1 - Informatics
advertisement
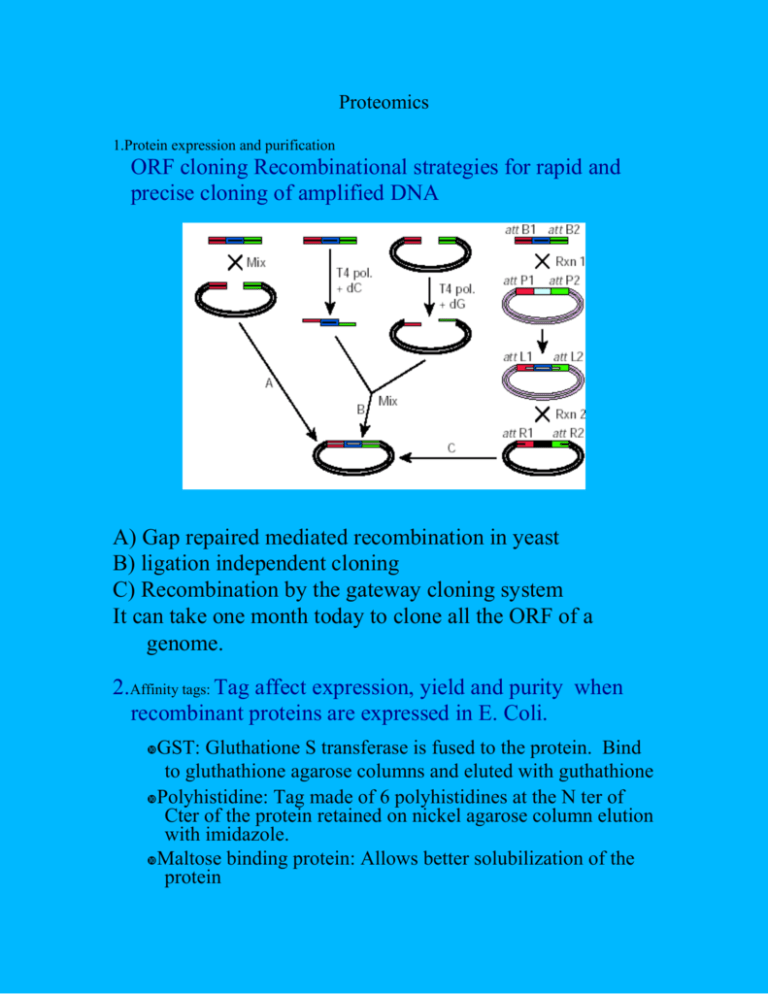
Proteomics 1.Protein expression and purification ORF cloning Recombinational strategies for rapid and precise cloning of amplified DNA A) Gap repaired mediated recombination in yeast B) ligation independent cloning C) Recombination by the gateway cloning system It can take one month today to clone all the ORF of a genome. 2.Affinity tags: Tag affect expression, yield and purity when recombinant proteins are expressed in E. Coli. GST: Gluthatione S transferase is fused to the protein. Bind to gluthathione agarose columns and eluted with guthathione Polyhistidine: Tag made of 6 polyhistidines at the N ter of Cter of the protein retained on nickel agarose column elution with imidazole. Maltose binding protein: Allows better solubilization of the protein Cellulose binding protein Calmodulin-binding peptides: bind to calmodulin agarose column and are eluted with the chelator EGTA. Myc and flag tag are used for immunoprecipitation and detection by western blot. Green fluorescent protein are used to detect the localization of the protein in living cells and for the detection of protein interaction through fluorescence energy transfer. 3.Protein complex Two proteins become in contact The recognition area define the interface Protein complexes are formed by shape and charge complementarity with or whitout conformational change. As rigid bodies (non conformational change) they generally have a standard interface less than 2000A2 With conformational changes they generally form larger complexes More than 2000 A2 Large interface involve more than one patch of recognition. Forces involved in protein-protein interface can be hydrophobic, and/or electrostatics Protein complexes can be transient of stable. 4.Yeast 2-hybrid system a) The yeast two-hybrid system. DNA-binding and activation domains (circles) are fused to proteins X and Y; the interaction of X and Y leads to reporter gene expression (arrow). b) A standard two-hybrid search. Protein X, present as a DNA-binding domain hybrid, is screened against a complex library of random inserts in the activationdomain vector (square brackets). c) A two-hybrid array approach. Protein X is screened against a complete set of full-length open reading frames (ORFs) present as activation-domain hybrids (shown as yeast transformants spotted onto microtitre plates). d) A two-hybrid search using a library of full-length ORFs. The set of ORFs as activation-domain hybrids (microtitre plates in square brackets) is combined to form a low-complexity library. e) A two-hybrid pooling strategy. Pools of ORFs as both DNA-binding domain and activation-domain hybrids (square brackets) are screened against each other. 5.Mass spectrumetry Tandem Affinity Purification high-throughput mass-spectrometric protein complex identification (HMSPCI) Bait proteins are tagged with a Flag epitope Immunoprecipitation 1D SDS PAGE Excision and digestion of the bands with trypsin MS/MS Protein identification Protein identification via MS/MS spectrometry











