3 - Educarm
advertisement

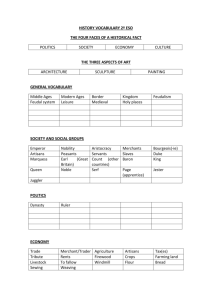
IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 UNIDAD DIDÁCTICA: TITLE: THE EARLY MIDDLE AGES 1. Introduction and description of the didactic unit. JUSTIFICATION This didactic unit is the first one which has been scheduled for the second year of secondary school (ESO). The contents that have been included in it link into to the historical speech developed in the last unit of the subject of Social Science in first year of ESO. In this unit, students will deal with the crisis of the Roman Empire, focusing with spread of Islam in the early Middle Ages. The classbook used in this academic year is RAMÍREZ MURIANA, D. (Ed.). Geografía e Historia, 2º ESO, Ed. Santillana, Madrid 2007. For that reason, most of the activities that appear in different sessions have been extracted from it and some others have been created by the teacher. The PowerPoint Presentation has been created by the teacher. A part of that, different resources have been used, such as blackboard, computer and projector and, above all, different fotocopies with vocabulary or content in English. GROUP: Second group of ESO NUMBER OF SESSIONS: 7, including the exam. BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Students have prior knowledge of the origin of the Roman Empire, its heyday, the causes of its decline and Germanic settlement in Roman territory. 2. Didactic Objectives: 1. To understand the causes of the Roman Empire’s crisis and the consequences of its disappearance. 2. To analyze the main characteristics of the kingdoms created by Germanic peoples. 3. To learn the basic features of the Byzantine Empire and its heyday during the reign of Justinian. 4. To know the origin of Islam and fundamental precepts of this religion. 5. To describe the space by which Islam spread in various stages of its history. 6. To understand the importance of Islamic civilization and islamic culture. 7. To know who Charlemagne was and how the empire he created was organized. 1 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 Evaluation criteria: 1. To identify basic characteristics that led to main artistic styles of the Middle Ages and the Modern Age to contextualize the stage where they were originated, and apply this knowledge to the analysis of tasks of relevant and representative art. 2. To do a simple descriptive work (observation, newspapers, books, websites, etc..), selecting relevant information, integrating it into an outline or script and communicating properly, using the proper vocabulary in the results of the study individually or in groups, supported by teacher assistance. 3. Contents: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The end of the Roman Empire. The Germanic kingdoms. The Byzantine Empire. Islam in the Middle Ages. The Carolingian Empire. 4. Sessions and learning activities: SESSION Nº1 EXHIBITION TIME. CONTENT: 55 minutes The end of the Roman Empire. The Germanic kingdoms. EDUCATIONAL - Power Point about the contents of the lesson. (Source: Teacher) RESOURCES - Documentary: Expansion of Byzantine empire and musulman power. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UzZZPiYbAX8&feature=relmfu (Source: Artehistoria) ACTIVITIES 1. What factors provoked the split of the Roman Empire in two parts? How are they called? 2. Why the Germans entered the Roman Empire? 3. What do you think? : a. What was the first meaning of barbarian? What does it mean today? b. Why did the Germanic tribes adopt Latin as their 2 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 language and Christianity as their religion? 4. Are these statements true or false? Correct the false sentences: A. The Germanic tribes came from Africa. B. Germanic tribes invaded Rome when the Romans were weak. C. New cities and trade routes appeared after the fall of the Roman Empire. D. Theodosius was the last emperor. 5. After watching the documentary, name different Germanic kingdoms that were introduced in the Roman Empire and the modern country originated. SESSION Nº2 EXHIBITION TIME CONTENT EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES ACTIVITIES 55 minutes The Byzantine Empire. - Interactive resource: http://www.librosvivos.net/smtc/homeTC.asp?TemaClave=1 103 (Source: Libros Vivos.net) 6. What is the Byzantine Empire? 7. What are the key points from Byzantine Empire? 8. What military features helped the military expansion of Byzantine Empire? 9. Answer the following questions: -Why it is said that Byzantine Empire was influenced by religion? - What is the Justinian’s Code? -Where Byzantine Empire was extended in its heyday? -What happened with those territories after the death of Justinian? - List the most important cities in the Byzantine Empire. 10. Sum up in the following chart the main characteristics from Byzantine Empire in Justinian times. 