Air Masses & Fronts: Notes
advertisement

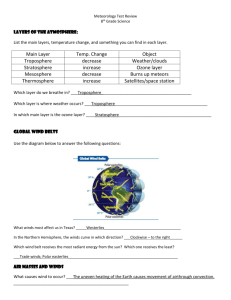
Air Masses & Fronts: Notes Air Masses : large body of air that takes on the conditions, humidity, and temperature of a particular area as it passes over. Four Air Masses: 1. Maritime 2. Continental 3. Polar 4. Tropical : forms over water; brings wet weather : forms over land’ brings dry weather : forms over polar region; brings cold weather : forms over tropics; brings warm weather Front : boundary where two air masses with different temperature and humidity meet. Weather at this boundary is usually cloudy and stormy. Four Fronts: 1. Cold 2. Warm 3. Occluded 4. Stationary Wind : thunderstorms, heavy rain, snow : drizzly precipitation : cool temperature large precipitation : similar to warm front : the result of uneven heating of Earth’s surfaces Convection : movement of heat through the air or water. Convection Current : results from temperature differences. Warm air rises, it expands and cools. Cold air moves in to replace warm air. This movement continues in a circular movement. Convection Current Hot Air rises Cold Air Sinks Two Types of Wind: 1. Local Winds: caused by convection currents which occur short distances. a. Land Breezes : Happens during the night when the cool land air moves from land toward the sea. b. Sea Breezes : happens during the daytime when cool sea air moves from sea toward the land. 2. Global Winds : move in a particular direction and travel over long distances from Earth’s rotation. They form between the equator and the poles as a result of giant convection currents that circulate. a) Trade Winds : winds flow toward equator b) Westerlies c) Easterlies : winds flow from west to east : winds flow from east to west Weather changes occur where global winds meet. Jet Stream : a) Long narrow areas of air b) Located in upper troposphere c) Travel about 200 km/hr d) Move air masses and weather west to east e) Pilots take advantage of jet stream and fly into them when traveling east and avoid them when traveling west (moves plane faster – saving time and gas).