The Habitats - Tewksbury Township Schools
advertisement
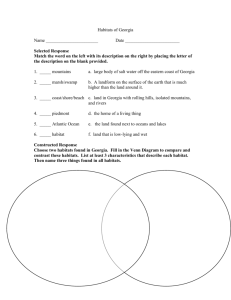
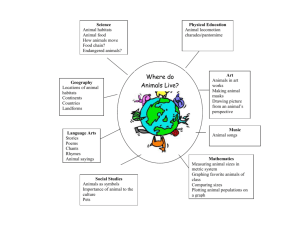
Unit Overview Content Area: Spanish Unit Title: Los Habitats (The Habitats) Unit: 3 Target Course/Grade Level: 3rd grade Timeline: 7-8 weeks (ongoing for school, home, and other habitats) Unit Summary Various habitats are explored in this unit. There is an emphasis put on two common habitats of a third grade student, the school and the home. In addition, land and sea habitats are introduced, with students finding sources of food, water, and shelter for animals in each habitat. Simple sentences are formed to describe student preferences. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Science, Social Studies, English Language Arts 21st century themes and skills: Critical Thinking and Problem Solving; Collaboration, Teamwork, and Leadership; Cross-Cultural Understanding and Interpersonal Communication Unit Rationale It is important for elementary school children to learn a world language so they can communicate with the ever growing diverse population of the United States. Learning Targets Standards 7.1 World Languages All students will be able to use a world language in addition to English to engage in meaningful conversation, to understand and interpret spoken and written language, and to present information, concepts, and ideas, while also gaining an understanding of the perspectives of other cultures. Through language study, they will make connections with other content areas, compare the language and culture studied with their own, and participate in home and global communities. 9.1 21st – Century Life & Career Skills All students will demonstrate the creative, critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills needed to function successfully as both global citizens and workers in diverse ethnic and organizational cultures. Content Statements: Interpretive Mode Linguistic: The Novice-Mid language learner understands and communicates at the word level and can independently identify and recognize memorized words and phrases that bring meaning to text. Cultural: Personal identity is developed through experiences that occur within one’s family, one’s community, and the culture at large. (Topics that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: self, friends, family, pets, physical/personality descriptions, school, likes/dislikes, and pastimes.) Observing and participating in culturally authentic activities contribute to familiarization with cultural products and practices. (Topics and activities that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: authentic celebrations, songs, and dances.) Healthy eating habits and fitness practices may vary across cultures. (Topics that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: foods, shopping, eating at home or in restaurants, and wellness practices.) Many products and practices related to home and community are shared across cultures; others are culturespecific. (Topics that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: home life, places in the community, activities within the community, and travel.) What is perceived as “basic needs” varies among and within cultures. (Topics that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: safety, food, shelter, and purchase and sale of goods such as toys, games, travel, and luxury items.) Maps, graphs, and other graphic organizers facilitate understanding of information on a wide range of topics related to the world and global issues. They make complex concepts more accessible to secondlanguage learners who have limited proficiency in the language. (Content areas that assist in the development of this understanding should include, but are not limited to: history, economics, science, and geography.) Learning about age- and developmentally appropriate content that is of high interest to students and has a direct connection to the cultural contexts of the target language cultivates an awareness of the shared human experience. (Content that assists in the development of this understanding should include, but is not limited to: all content areas and popular culture.) The ability to recognize a problem and apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills to solve the problem is a lifelong skill that develops over time. Collaboration and teamwork enable individuals or groups to achieve common goals with greater efficiency. Effective communication skills convey intended meaning to others and assist in preventing misunderstandings. Content Statements: Interpersonal Mode Linguistic: The Novice-Mid language learner understands and communicates at the word level and can use memorized words and phrases independently to: Respond to learned questions. Ask memorized questions. State needs and preferences. Describe people, places, and things Cultural: The Novice-Mid Cultural Content Statements remain the same for all the strands. Content Statements: Presentational Mode Linguistic: The Novice-Mid language learner understands and communicates at the word level and can use memorized words and phrases independently to: Make lists. State needs and preferences. Describe people, places, and things. Cultural: The Novice-Mid Cultural Content Statements remain the same for all the strands. CPI # 7.1.NM.A.1 Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) for Interpretive Mode Recognize familiar spoken or written words and phrases contained in culturally authentic materials using electronic information sources related to targeted themes. 