3 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 Government Economy Culture SESSION Nº 3 EXHIBITION TIME. CONTENT: EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES ACTIVITIES 55 minutes The Byzantine Empire. - Interactive resource: http://www.librosvivos.net/smtc/homeTC.asp?TemaClave=1 103(Source: Libros Vivos.net) 11. Use a modern political map of Europe and find: a. The modern names of Byzantium and Constantinople. b. Byzantine settlements which are now capital cities. c. Some modern countries which were part of the Empire. 12. Choose the best answer: The byzantine architecture is the synthesis between… a) The roman architecture and oriental architecture. b) The Japanese architecture and the roman architecture. c) The muslim architecture and the greek arquitecture. 13. What features were inherited by byzantine mosaic? Where can we find one famous byzantine mosaic? 14. Answer the following questions: -Explain the main differences between: a) Orthodox Church and Catholic Church; b) a painting and a mosaic. -What is an icon? What is a greek cross plan? -What is the Schism of the East? When it happened? -Why byzantine empire was influenced by religion? 15. Why did over the Byzantine Empire? 4 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 SESSION Nº 4 EXHIBITION TIME. CONTENT: EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES 55 minutes Islam in the Middle Ages. - Interactive resource: http://www.librosvivos.net/smtc/homeTC.asp?TemaClave=1 149 (Source: Libros Vivos.net) - Documentary about Islamic Religion: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=maEEygFdNIA (Source: Artehistoria) ACTIVITIES 16. When Islamic religion appeared? Where it appeared? 17. What is Koran? 18. What is the most representative religious building from Islam? 19. Answer the following questions: -Explain the difference between: a) Monoteism and polytheism. b) muslim and arab. c) caliph and ulema. -How do muslims call to God? 20. Write five pillars of Islam. Add other aspects about Muslim religion. 21. Think about this concept: -What medieval aspects from Islam are present yet? 5 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 SESSION Nº 5 EXHIBITION TIME. CONTENT: 55 minutes The Carolingian Empire. EDUCATIONAL -Documentary about feudalism in Europe: RESOURCES http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=27xdhmswJx4&feature=relmfu (Source: Artehistoria) ACTIVITIES 22. Answer the following questions: - What is the capital of Charlemagne’s empire? - Carolus means Charles in Latin. What do you think that the word Carolingian means? - What does “swear fidelity” mean? 23. Search the main ideas in the text: -How the Carolingian empire was governed? -How did they live in those times? -What territories were conquered by Charlemagne? 24. Complete the following sentences about The Carolingian Empire: THE CAROLINGIAN EMPIRE: -Its heyday was… -During the following centuries… -The main king was… -Which was crowned in… -Its economy was supported by… -Made by… -Society was composed by… 6 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 SESSION Nº 6: EVALUATION 25. Complete the following chart: ACTIVITIES 1.Germanic kingdoms 2. Byzantine Empire 3. Islam 4. Carolingian Empire a. Who governed? b. Was it a rural or an urban civilization? c. What were their most important economic activities? d. What was their religion? e. Was it polytheistic or monotheistic? f. What was its level of cultural development? 26. Link the following terms: a) Teodosius 1. Main byzantine emperor. b) Barbarians 2. Disappearance of the Eastern Roman Empire. c) Charlemagne 3. Roman empire division. d) Justinian 4. Franks king. 27. Write a timeline and place the following events: - Islam origin - Roman empire division by Theodosius. - Disappearance of the Western Roman Empire. - Disappearance of the Eastern Roman Empire. - Charlemagne’s reign. - Justinian’s reign. 7 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 SESSION Nº 7: EXAM 1) ¿En qué partes dividió el emperador Teodosio el imperio romano en el 395? (1 pto.) 2) ¿Qué significa bárbaro? Cita las diferentes tribus germanas y los territorios que ocuparon tras la caída del imperio romano. (1 pto.) 3) ¿Qué es el imperio bizantino? (1 pto.) 4) ¿Qué es el Cisma de Oriente y cuándo se produjo? Explica las diferencias entre la iglesia católica y la ortodoxa. (1 pto.) 5) ¿Cuáles son las manifestaciones artísticas del arte bizantino? ¿y del arte islámico? Señala las partes más importantes de cada uno de ellas. (1 pto.) EXAM 6) Comenta los aspectos más importantes de las diferentes etapas de la historia del Islam durante la Edad Media. (1 pto.) 7) What is the Justinian’s Code? (1 pto.) 8) Why did over the Byzantine empire? (1 pto.) 9) What’s the name of the Islam’s holy book? (1 pto.) 10) What are the five pillars of Islam? (1 pto.) 8 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 Digital Educational Resource used in session nº1, made by the teacher (a PowerPoint Presentation): 9 IES RAMÓN Y CAJAL. MEMORIA CIENCIAS SOCIALES / SECCIÓN BILINGÜE INGLÉS. 1º y 2º ESO. CURSO 2011-12 Profesora DNL de Ciencias Sociales. Silvia Bahamonde Bago. 10