Neolithic period
advertisement

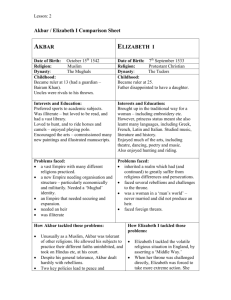
Artistic Developments In the age before photography, television and the Internet, paintings had an important role. Portraits acted as family albums, whilst other pictures served as public broadcasts, visual diaries and newsflashes. Looking at the paintings produced by the Mughals unlocks much of their history and lifestyle. Art is not static, meaning that it does not always stay the same, but often responds to external pressures which can motivate change in design. Some factors that can cause changes are: The influence of other artists A patron’s taste A society’s religious convictions Developments in materials Artistic influence In western art, Picasso was influenced by African masks. The Constructivists’ conviction that art should imitate the forms of modern technology affected their style of work. Mughal art responded to similar pressures and changes. Developments in art materials Even something as simple as the invention of the tube of paint, meant that artists were able to work directly from nature for the first time. Before, they had had to grind pigments and work paint in bowls or shells in small quantities – an expensive, highly skilled, cumbersome and studio-bound process. With tubes of paints, the French Expressionists could walk on to a hillside, sit down and paint. The immediacy of this meant that they could quickly capture the shifting light, or the movement in trees, giving pictures a more ‘alive’ look than had been previously managed. Toulouse-Lautrec used the new invention of photography to help him capture lines and movement in his painting. If you look at some of his pictures you may appreciate this fact. Ancient Civilizations – Page 1 of 3 www.mughalindia.co.uk Ancient Civilizations – Page 2 of 3 www.mughalindia.co.uk A patron’s taste Akbar’s personality and his attitude to his reign as Emperor, filtered into his patronage of the arts. Akbar was keen to bring the diverse elements of his Empire together and so was tolerant of other religions. Akbar’s religious broadmindedness is directly reflected in the paintings and illustrated manuscripts he commissioned. Many Mughal paintings act as illustrations to Akbar’s biography, the Akbarnama. Akbar loved outdoor pursuits such as hunting and falconry, and his active lifestyle is reflected in vibrant and energetic scenes. A society’s religious convictions Akbar insisted that important Hindu religious works should be translated in to Persian and illustrated. These manuscripts included the Mahabharata, the Ramayana and the Harivamsha. Akbar’s tolerance of other religions earned him loyalty and popularity with his diverse subjects, even if did infuriate the Ulema, the strict Muslim theologians and lawyers of his day. Ancient Civilizations – Page 3 of 3 www.mughalindia.co.uk