Appendix 3
advertisement

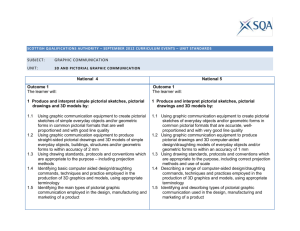
Appendix 3: National 4 and National 5 comparison Graphic Communcation Graphic Communication Graphic types Manual techniques Computer-aided techniques Skills in applying drawing standards, protocols and conventions National 4 The ability to understand and produce graphic responses for simple and straightforward preliminary, production and promotional graphics. Demonstrate the necessary skills, knowledge and application of simple and effective techniques when using graphic instruments or devices, and a range of common graphics media. Hardware and software — simple and common techniques associated with and uses of: computer aided design/ draughting, desktop publishing, digital capture and similar input devices as they support the creation of orthographic and pictorial views. Recognised drawing standards, protocols and conventions in engineering and construction, symbols and standards. Line types (including dimension lines, centre line, hidden detail), dimensioning (linear, radial and diameter), and symbols for sections, hatching, symbols for building construction, and third angle projection system in generating elevations and plans. Geometric shapes and forms, and everyday objects Common simple geometric forms and simple everyday objects consisting: squares, rectangles, circles right cylinders, square and equilateral triangular prisms and pyramids, components based on those forms, combinations of two components. Views and techniques Orthographic projection of simple geometric forms and simple everyday objects in third angle National 5 The ability to understand and produce graphic responses for: preliminary, production and promotional graphics. Demonstrate the necessary skills, knowledge and application of effective techniques when using graphic instruments or devices, and a range of common graphics media. Hardware and software — techniques associated with and uses of: computer aided design/ draughting , desktop publishing, digital capture and similar input devices as they support the creation of orthographic and pictorial views Recognised drawing standards, protocols and conventions in engineering and construction, symbols and standards. Line types (including dimension lines, centre line, hidden detail), dimensioning (linear, radial, diameter, angular, square, across flats, across corners), and symbols for sections, hatching, symbols for building construction, and third angle projection system. Common geometric forms and everyday objects consisting: squares, rectangles, circles, hexagons, octagons, right prisms, pyramids, cones, and cylinders, partial or single cuts to these forms, components based on geometric forms, combinations of two components. Orthographic projection of geometric forms and everyday objects in third angle projection, projection, where relevant -plans and elevations, simple true shapes parallel to vertical or horizontal planes, basic surface developments of straight sided objects with simple cuts, sectional views, assembly drawings, exploded isometric views of two simple and rectilinear parts. Pictorial views including isometric and oblique containing straight sided parts, and simple planometric views. true lengths and true shapes, surface developments, sectional views, assembly drawings, exploded isometric views of three parts. Pictorial views including isometric, oblique containing curved parts and planometric. Building construction drawings: Location plans, site layouts/block plans, floor plans, simple sectional views, elevations and, schematic diagrams. Location plans, site layouts/block plans, floor plans, sectional views, elevations and, schematic diagrams. Skills and techniques in sketching (use of paper-based and/or electronic slates or similar devices) Skills in illustration techniques using manual and/or computer-aided formats Skills and creativity in producing effective promotional graphics Sketching techniques including: proportion, line quality, vanishing points, line sketching using single and two-point perspective, in communicating simple straight-sided everyday objects. Sketching techniques, including: proportion, line quality, vanishing points, line sketching using single and two-point perspective, and representations of geometric forms and everyday objects. Representations of light, shade, shadow, reflection, tone, gradient, texture, layout, and display techniques. Representations of light, shade, shadow, reflection, tone, gradient, texture, layout, and display techniques. Public information symbols, flow charts and similar, informational graphics with considerations of, alignment, unity and depth, elements and principles of the use of colour (warm, cool, contrast, harmony), reflection and shade. Techniques in the creation of simple promotional graphic displays and including those for research/investigation and generating ideas. Public information symbols, flow charts and similar, informational graphics, alignment, dominance, unity and depth, elements and principles of the use of colour, (warm, cool, contrast, harmony, advancing, receding, mood), reflection and shade. Using techniques to create promotional graphic displays and including those for research/investigation and generating ideas. Using technology in graphic communication Ranges, features and uses of common graphic hardware and software, computer systems, file management; digital input and output devices and the advantages Ranges, features and uses of graphic hardware and software, including animation packages, computer systems, file management; digital input and Computer aided design/ draughting Desktop publishing Graphic communication technology: impact on society and the environment Safe working and limitations of computer aided design/ draughting. output devices and the advantages and limitations of computer aided design/ draughting. In communicating simple, straight sided everyday objects, techniques, customs and practices across a range of packages: generic drawing and editing commands and terms (including: copy, zoom, mirror, trim line, rotate, scale, extrude, import, export), basic 3D modelling techniques (including extrusion, revolved solids, fillet, chamfer), techniques in the production of orthographic and pictorial work using computer aided design/ draughting , and the use and function of computer aided design/ draughting libraries. Techniques, customs and practices across a range of packages, generic terms and techniques such as: copy/cut/paste, text box, handles, colour fill, margin, single and multipage format, title, extended text, alignment, heading, cropping, transparency, drop shadow, rotate, justification, paper sizing, reverse, gutter, caption, header and footer. Simple planning strategies, thumbnails and annotation Techniques, customs and practices across a range of packages: generic drawing and editing commands and terms (including: copy, zoom, mirror, trim line, rotate, scale, extrude, import, export), 3D modelling techniques (including extrusion, revolved solids, shell, subtraction, union, fillet, chamfer), techniques in the production of orthographic and pictorial work using computer aided design/ draughting, and the use and function of computer aided design/draughting libraries. Techniques, customs and practices across a range of packages, generic terms and techniques such as: copy/cut/paste, text box, handles, colour fill, margin, single and multi-page format, title, extended text, alignment, heading, cropping, text wrap, flow text along a path, bleed, transparency, drop shadow, rotate, justification, paper sizing, reverse, gutter, caption, header and footer. Planning strategies, thumbnails and annotation. The impact and influence of graphic communication activity on society and the environment — for example: the paperless office, use of recycled materials, computer aided design/ draughting as it supports manufacturing and other industries, DTP in marketing and promotional activities, remote working, communication crossing international boundaries using a common graphical language. The safe working practices and systems which support graphic communication activities in studios and other such working environments.