Continental Drift
advertisement

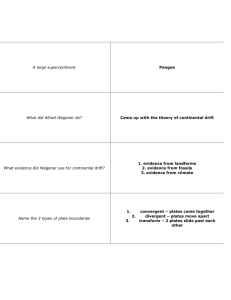
Continental Drift- early version of plate tectonic theory. Alfred Wegner- German meteorologist- father of continental drift (1910). All continents were once joined to form a supercontinent (Pangaea) Southern part of Pangaea (India, Australia, Antarctia, S. America, Africa) called Gondwana Wegner’s svidence for continental drift: 1) jigsaw fit of S. America and African coasts 2) Freshwater fossil reptile (Mesosurus) in S. America and Africa. 3) Fossil plants (Glossopteris) similar on both sides of S. Atlantic 4) Glacial deposits found on southern continents 5) NOT rock magnetism studies (comes later in 1960’s) Not accepted by European or American geologists- no mechanism for continents to move Arthur Holmes – suggested (1926) convection in mantle as cause of drift (he was correct) . 1960’s- study of magnetism in rocks on continents. Volcanic rocks act as magnetic compasses Rocks on different continents gave different north poles: the magnetic north pole had moved (polar wandering) OR The continents had drifted (correct interpretation) Study of magnetic stripes in lava on ocean floor Vine, Mathews and Morley (1963) discovered magnetic stripes on midocean ridge floor: 1) Symmetrical about ridge 2) Alternating positive and negative magnetic anomalies 3)Anomalies get older symmetrically away from ridge axis Sea-floor spreading: new ocean crust is created at mid-ocean ridge Earth’s magnetic field “flip-flops” back and forth New lava on ocean floor records the flip-flop reversals Mid-ocean ridge is boundary between two plates moving apart. New ocean crust being created at mid-ocean ridge Theory of Plate Tectonics Ocean crust being created at ocean ridges, but destroyed at Subduction zones (Benioff-Wadati zones). Subduction zones have these features: 1) Deep ocean trenches 2) Linear zones of very deep earthquakes The earth’s outer layer consists of 7 large rigid plates and several smaller plates. Plates are moving with respect to one another at 5 – 10 cm/year Some plates all ocean crust, some all continental crust, and some a mixture of both. Two types of crust Ocean crust: volcanic rock (basalt) – relatively young (0 – 200 million yrs old) and heavy Continental crust: igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks- very old (billions of years). Thick (~30 km), and lighter than ocean crust. 3 types of plate boundaries: 1) divergent boundary – new ocean crust created (mid- ocean ridge) 2) convergent boundary – old ocean crust destroyed (subduction) 3) transform boundary- plates slide past each other END