Summary
advertisement

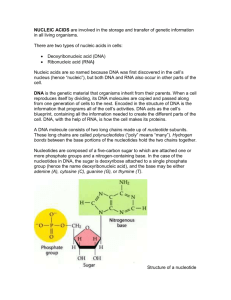
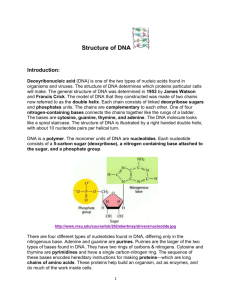
Chapter 19 1) Know the basic structures of nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids. 2) Know the difference between the syn and anti conformation of nucleotides and nucleosides. 3) Know the actual structures of the 4 deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), and the 4 ribonucleotide triphosphates (ATP, CTP, GTP, UTP). Know which ones are purines and which ones are pyrimidines. Draw all in anti conformation. 4) Be able to draw the structure of short DNA and RNA molecules (3 to 4 nucleotides long). Structure of each nucleotide must be correctly drawn, as should the phosphodiester linkage between each nucleotide. Draw all nucleotides in the anti conformation. Know which side is the 5’ end and which side is the 3’end. 5) Know the different functions of nucleotides a. storage and flow of genetic information b. energy transfer •ATP is central to energy metabolism •GTP drives protein synthesis •CTP drives lipid synthesis •UTP drives carbohydrate metabolism 6) Understand what is base pairing. Know how many H-bonds form between which bases. 7) DNA double helix (B-form) (know the following) a. DNA is a right handed antiparallel double helix b. Bases are oriented perpendicular to sugar phosphate backbone c. Bases are positioned in the hydrophobic interior of double helix d. Bases form “stacked” structure. e. Vander waals forces form attractive forces between stacked bases. f. Hydrophobic environment strengthens H-bonding of complementary bases (no competition with water) g. Know how many base pairs per turn h. Know the importance of the major and minor groves. i. Repulsive interactions of phosphate groups on the DNA backbone are neutralized by divalent cations like Mg2+. 8) DNA supercoiling (know the following) a. Compensates for over- or under-winding of double helix b. Important in allowing enzymes involved in replication and transcription access to individual DNA strands. c. Topoisomerases and gyrase are enzymes that introduce or remove supercoils. 9) Cruciform structure – formed from intrastrand hydrogen bonding. Typically occur with palindromic sequences. 10) Eukaryotic genome structure (Know the following) a. DNA is packaged with proteins to condense its length b. Nucleosomes i) DNA is wound around a histone protein complex called the core particle ii) The core particle is composed of two H2A, two H2B, two H3 and two H4 proteins (these are histones) iii) Forms bead on a string structure. iv) H1 protein connects adjacent ore particles to form what is called the nucleosome complex. c. Solenoid structure condenses multiple nucleosome complexes to more compressed structure. 11) RNA (know the following) a. Single stranded molecule b. Chemically less stable than DNA c. presence of 2’-OH makes RNA more susceptible to hydrolytic attack (especially form bases) d. Prone to degradation by Ribonucleases (Rnases) e. Has secondary structure. Can form intrachain base pairing (i.e.cruciform structures).