76KB
advertisement
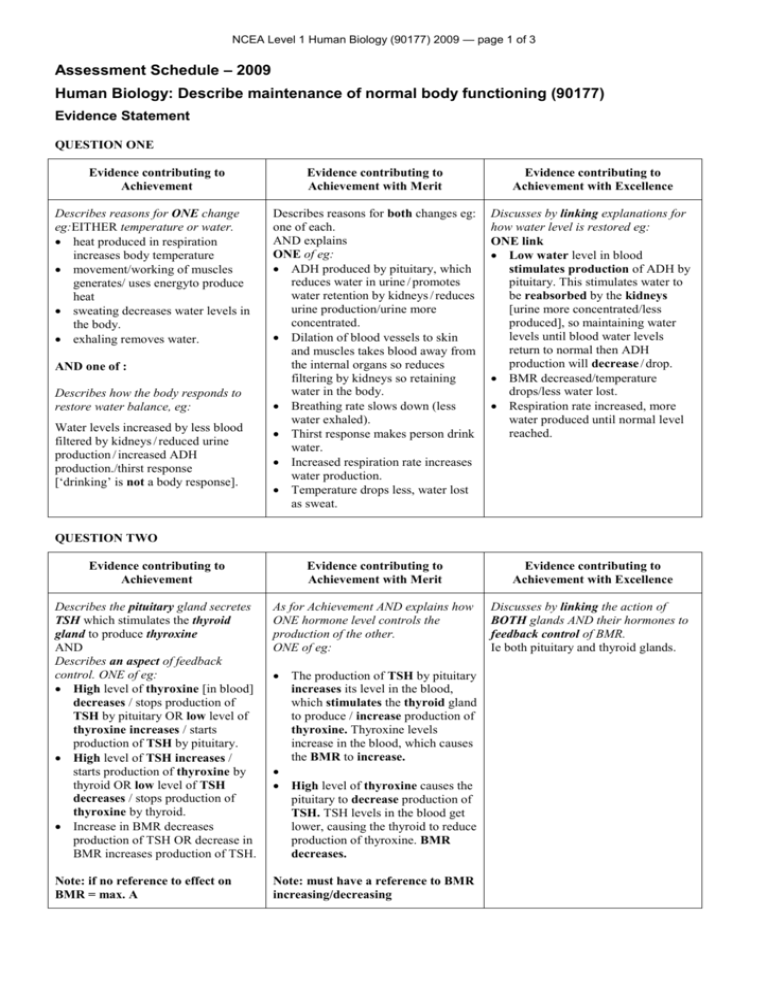
NCEA Level 1 Human Biology (90177) 2009 — page 1 of 3 Assessment Schedule – 2009 Human Biology: Describe maintenance of normal body functioning (90177) Evidence Statement QUESTION ONE Evidence contributing to Achievement Evidence contributing to Achievement with Merit Evidence contributing to Achievement with Excellence Describes reasons for both changes eg: one of each. AND explains ONE of eg: ADH produced by pituitary, which reduces water in urine / promotes water retention by kidneys / reduces urine production/urine more concentrated. Dilation of blood vessels to skin and muscles takes blood away from the internal organs so reduces filtering by kidneys so retaining water in the body. Breathing rate slows down (less water exhaled). Thirst response makes person drink water. Increased respiration rate increases water production. Temperature drops less, water lost as sweat. Discusses by linking explanations for how water level is restored eg: ONE link Low water level in blood stimulates production of ADH by pituitary. This stimulates water to be reabsorbed by the kidneys [urine more concentrated/less produced], so maintaining water levels until blood water levels return to normal then ADH production will decrease / drop. BMR decreased/temperature drops/less water lost. Respiration rate increased, more water produced until normal level reached. Evidence contributing to Achievement Evidence contributing to Achievement with Merit Evidence contributing to Achievement with Excellence Describes the pituitary gland secretes TSH which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine AND Describes an aspect of feedback control. ONE of eg: High level of thyroxine [in blood] decreases / stops production of TSH by pituitary OR low level of thyroxine increases / starts production of TSH by pituitary. High level of TSH increases / starts production of thyroxine by thyroid OR low level of TSH decreases / stops production of thyroxine by thyroid. Increase in BMR decreases production of TSH OR decrease in BMR increases production of TSH. As for Achievement AND explains how ONE hormone level controls the production of the other. ONE of eg: Discusses by linking the action of BOTH glands AND their hormones to feedback control of BMR. Ie both pituitary and thyroid glands. Note: if no reference to effect on BMR = max. A Note: must have a reference to BMR increasing/decreasing Describes reasons for ONE change eg:EITHER temperature or water. heat produced in respiration increases body temperature movement/working of muscles generates/ uses energyto produce heat sweating decreases water levels in the body. exhaling removes water. AND one of : Describes how the body responds to restore water balance, eg: Water levels increased by less blood filtered by kidneys / reduced urine production / increased ADH production./thirst response [‘drinking’ is not a body response]. QUESTION TWO The production of TSH by pituitary increases its level in the blood, which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce / increase production of thyroxine. Thyroxine levels increase in the blood, which causes the BMR to increase. High level of thyroxine causes the pituitary to decrease production of TSH. TSH levels in the blood get lower, causing the thyroid to reduce production of thyroxine. BMR decreases. NCEA Level 1 Human Biology (90177) 2009 — page 2 of 3 QUESTION THREE Evidence contributing to Achievement Describes any THREE short-term effects