DNA Model Kit – Lab report
advertisement

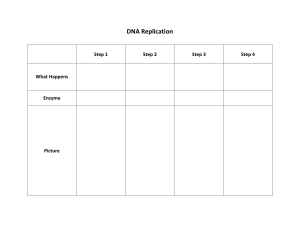
Bio H – Molecular Biology DNA Model Kit Begin by checking your kit for the following components: Pieces Red straws White straws (rigid) Blue straws Gray Straws Black with 3 prongs Yellow with 2 prongs White with 2 prongs White flexible tubes Long green or gray straw Black or gray with 4 prongs What they represent Adenine base (A) Thymine base (T) Guanine Base (G) Cytosine Base (C) Deoxyribose sugar Phosphate group Hydrogen bond Phosphodiester (covalent) bond Support for helix Support stand Objective: To build a 3D helical model of DNA by linking together nucleotides in the proper arrangement. Procedure: 1. Begin by building 10 separate nucleotides. Make sure each nucleotide has a Sugar, a Phosphate and a Base and that the pieces are linked together using the proper bond. Show me your 10 nucleotides BEFORE linking them and I will sign here ______________ 2. When you are done building the 10 nucleotides, use 5 of them to build a SINGLE chain with the following sequence: AGACT 3. Once you have that chain built, match the remaining 5 nucleotides to fill in the second chain. Make sure you are pairing up complementary bases! Also make sure that the correct bond is between bases 4. Once your DNA ladder is complete, twist all the center hydrogen bonds so the center holes face down. Thread the LONG light green straw through all those center holes. 5. Show me your completed model and I will sign here _______________________. Bio H – Molecular Biology Questions: 1. Differentiate between hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds in terms of both their strength and location in the DNA double helix. 2. What is the significance of the sequence of bases? 3. Why is it that only certain bases can “pair up?” 4. How does replication ensure the information in one cell gets passed on exactly as it is to another cell? 5. Say DNA polymerase makes a mistake during replication and inserts a G where there should be a T. What is the formal name for this “mistake?” 6. What is the only time that DNA replication is necessary?