __________________ weather. c) Here’s how it works: -Areas of __________ pressure are caused by massive amounts of air ___________________ from the upper troposphere down towards the ground. -As the air molecules sink, they take their ______________ with them. -Air pressure is a ______________. -Force = ______________ x _________________________. -More mass of air molecules coming to ground level means _________ air pressure. -As this air sinks it takes whatever water vapor it is holding along with it. -As altitude decreases in the troposphere, the temperature _______________________. -The higher the temperature is, the farther from the _________ ______________ you get. -Warmer air is less dense so it has more space to hold water vapor so ____________________ _________________________ drops. -This means that condensation does not occur so no clouds form. -Because there are no clouds, there will be no ___________________________.