7.1.NM.A.2 Demonstrate comprehension of simple, oral and written directions, commands, and requests through appropriate physical response. 7.1.NM.A.3 Recognize a few common gestures and cultural practices associated with the target culture(s). 7.1.NM.A.4 Identify familiar people, places, and objects based on simple oral and/or written descriptions. 7.1.NM.A.5 Demonstrate comprehension of brief oral and written messages using age- and levelappropriate, culturally authentic materials on familiar topics. 9.1.4.A.5 Apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills in classroom and family settings 9.1.4.C.1 Practice collaborative skills in groups, and explain how these skills assist in completing tasks in different settings (at home, in school, and during play). CPI # Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) for Interpersonal Mode 7.1.NM.B.2 Give and follow simple oral and written directions, commands, and requests when participating in age-appropriate classroom and cultural activities. 7.1.NM.B.3 Imitate appropriate gestures and intonation of the target culture(s)/language during greetings, leave-takings, and daily interactions. 7.1.NM.B.4 Ask and respond to simple questions, make requests, and express preferences using memorized words and phrases. 7.1.NM.B.5 Exchange information using words, phrases, and short sentences practiced in class on familiar topics or on topics studied in other content areas. 9.1.4.D.1 CPI # 7.1.NM.C.2 Use effective oral and written communication in face-to-face and online interactions and when presenting to an audience. Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) for Presentational Mode Imitate, recite, and/or dramatize simple poetry, rhymes, songs, and skits. 7.1.NM.C.3 Copy/write words, phrases, or simple guided texts on familiar topics. 7.1.NM.C.5 Name and label tangible cultural products and imitate cultural practices from the target culture(s). Unit Essential Questions How does language help form a community? Why do we use language in school and at home? Unit Enduring Understandings A habitat is the place where an animal or plant naturally lives and grows. Since humans are mammals, we have habitats too. Language is an integral part of holding a community together. Since language is spoken or written words, we are able to express our thoughts and feelings by means of language when we are in school, at home, or traveling. Animals need food, water, and shelter to survive in a habitat. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Describe their school habitat, specifically their classroom. Identify classroom objects in the target language. Use cognates to translate school subjects. Explain why it is important to have rules in a habitat. Create sentences to describe classroom objects. Speak about their likes and dislikes, regarding home activities. Name 5 rooms in the house in the target language. Describe what an animal needs in order to survive in a land or sea habitat. Recognize masculine and feminine vocabulary words. Use singular/plural agreement with nouns and adjectives (el gato negro, los gatos negros). Evidence of Learning Summative Assessment Classroom riddles solved with clues and crossword puzzles Labeled rooms in a house Habitat drawing with labels Simple sentences, classroom, sea animals, and forest animals skill sheets Spoken sentences about home activity preferences, using sentence starters and action verbs Vocabulary term exercises Equipment needed: Classroom objects Classroom Rules Poster and Character Education Traits Sentence Starters and Verb Cards House Template Construction paper, markers, crayons Animals and rooms in the house posters Song posters Flashcards, picture cards CDs and CD player Computer, SMARTBoard, ELMO Teacher Instructional Resources: My School, Mi Escuela, Gladys Rosa-Mendoza My House, Mi Casa, Gladys Rosa-Mendoza My Room, Mi Cuarto, Rebecca Emberley Who Lives in the Sea? Quien Vive en el Mar?, Gladys Rosa-Mendoza Teach Them Spanish! Grade 3 -Instructional Fair Skills for Scholars, Grade 3 -Frank Schaffer Publications The Complete Book of Spanish -School Specialty Publishing Animals: Digital Flashcards in Power Point CDs: Spanish -Twin Sisters Productions Sing, Dance, Laugh, and Eat Tacos! -Barbara MacArthur Rock’N Learn Spanish Vol. 1 Viva! Es sabado! -School Specialty Publishing Formative Assessments Listening activities Description of favorite room in house Teacher observation Role playing: animals and survival Think, pair, share Group/individual oral participation (songs/activities for classroom, home activities, and animals) Integration of Technology: Computer, internet, SMARTBoard, ELMO, CD player with CDs, digital flashcards in power point Technology Resources Click the links below to access additional resources used to design this unit: http://www.learn4good.com/kids/learning_spanish http://www.uni.edu/becker/children.html http://www.123teachme.com/learn_spanish/children http://www.spanishfun.net http://www.enchantedlearning.com Opportunities for Differentiation VAKT learning modalities – instructional and assessments Student centered activities Cooperative grouping Multiple intelligence learning styles Additional independent activities for higher leveled learners Questioning/discussion techniques Teacher Notes: