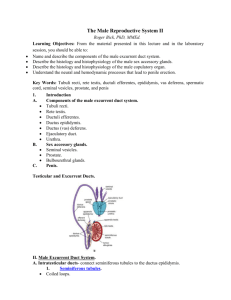
The extra testicular duct system
advertisement

The extra testicular duct system The ductus epididymis is along convoluted tubule that is surrounded by connective t issue and then smooth muscle layer asection throuth the ductus epididymis shows both cross-section and longitudinal section some parts of the ductus contain mature sperm . The pseuedostratified columnar epithelium consists of tall columnar principal cells with long nonmotile stereocilia and small basal cells which obsorb the testicular fluid that was not absorbed in the ductuli efferentes during the passage of sperm from the testes the principal cells in the epididymis also phagocy tose the remaining residual bodies that were not removed by the sertoli cells in the somniferous tubules aswellas any abnormal or degenerating sperm cells these cells also produce glycoprotein that inhibits capacitating or the fertilizing ability of the sperm until they are deposited in the female reproductive tract. Ducts (vas) deferens section The vas deferens exhibits a narrow & irregular lumen with longitudinal mucosal folds a thin mucosa a thick muscular is and adventitia . The lumen of the ducts deferens is lined by pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium with stereocilli. The epithelium of the ducts deferens is some what lower than in the ducts epididymis .the underlying thin lamina propria consist of compact Collagen fibers. The thick muscular consist of three smooth muscle layers : 1-athinner inner longitudinal muscle layer 2-athick middle circular muscle layer 3-athinner outer longitudinal muscle layer The muscular is surrounded by adventitia in which abundant blood vessel(venule&arteriol) and nerves are fond. The the ampulla's of the ducts deferens (transfer section) the terminal portion of the adventitia of the ducts 1 deferens merges with connective tissue of the spermatic cord the ampulla's of the ducts deferens (transverse section) the terminal portion of the vas deferenenlarges in to an ampulla's. The ampulla differs from the ducts deferens mainly in the stricture of its mucosa .the lumen of the ampulla's is larger than of the vas deferens the mucosa also exhibits numerous irregulcer ,branched mucosal folds &deep glandular diverticula's or crypts, between the folds that attend to the surrounding muscle layer .the secretory epithelium that linesthelumen &the glandular diverticula's is simple columnar or cuboidal below the epithelium is the lamina propria.the smooth muscle layers in the muscular are similar to those in the vas deferens & than surrounded by connective tissue Seminal vesicle The paired seminal vesicles are elongated glands on the posterior side of the bladder .the excretory duct from each seminal vesicle joins the ampulla's of each ducts deferens to form the ejaculatory duct which then runs throng the prostate gland to open in to the urethra Its highly convoluted and irregular Lumina across section through it a-primary mucosal folds b-secondary mucosal folds Which frequently anastomase and form it regular cavities chambers or mucosal crypts .the lamina propria projects in to and form the core of the larger primary folds and the smaller secondary folds extend far in to the lumen of the seminal vesicle . The glandular epithelium of the seminal vesicles varies in appearance .usually however its low pseudo stratified and low columnar or cuboidal. The muscular is consist of an inner circular muscle layer and an outer longitudinal muscle layer this arrangement of the smooth muscle often is difficult 2 to observe because of the complex folding of the mucosa .the adventitia surrounds the muscular and blends with the connective tissue the seminal vesicles produced yellowish viscous fluid that contains a high concentration of fructose .which is the main carbohydrate component of semen Fructose is metabolized by sperm and servers as the main energy source for sperm motility .Semi Nal vesicles produced most of the fluid. Penile urethra(transverse section ) The penile urethra extends the entire length of the penis and is surrounded by the corpus spongiosu M .this illustration shows transverse section through the lumen of the penile urethra and the surrounding corpus spongiosum . the lining of this portion of the penile urethra and the surrounding corpus spongiosum the lining of this portion of the urethra is apseudostratified or stratified columnar epithelium athin underlying lamina propria numerous irregular outpockets or urethral lacunae with mucous cells are found in the lumen of the penile urethra the urethral lacunae are connected with the branched mu-cous urethral glands (of litter) in the surrounding connective tissue of the corpus spon-giosum and are found throughout the length of the penile urethra the ducts from the ure-thral glands open into the lumen of the penile urethra the corpus spongiosum consists of cavernous sinuses that are lined by enothe-lial cells and separated by connective tissue trabeculae that contain smooth muscle fibers and collagen fibers numerous blood vessels (arteriole and venule)supply the corpus spongio-sum the internal structure of the corpus spongiosum is similar to that of the corpora cavernosa described in figure 3