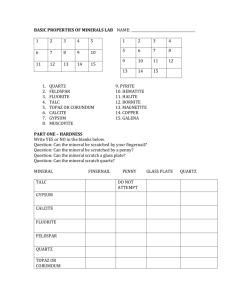
MINERAL IDENTIFICATION
advertisement
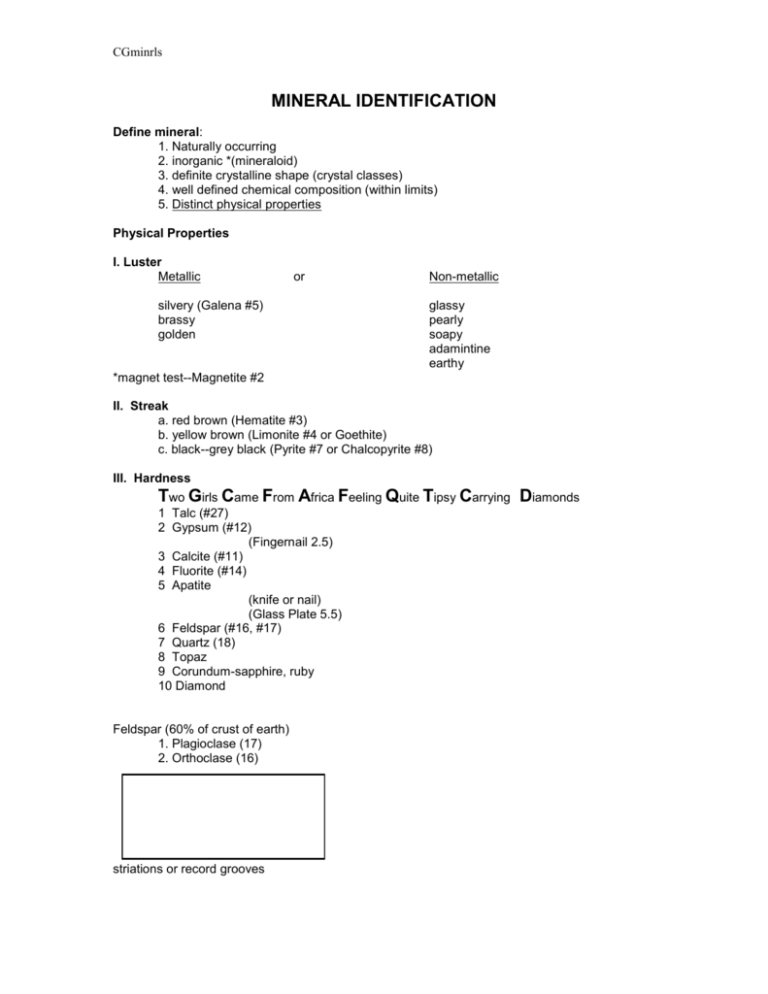
CGminrls MINERAL IDENTIFICATION Define mineral: 1. Naturally occurring 2. inorganic *(mineraloid) 3. definite crystalline shape (crystal classes) 4. well defined chemical composition (within limits) 5. Distinct physical properties Physical Properties I. Luster Metallic or silvery (Galena #5) brassy golden Non-metallic glassy pearly soapy adamintine earthy *magnet test--Magnetite #2 II. Streak a. red brown (Hematite #3) b. yellow brown (Limonite #4 or Goethite) c. black--grey black (Pyrite #7 or Chalcopyrite #8) III. Hardness Two Girls Came From Africa Feeling Quite Tipsy Carrying Diamonds 1 Talc (#27) 2 Gypsum (#12) (Fingernail 2.5) 3 Calcite (#11) 4 Fluorite (#14) 5 Apatite (knife or nail) (Glass Plate 5.5) 6 Feldspar (#16, #17) 7 Quartz (18) 8 Topaz 9 Corundum-sapphire, ruby 10 Diamond Feldspar (60% of crust of earth) 1. Plagioclase (17) 2. Orthoclase (16) striations or record grooves CGminrls discontinuous wavy lines IV. Cleavage-Tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weakness (look for sets of parallel lines) 1. one direction--basal e.g. muscouite #20 biotite #21 2. two directions a. at right angles (prismatic) Feldspars b. not at right angles Feldspars Hornblende #25 3. Three directions a. all at right angles cubic e.g. halite (#13) galena (#5) b. Rhombohedral e.g. Calcite (#11) fizzes in HCL 4. Four way=Octohedral (fluorite #14) 5. 6 way=dodecahedral sphalerite (#1) 6. Fracture random breaks Quartz- concoidal fracture CGminrls V. Specific Gravity Specific gravity = Weight in air / weight in air - weight in water VI. Taste VII. Acid test (HCl) VIII. Diaphaneity (ability to transmit light) Transparent, Translucent, opaque IX. Tenacity Brittle, malleable, ductile,