Weather Forecasting Weather forecasting is a
advertisement

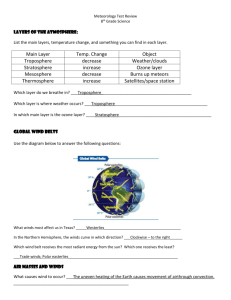
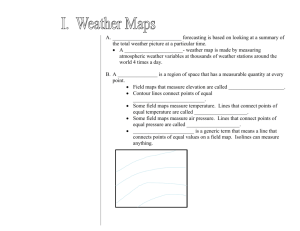
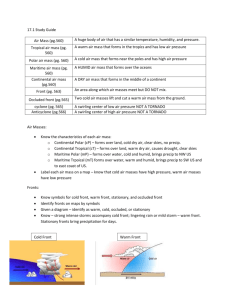
ATMOSPHERIC BEHAVIOR THAT CAUSES WEATHER Name________________________________________ Date __________________________Period_______ 8.10(B) identify how global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather using weather maps that show high and low pressures and fronts What Weather Means Weather is basically the way the atmosphere is behaving, mainly with respect to its effects upon life and human activities. The difference between weather and climate is that weather consists of the short-term (minutes to months) changes in the atmosphere. Most people think of weather in terms of temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, brightness, visibility, wind, and atmospheric pressure, as in high and low pressure. In most places, weather can change from minute-to-minute, hour-to-hour, day-to-day, and seasonto-season. Climate, however, is the average of weather over time and space. An easy way to remember the difference is that climate is what you expect, like a very hot summer, and weather is what you get, like a hot day with pop-up thunderstorms. Things That Make Up Our Weather There are really a lot of components to weather. Weather includes sunshine, rain, cloud cover, winds, hail, snow, sleet, freezing rain, flooding, blizzards, ice storms, thunderstorms, steady rains from a cold front or warm front, excessive heat, heat waves and more. What Climate Means In short, climate is the description of the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area. Some scientists define climate as the average weather for a particular region and time period, usually taken over 30-years. It's really an average pattern of weather for a particular region. When scientists talk about climate, they're looking at averages of precipitation, temperature, humidity, sunshine, wind velocity, phenomena such as fog, frost, and hail storms, and other measures of the weather that occur over a long period in a particular place. For example, after looking at rain gauge data, lake and reservoir levels, and satellite data, scientists can tell if during a summer, an area was drier than average. If it continues to be drier than normal over the course of many summers, than it would likely indicate a change in the climate. Weather Forecasting Weather forecasting is a prediction of what the weather will be like in an hour, tomorrow, or next week. Weather forecasting involves a combination of computer models, observations, and a knowledge of trends and patterns. By using these methods, reasonable accurate forecasts can be made up to seven days in advance. Weather symbols are used on my weather maps as shorthand for the conditions at weather observing stations. Forecasting Symbols A high pressure system is a whirling mass of cool, dry air that generally brings fair weather and light winds. When viewed from above, winds spiral out of a high-pressure center in a clockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere. These bring sunny skies. A high pressure system is represented as a big, blue H. A low pressure system is a whirling mass of warm, moist air that generally brings stormy weather with strong winds. When viewed from above, winds spiral into a lowpressure center in a counterclockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere. A low pressure system is represented as a big, red L. A front is a boundary between two different air masses, resulting in stormy weather. A front usually is a line of separation between warm and cold air masses. A cold front is a boundary between two air masses, one cold and the other warm, moving so that the colder air replaces the warmer air. A cold front is represented as a blue line with the teeth pointing toward the direction on movement. A warm front is a boundary between two air masses, one cool and the other warm, moving so that the warmer air replaces the cooler air. A warm front is represented as a red line with half circles pointing toward the direction on movement. A stationary front is a boundary between two air masses that more or less doesn’t move, but some stationary fronts can wobble back and forth for several hundred miles a day. A stationary front is represented as an alternating warm and cold front symbol. H L An occluded front is a combination of two fronts that form when a cold front catches up and overtakes a warm front. An occluded front is represented as a purple line with teeth and half circles. A trough on a weather map is an elongated area of relatively low pressure. Troughs bring cloudy and rainy weather. A trough is represented by a hash mark line. Directions: Use the information from the weather reading to answer the questions. 1. The passage defines weather as____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________. 2. The passage defines climate as_____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________. 3. Sarah visits Seattle this afternoon and finds that it is sunny and dry. She sends her best friend a text that says the climate in Seattle is warm and dry. Is she correct with this statement? Explain your answer 4. Make a Venn Diagram comparing Weather and Climate 5. Draw the symbol for a high pressure system______________________________________________. 6. The weather usually found in a high pressure system is… 7. Draw the symbol for a low pressure system______________________________________________. 8. The weather usually found in a low pressure system is… Directions: Use the information from the reading above and the map to make the weather forecast. United States Weather Map for Sunday, 10/28/12. 9. Based on the information on the weather map, forecast the weather in Flagstaff, Arizona. Explain your weather forecast using text evidence. 10. What kind of weather front is in Rapid City? What impact will this have on the weather there? 11. What kind of weather front is in Miami? What impact will this have on the weather there?