on normal body functioning; at least ONE from each substance eg: (Question Three (a)) Alcohol (short term) slows reactions / judgement impaired blood vessels dilate / face gets flushed / body loses heat heart works harder liver works to break down alcohol kidneys produce more urine / dehydration headaches / dizziness / nausea / vomiting. violent behaviour. Caffeine stimulation of body / heart / CNS / respiratory system alertness / concentration increased nervousness increased / becomes edgy / irritable / tense/hyperactive kidneys produce more urine / dehydration increased stomach acid. brain works faster. AND (Question Three (b)) Describes ONE long-term response to EITHER alcohol OR caffeine eg: Alcohol (long term effect) body may become addicted brain damaged / brain cells killed heart [muscle] damaged liver [cells] damaged / killed stomach lining damaged pancreas damaged. inhibits ADH. Caffeine body may become addicted persistent edginess / irritability / panic attacks / nervous tension pulse elevated / heart works faster, harder persistent stomach acidity levels / stomach lining damaged tendency to persistent dehydration. Evidence contributing to Achievement with Merit As for Achievement and explains ONE longterm response to excessive alcohol OR ONE long-term response to excessive caffeine eg: Alcohol (long term) Addiction means that the person cannot stop drinking alcohol [energy drinks] which increases damage to all body systems and can lead to death. Liver breaks down alcohol; excess alcohol kills / damages liver [cells] / impairing liver function, and may lead to hepatitis / cancer / cirrhosis. Excess alcohol damages brain / brain cells killed, causing memory loss / impairing learning / impaired judgement / responses all slower. Excess alcohol damages heart [muscle], impairing heart function, and may lead to heart failure/high blood pressure Excess alcohol damages stomach lining, which may lead to ulcers. Excess alcohol damages the pancreas impairing function / production of digestive enzymes, causing digestive problems. Possible impaired production of insulin causing diabetes. Excess alcohol may cause persistent dehydration, which may lead to impaired kidney functioning [alcohol is diuretic]. OR Caffeine (long term) Addiction means that the person cannot stop drinking caffeine [energy drinks] with flow-on effects to the nervous system [caffeine a stimulant], such as persistent edginess / irritability / panic attacks / nervous tension [which may impair judgement and create social problems]. Excess caffeine disrupts sleep patterns which may impair brain functioning / memory recall / reduce ability to concentrate and learn. Excess caffeine elevates pulse / heart works faster, harder, impairing heart function and may lead to heart failure. Excess caffeine causes persistent stomach acidity, which may damage stomach lining, leading to ulcers. Excess caffeine may cause persistent dehydration, which may lead to impaired kidney functioning [caffeine is diuretic]. Evidence contributing to Achievement with Excellence As for Merit and AND considers the addictive nature of drinks / substances linked to long-term damage to the body / body systems, which reduces quality of life and may cause premature death. Must mention Addiction Long term damage(to an organ) Effect on the body’s systems as a whole May lead to death NCEA Level 1 Human Biology (90177) 2009 — page 3 of 3 Judgement Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit 2A 2M OR 1E+1M Achievement with Excellence 2E+1A